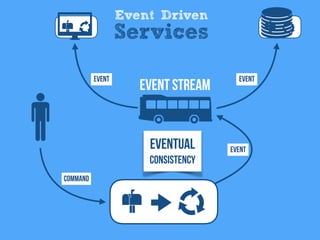
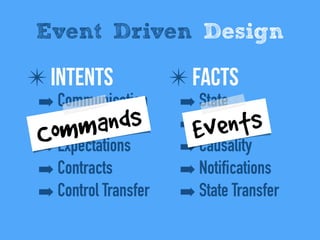
1) The document discusses how event-driven systems are reshaping modern architectures. It argues that modeling systems around publishing and reacting to events can help increase autonomy, loose coupling, scalability and other advantages.
2) Events represent immutable facts that accumulate over time and allow systems to manage uncertainty through eventual consistency. Well-designed events can help systems balance determinism and availability.
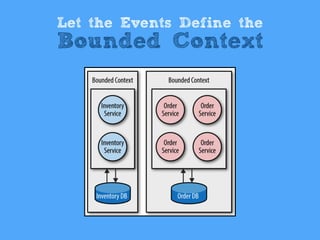
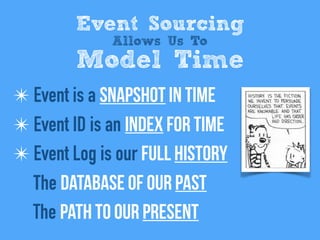
3) Event sourcing is presented as a cure for the "cardinal sin" of in-place updates, since it models the database as a cache of events from an immutable log. This allows for replay, auditing and other benefits like managing time within systems.