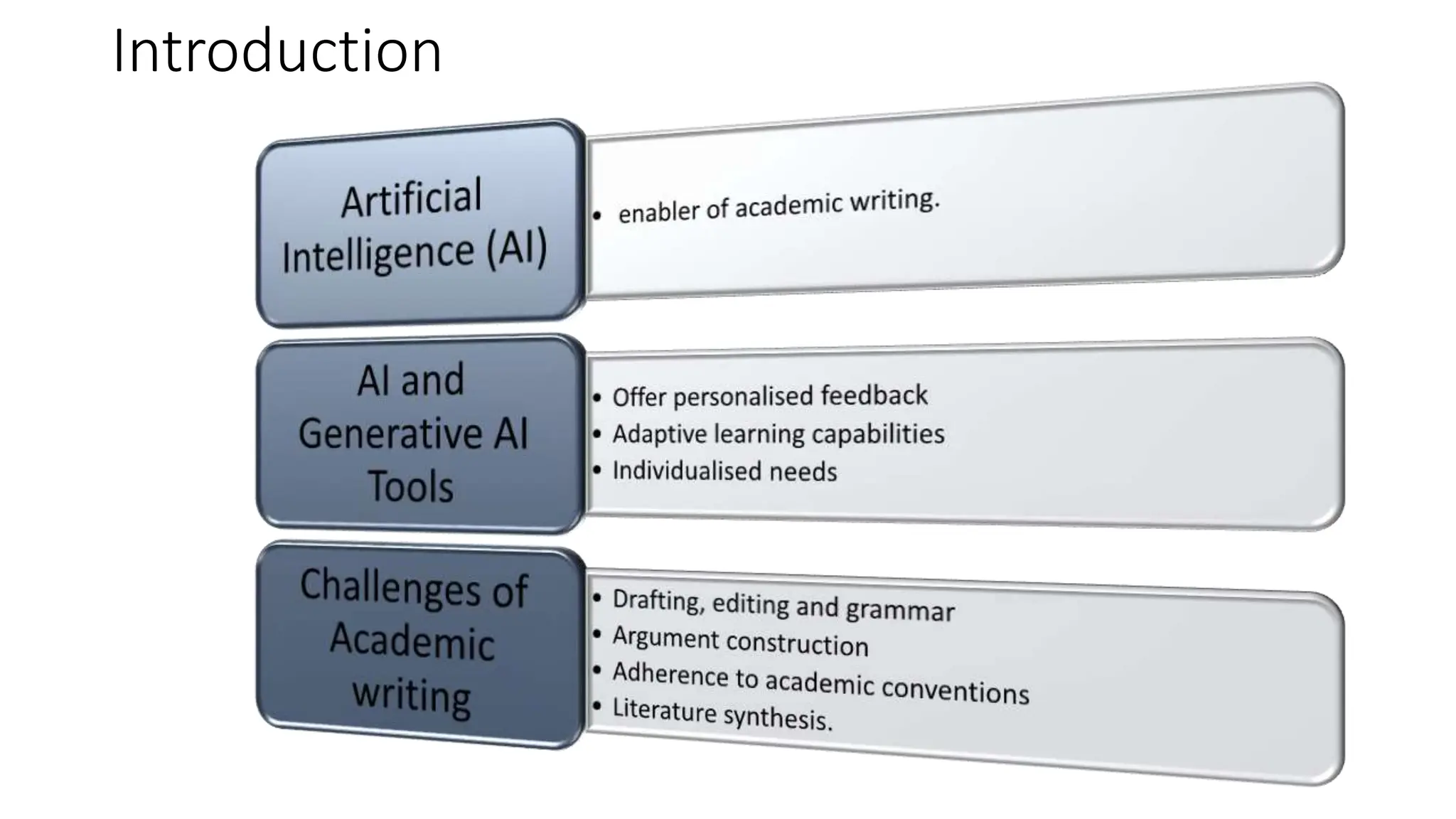
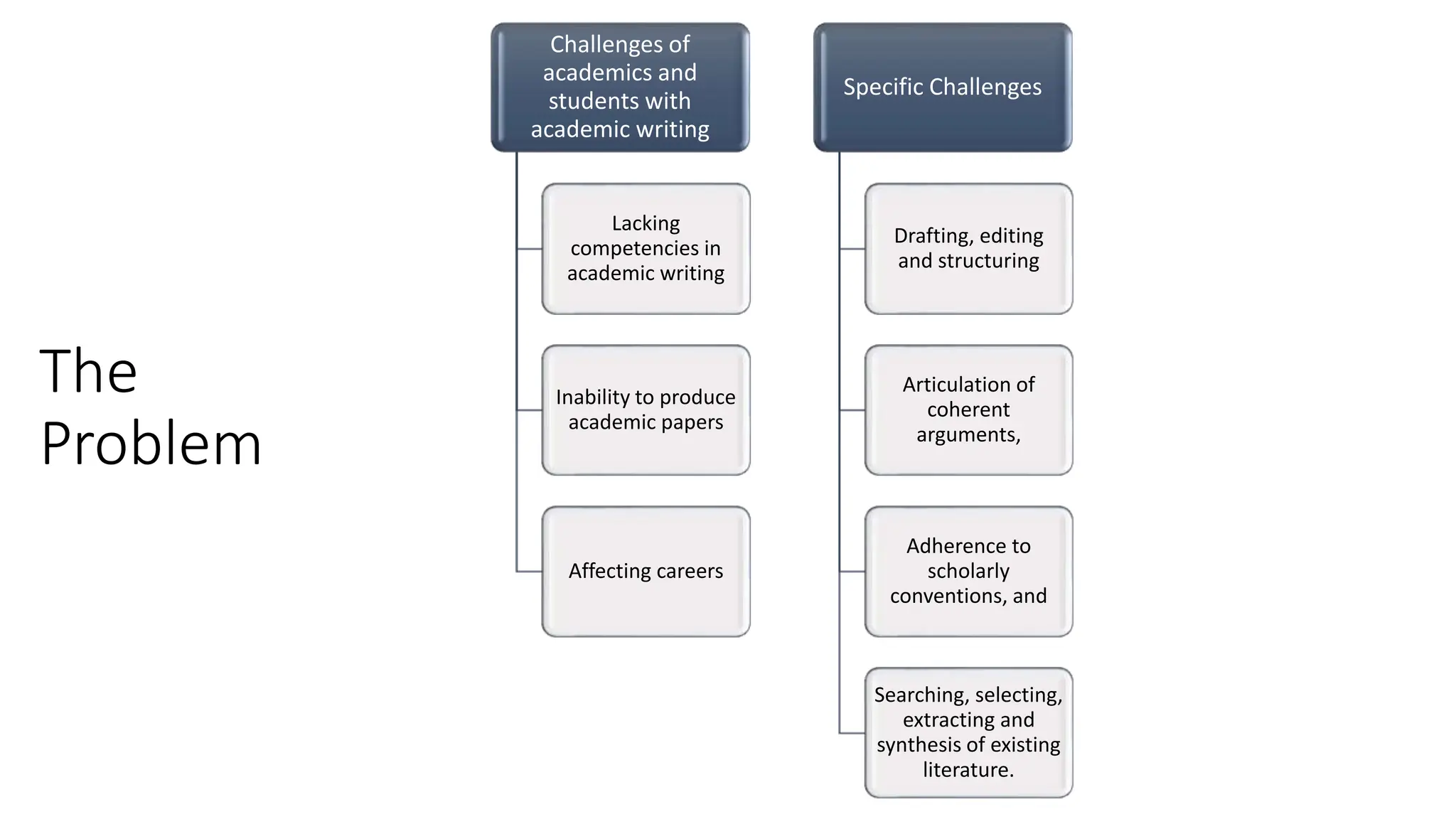
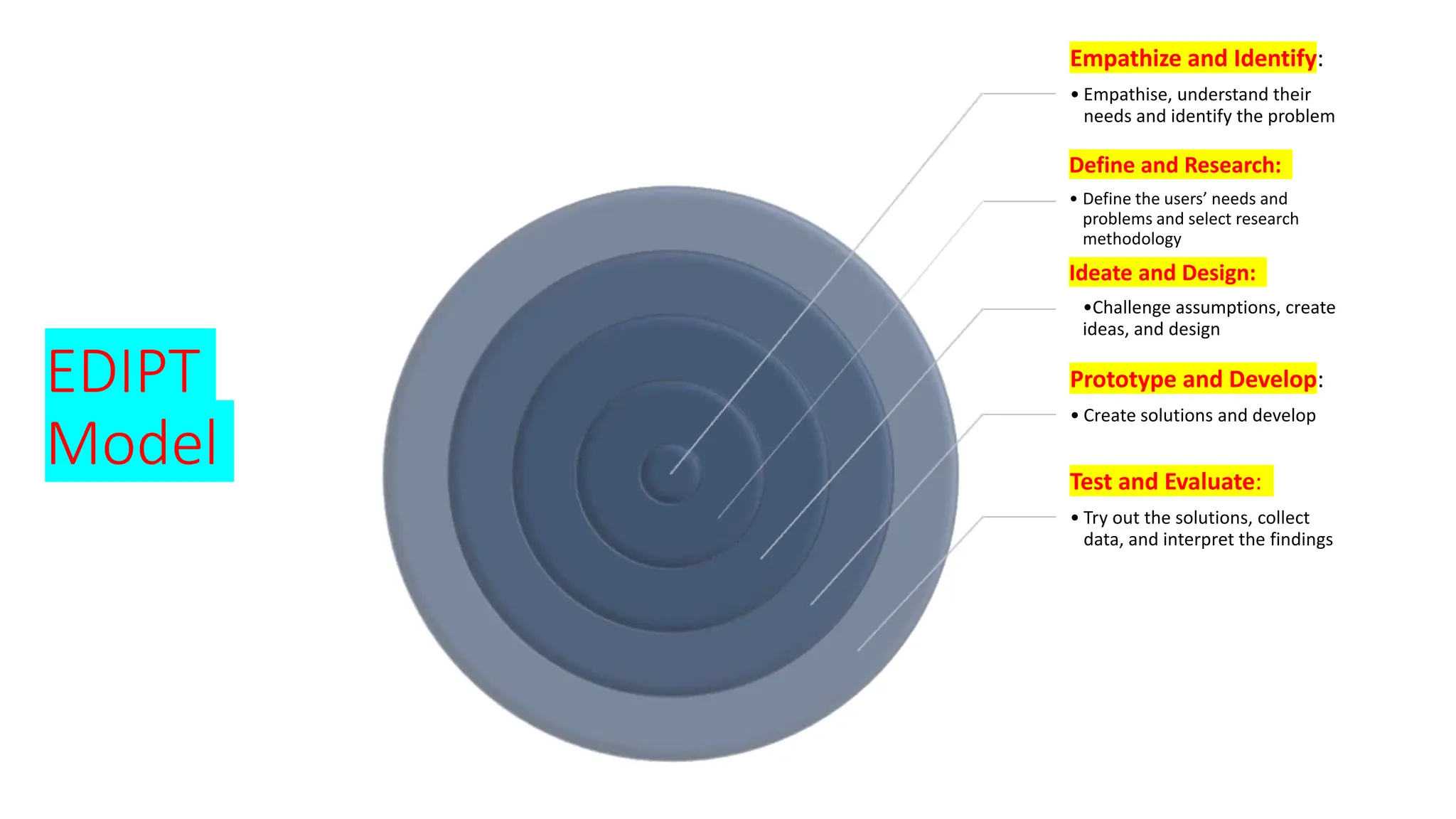
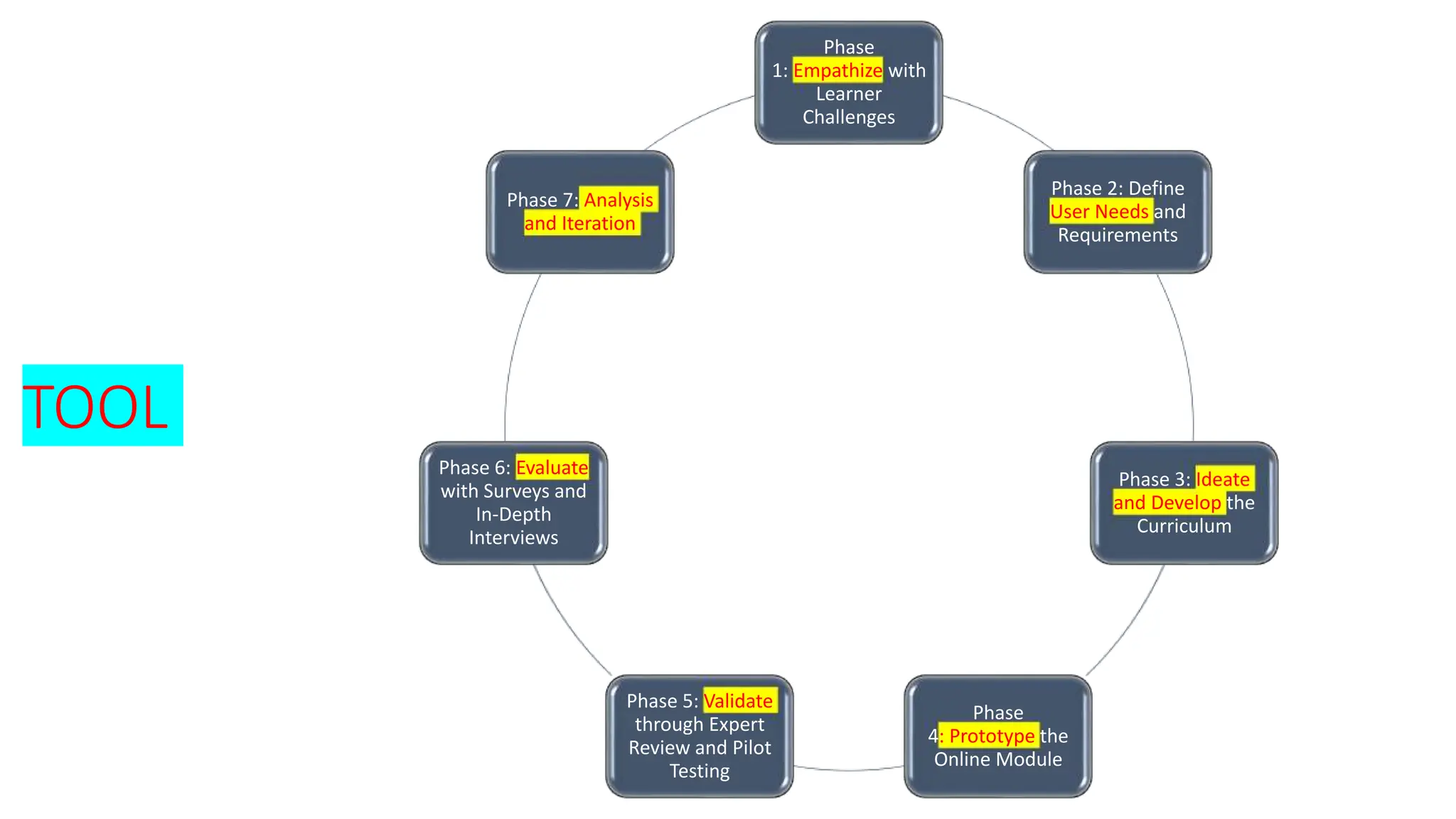
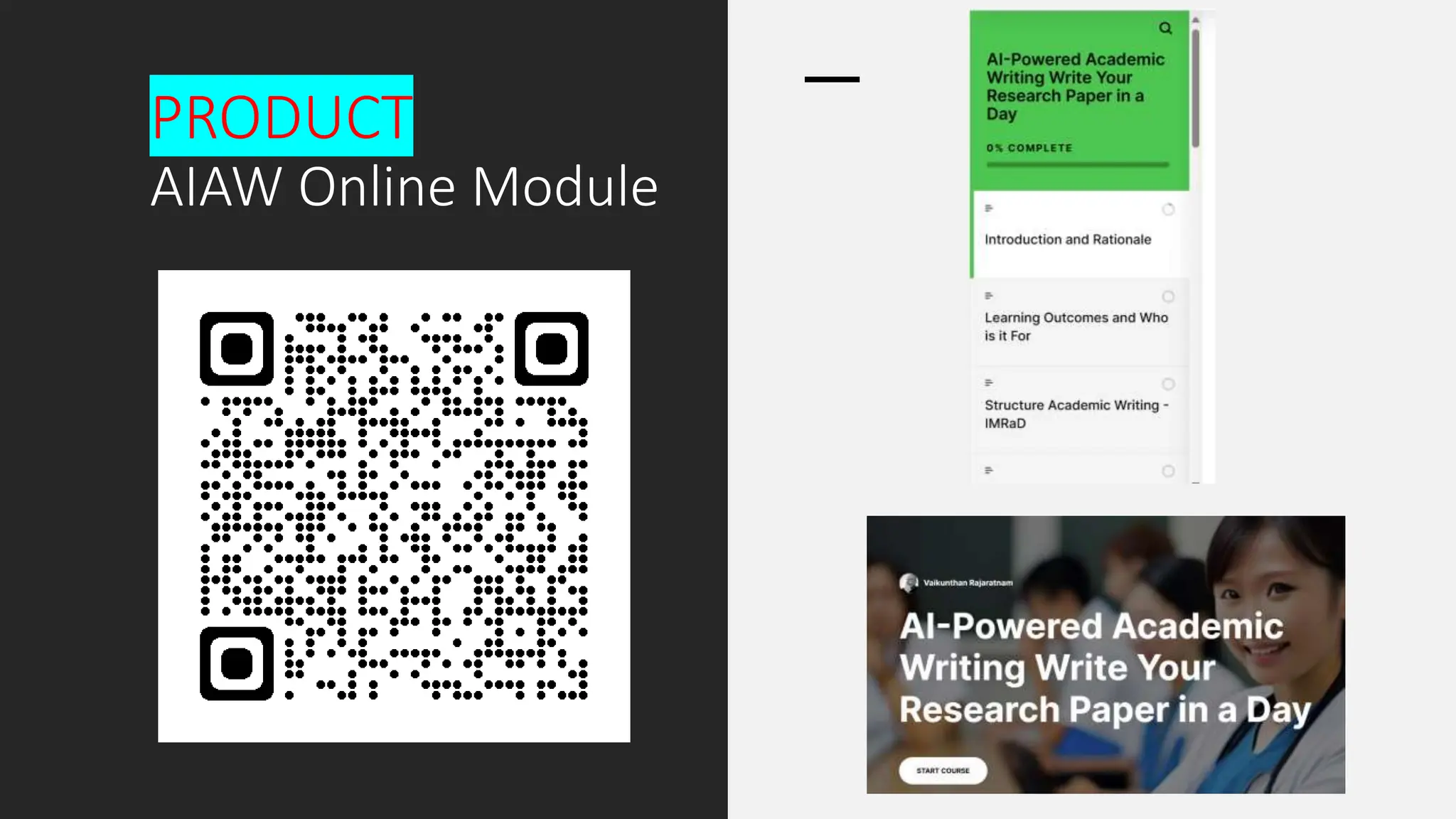
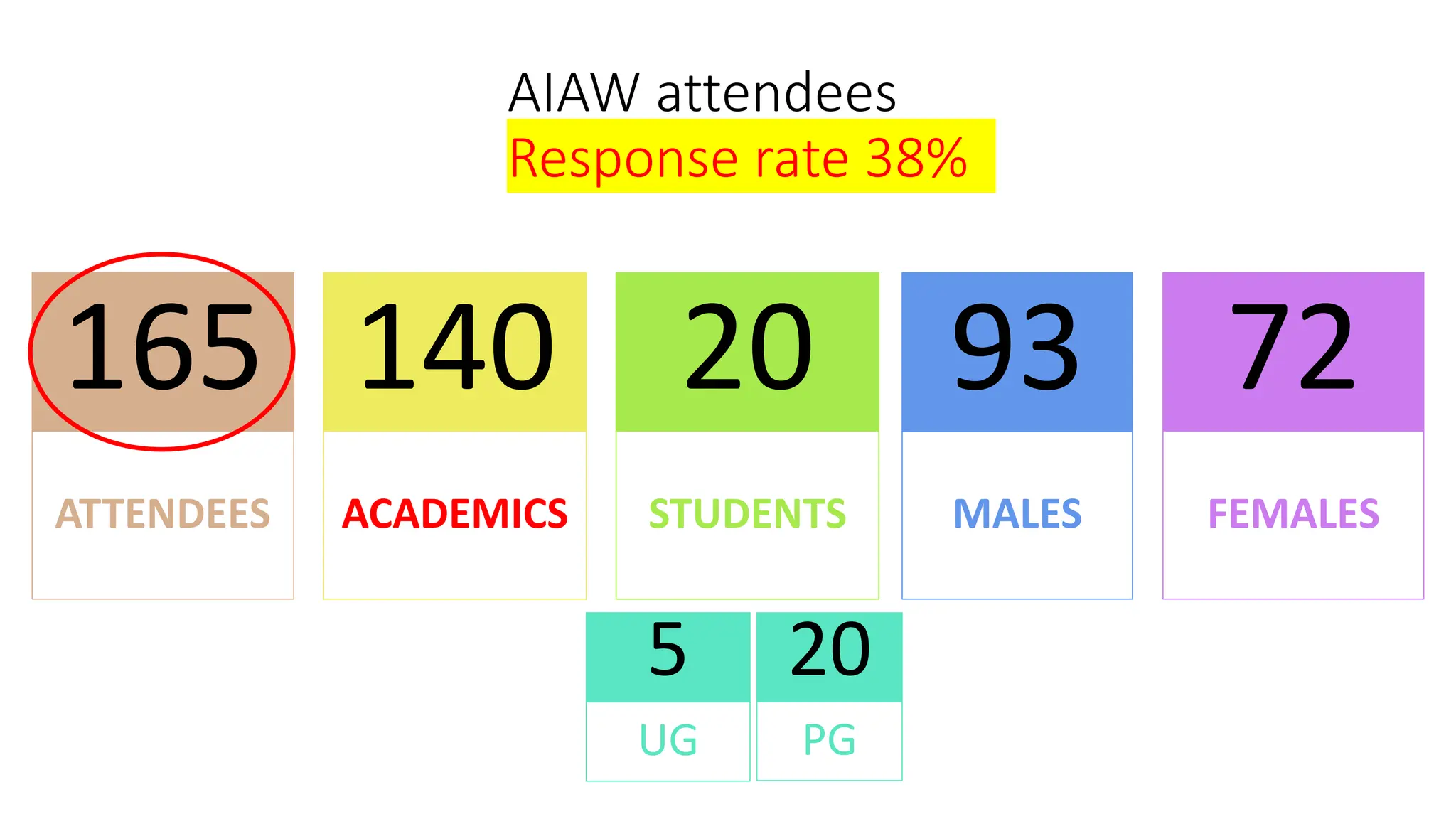
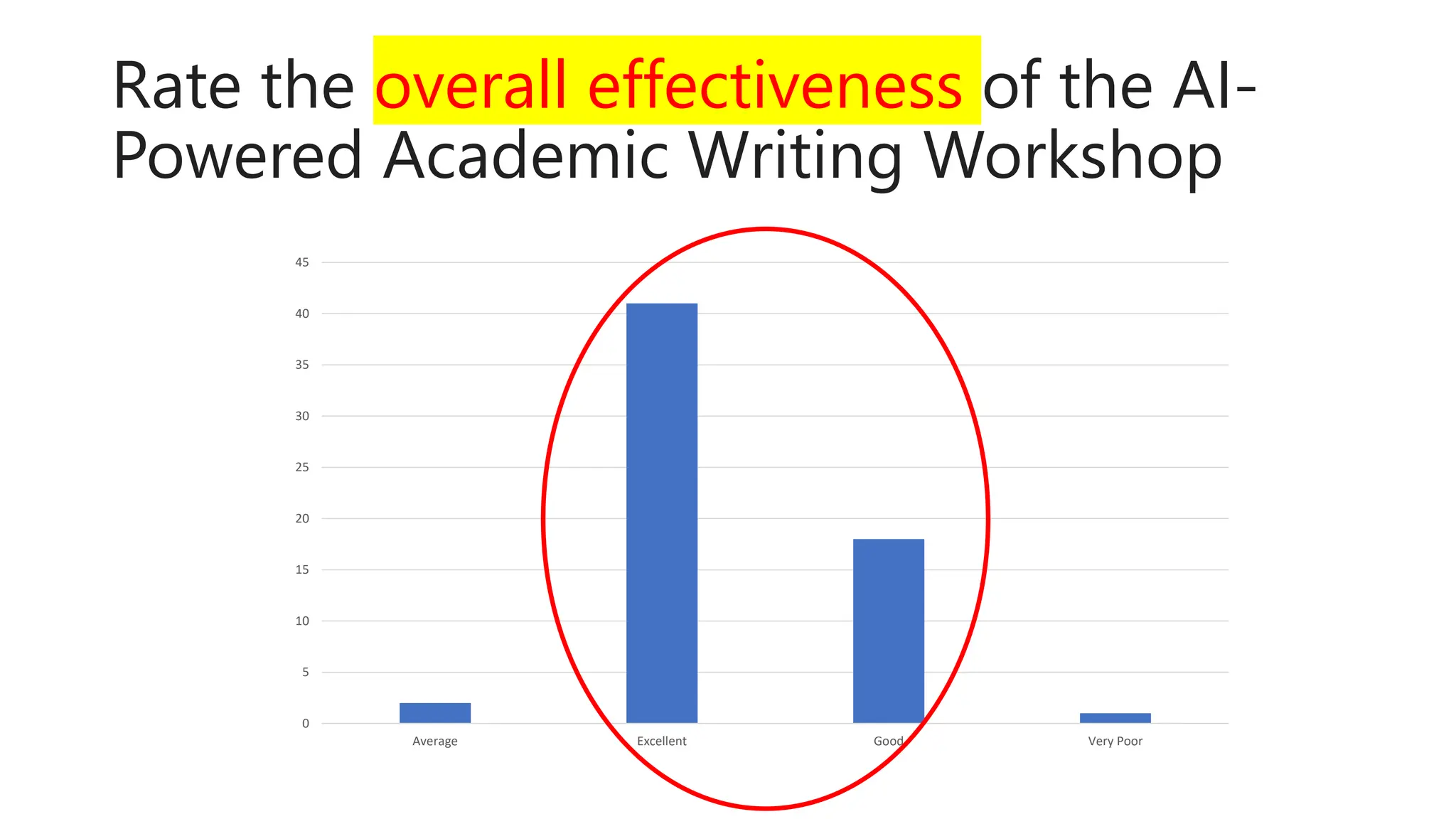
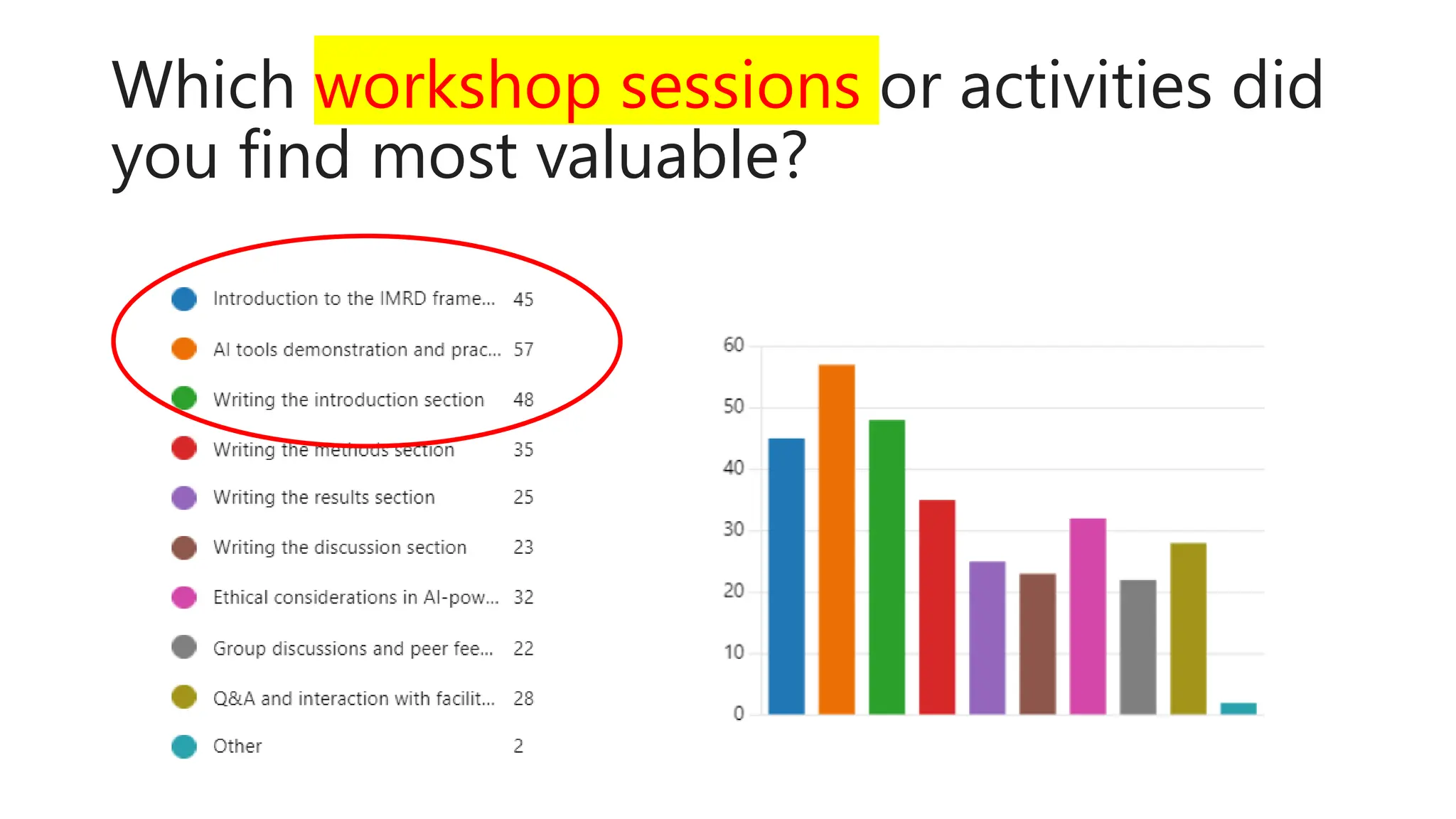
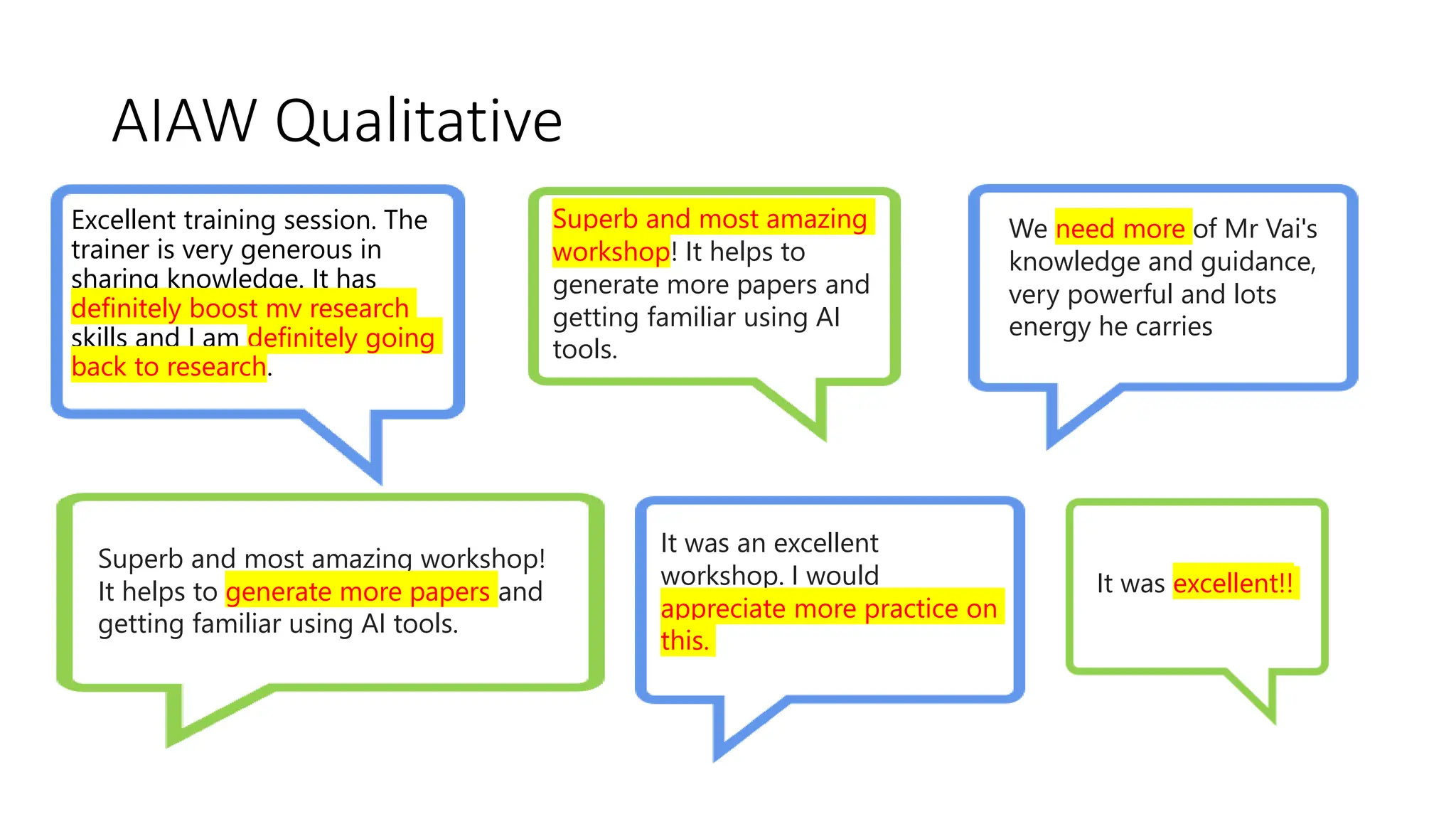
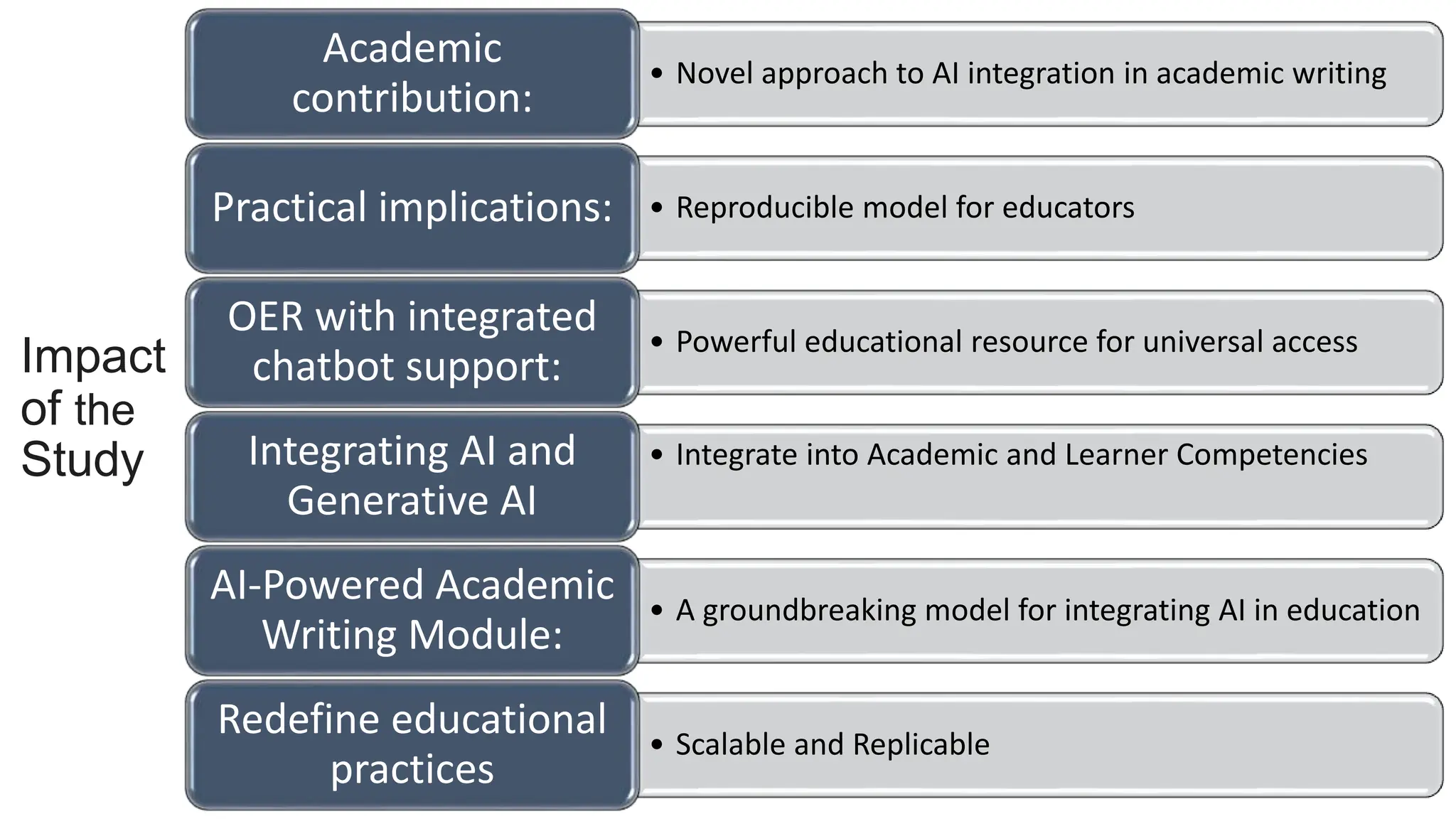
The document discusses the design, development, and validation of an AI-powered academic writing module aimed at addressing the challenges students and academics face in writing. Utilizing a user-centered approach and various methodologies, the module integrates AI tools and methods to enhance academic writing skills while receiving positive feedback from participants. Key findings indicate improved writing abilities, confidence, and the potential for broad application across educational frameworks.