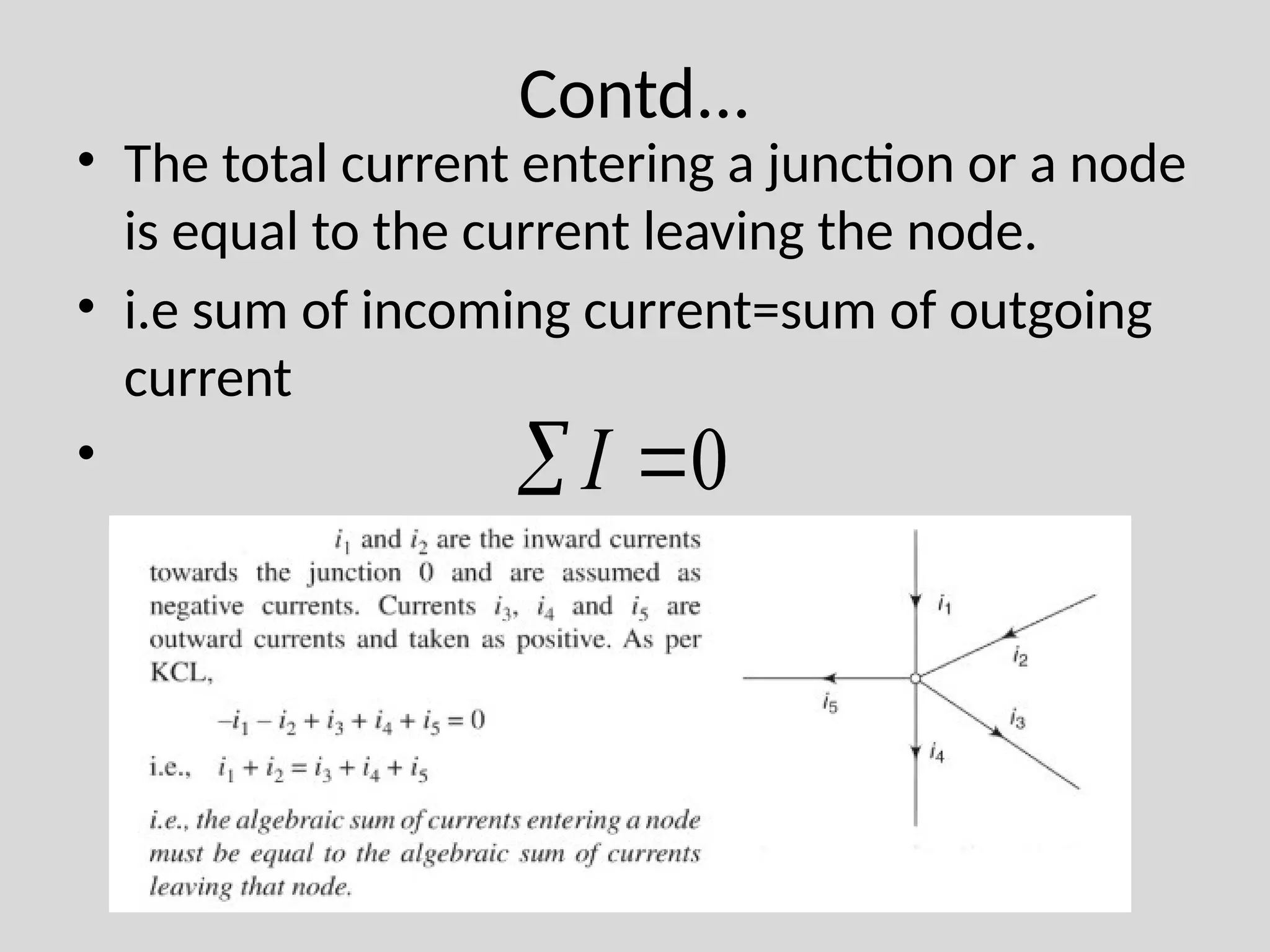
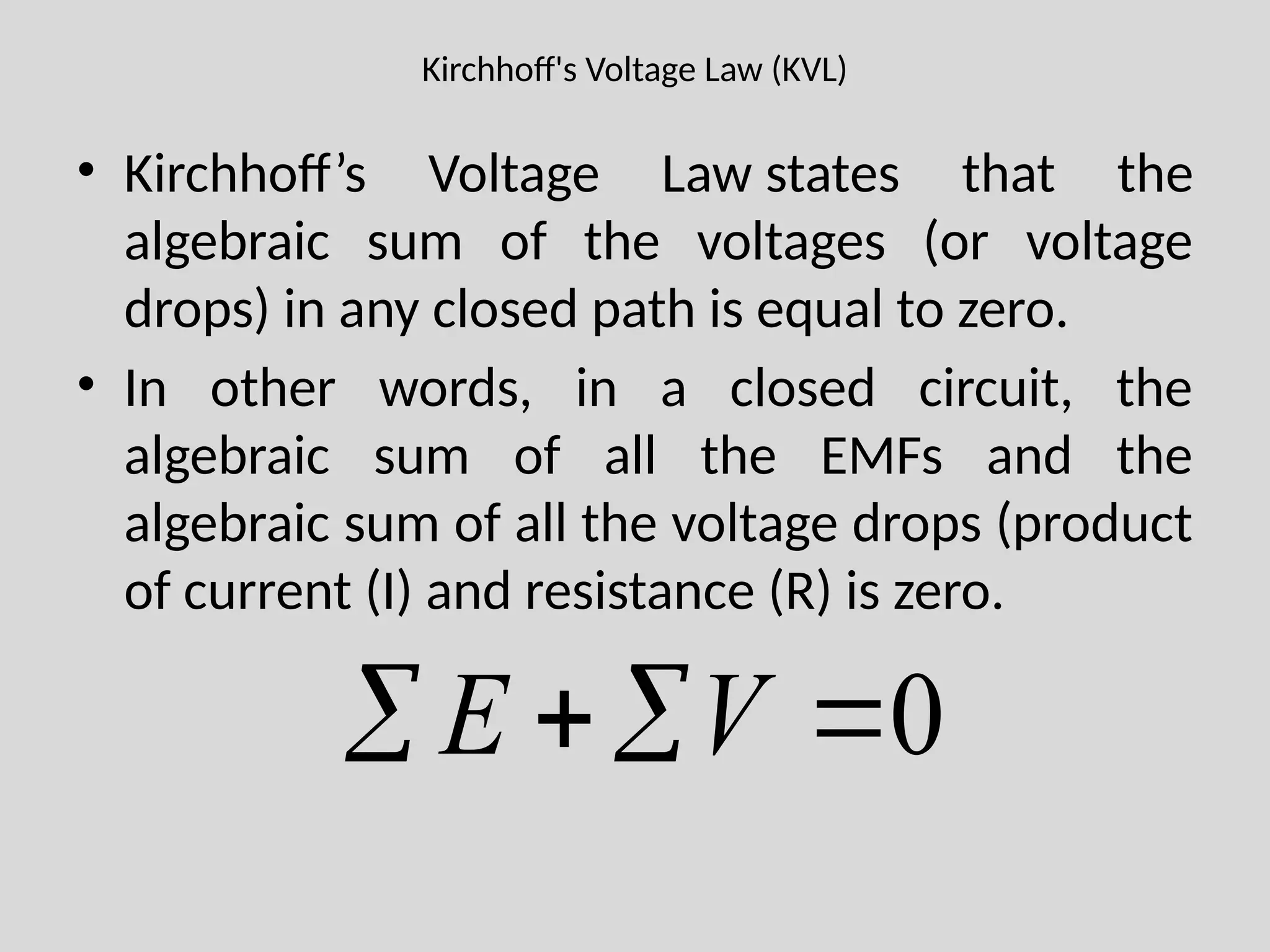
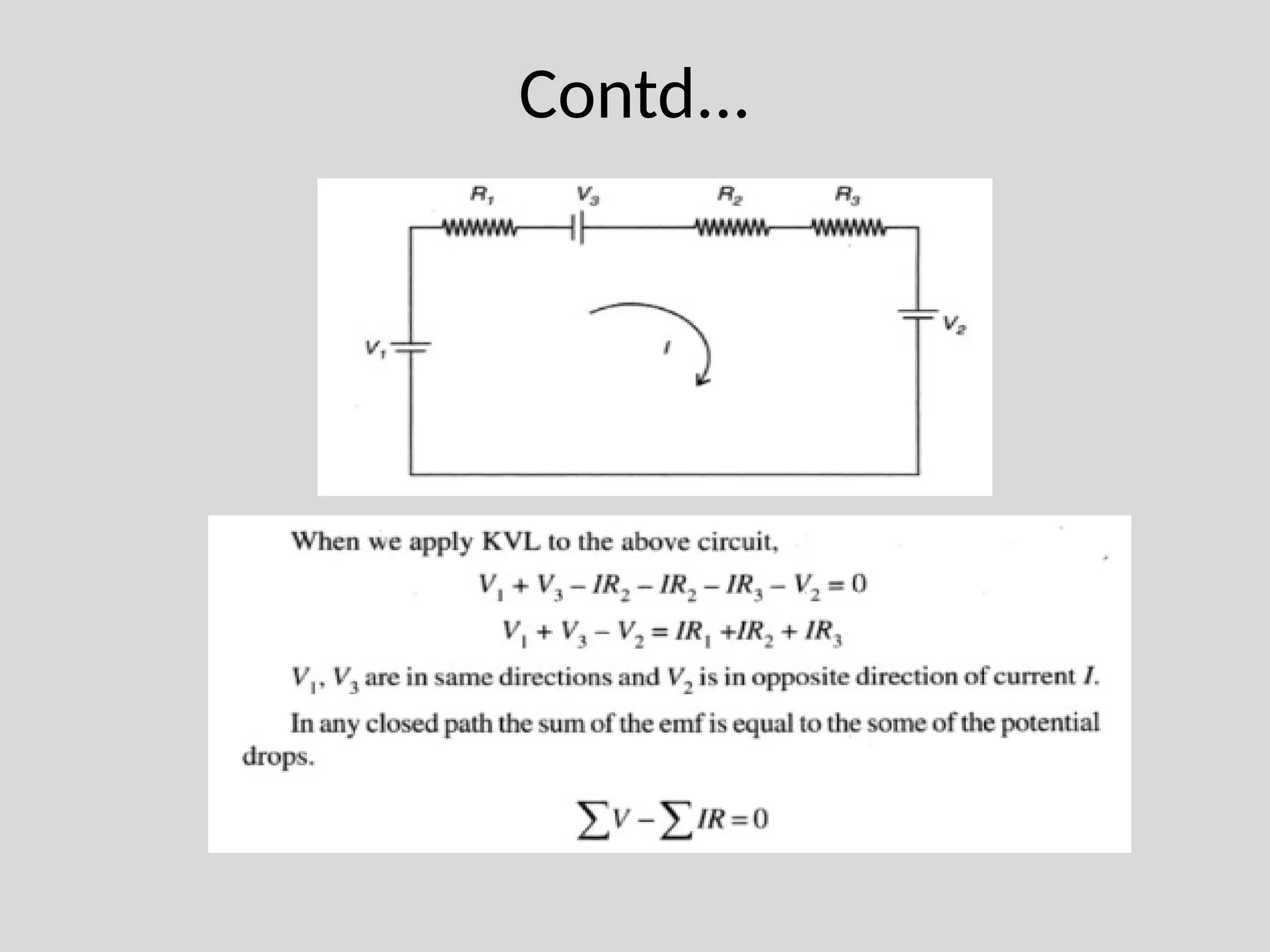
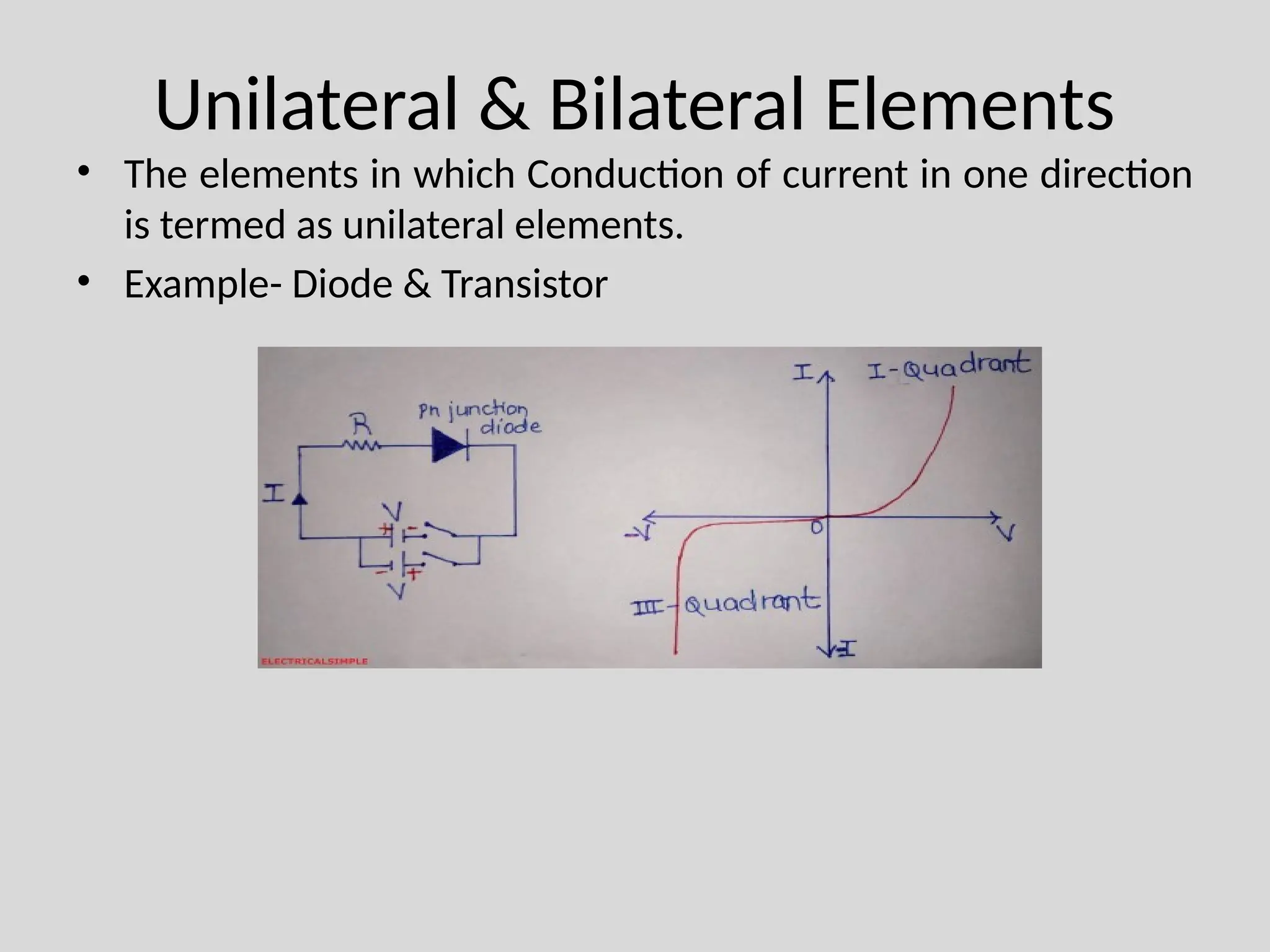
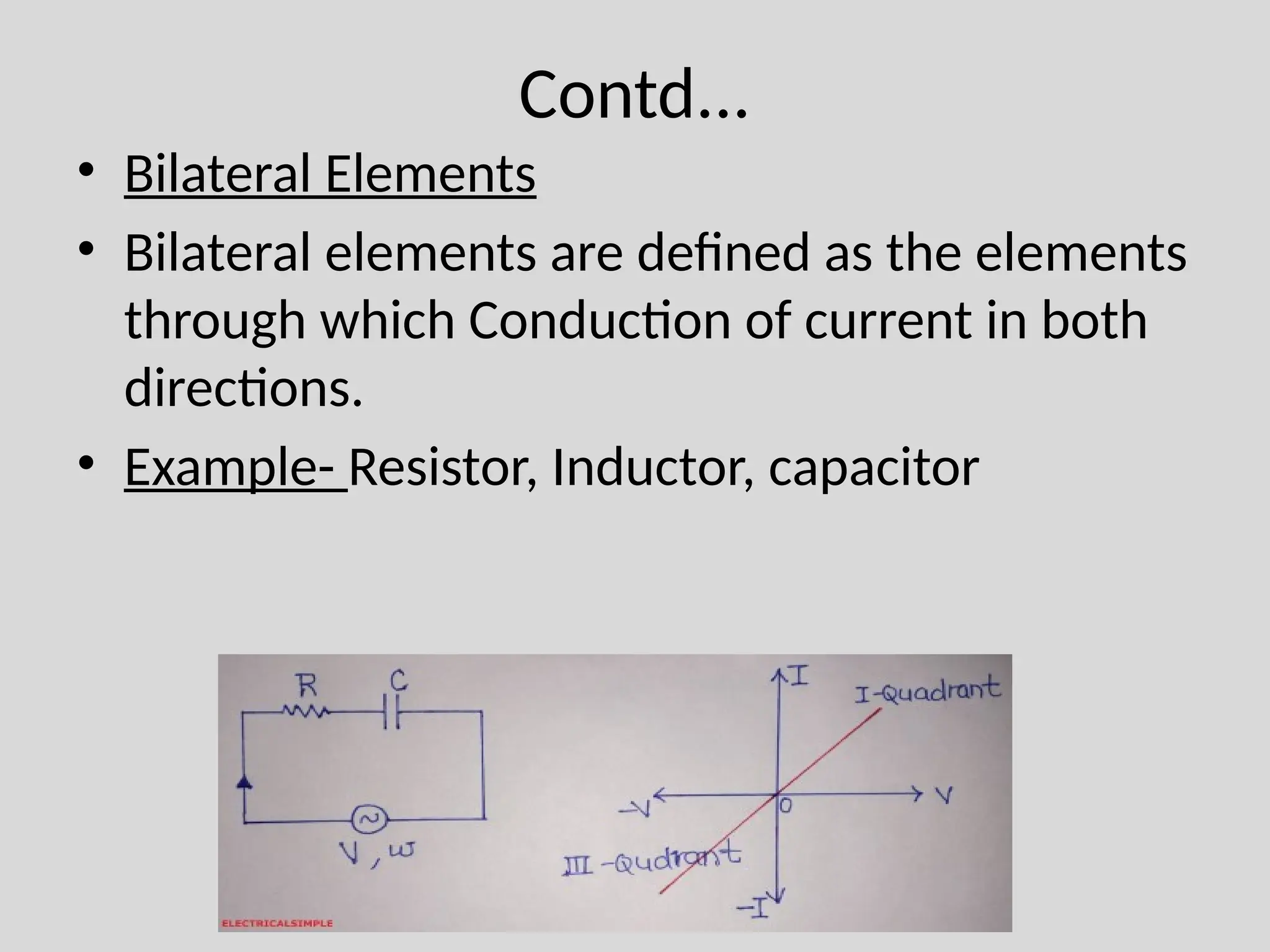
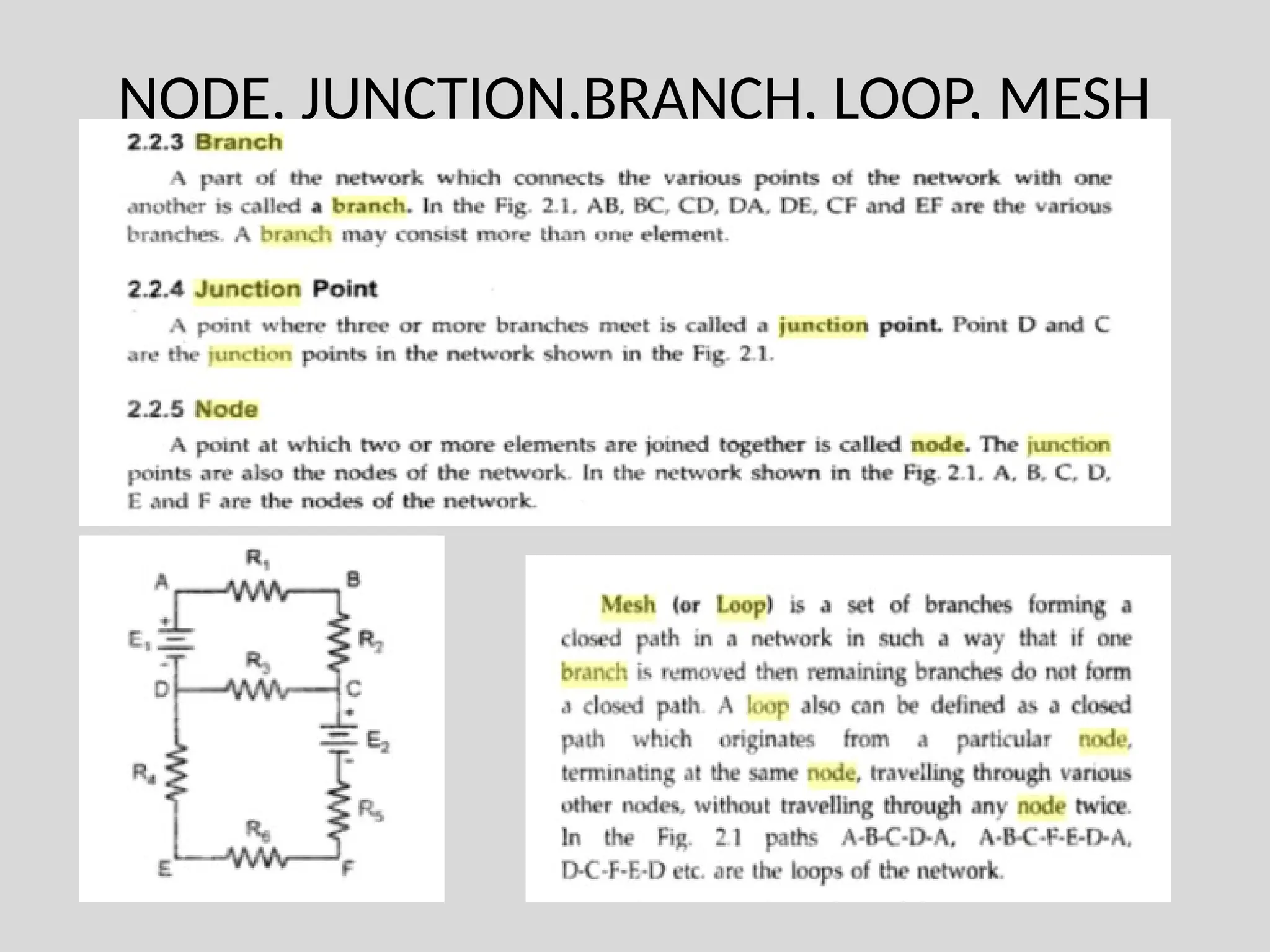
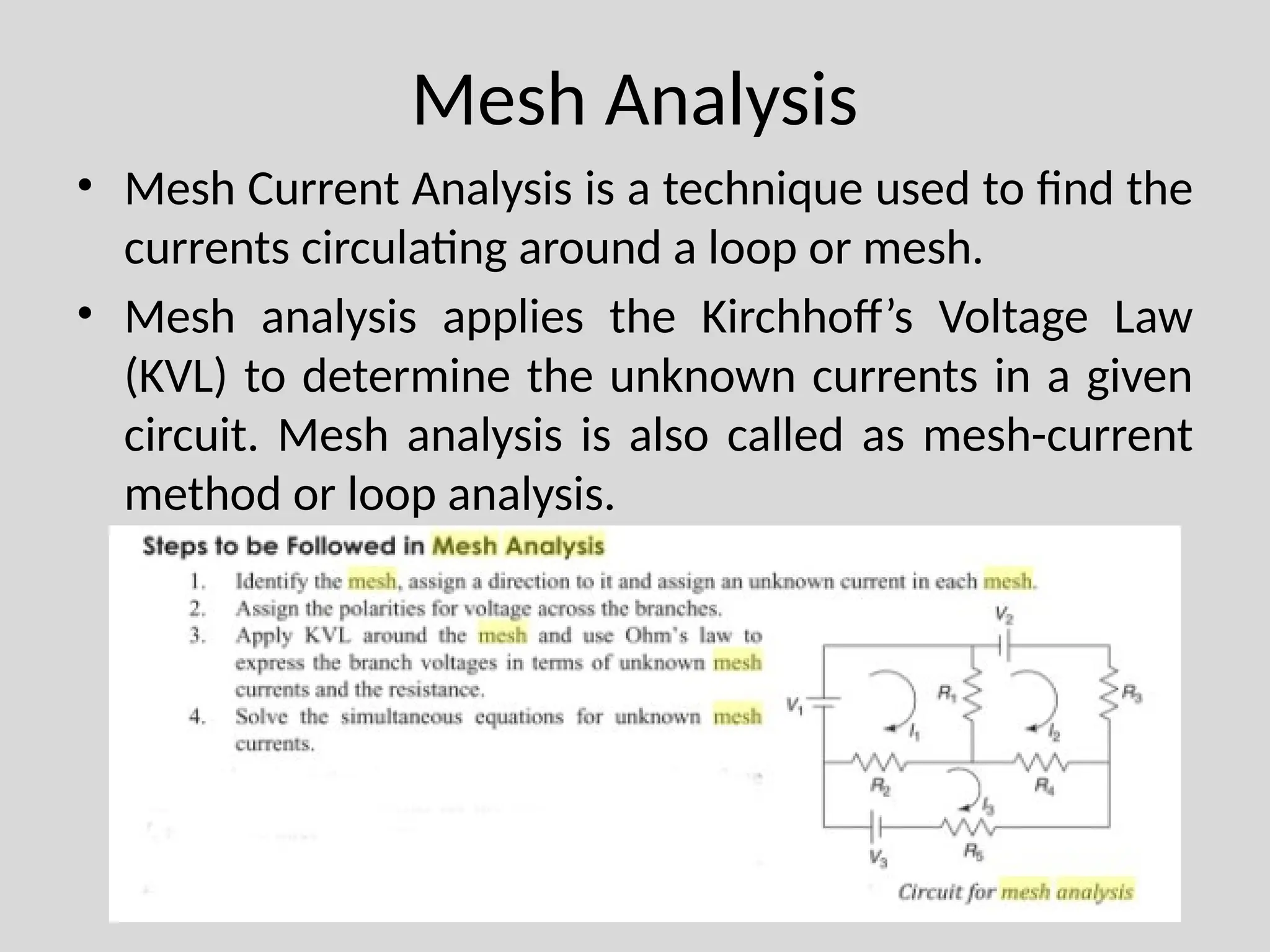
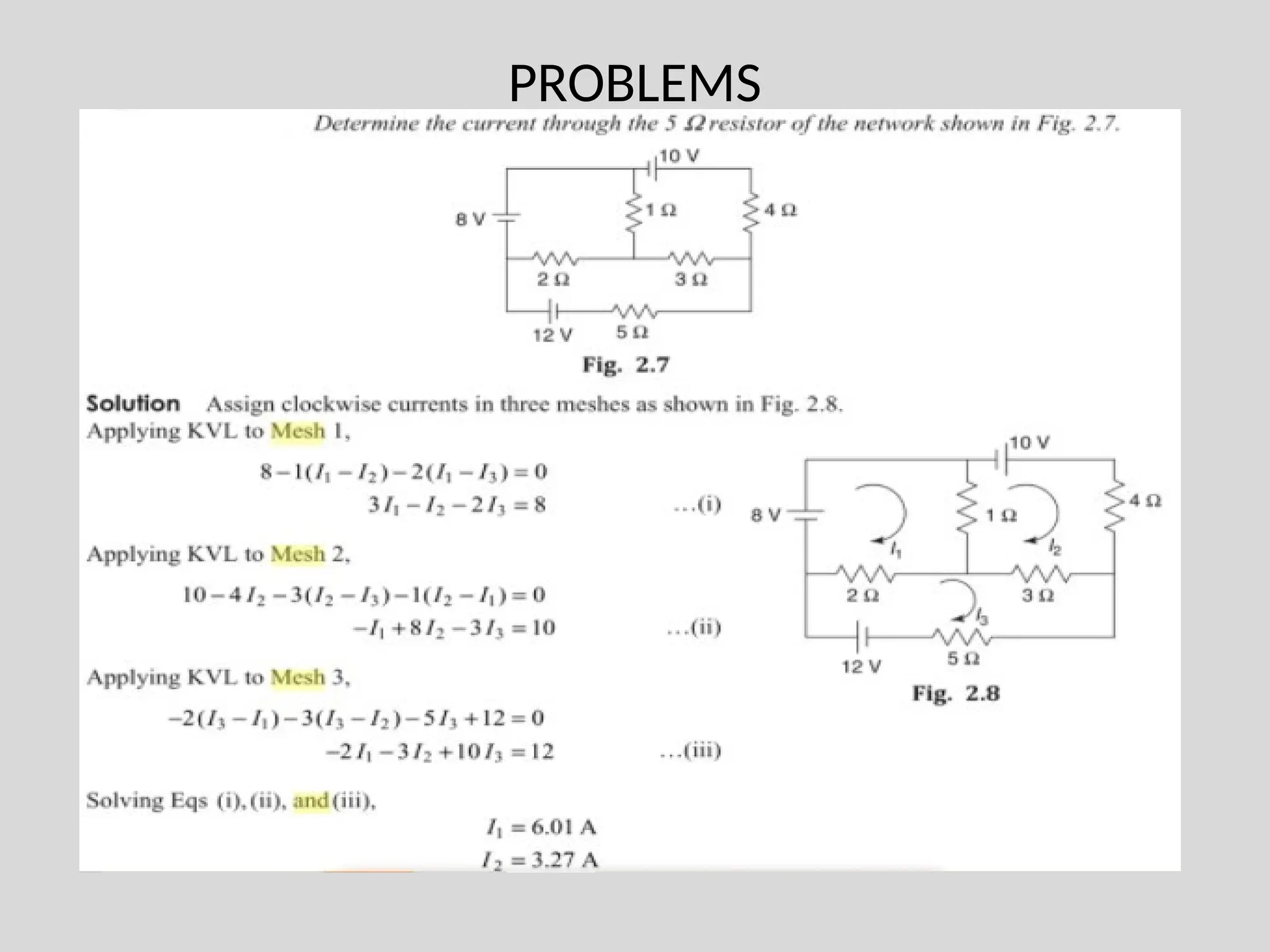
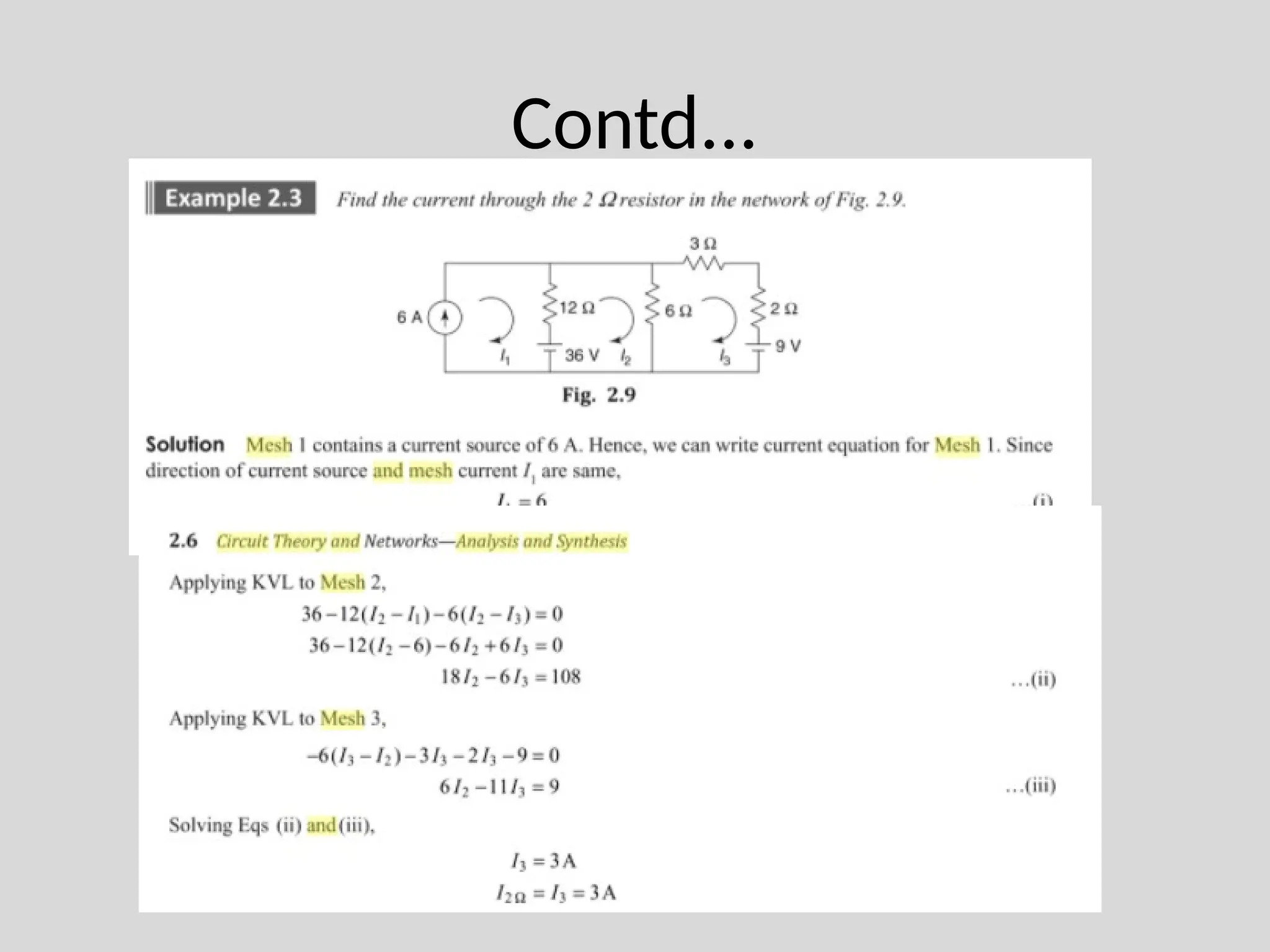
The document discusses Kirchhoff's laws, which include Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) stating that the total current entering a junction equals the current leaving it, and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) indicating that the sum of voltages in a closed path equals zero. It also differentiates between active and passive components, as well as unilateral and bilateral elements, and outlines linear versus nonlinear elements. Additionally, the document describes mesh analysis as a technique to determine unknown currents in circuits using KVL.