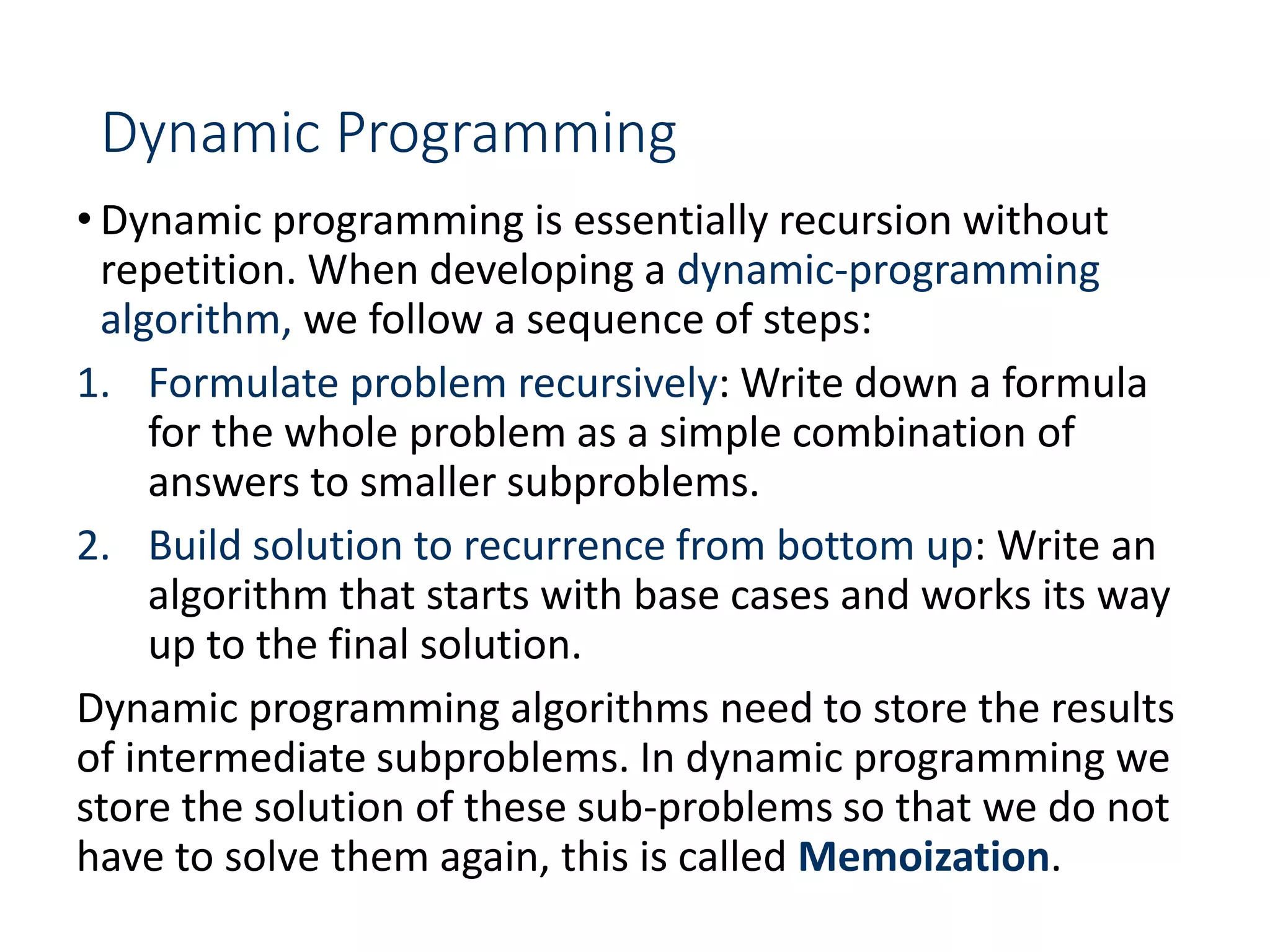
This document discusses dynamic programming and its application to problems involving matrix chain multiplication and edit distance. It provides examples of how dynamic programming can be used to solve problems involving overlapping subproblems more efficiently than naive recursive solutions. Specifically, it describes how dynamic programming formulations using memoization tables can compute matrix chain multiplications and edit distances in quadratic time rather than exponential time required by naive recursive approaches.









![Fibonacci Number: Memoization
•If we trace through the recursive calls to MEMOFIB,
we find that array F[ ] gets filled from bottom up.
I.e., first F[2], then F[3], and so on, up to F[n].
•We can replace recursion with a simple for-loop
that just fills up the array F[ ] in that order.
•This gives us our first explicit dynamic programming
algorithm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-11-2048.jpg)






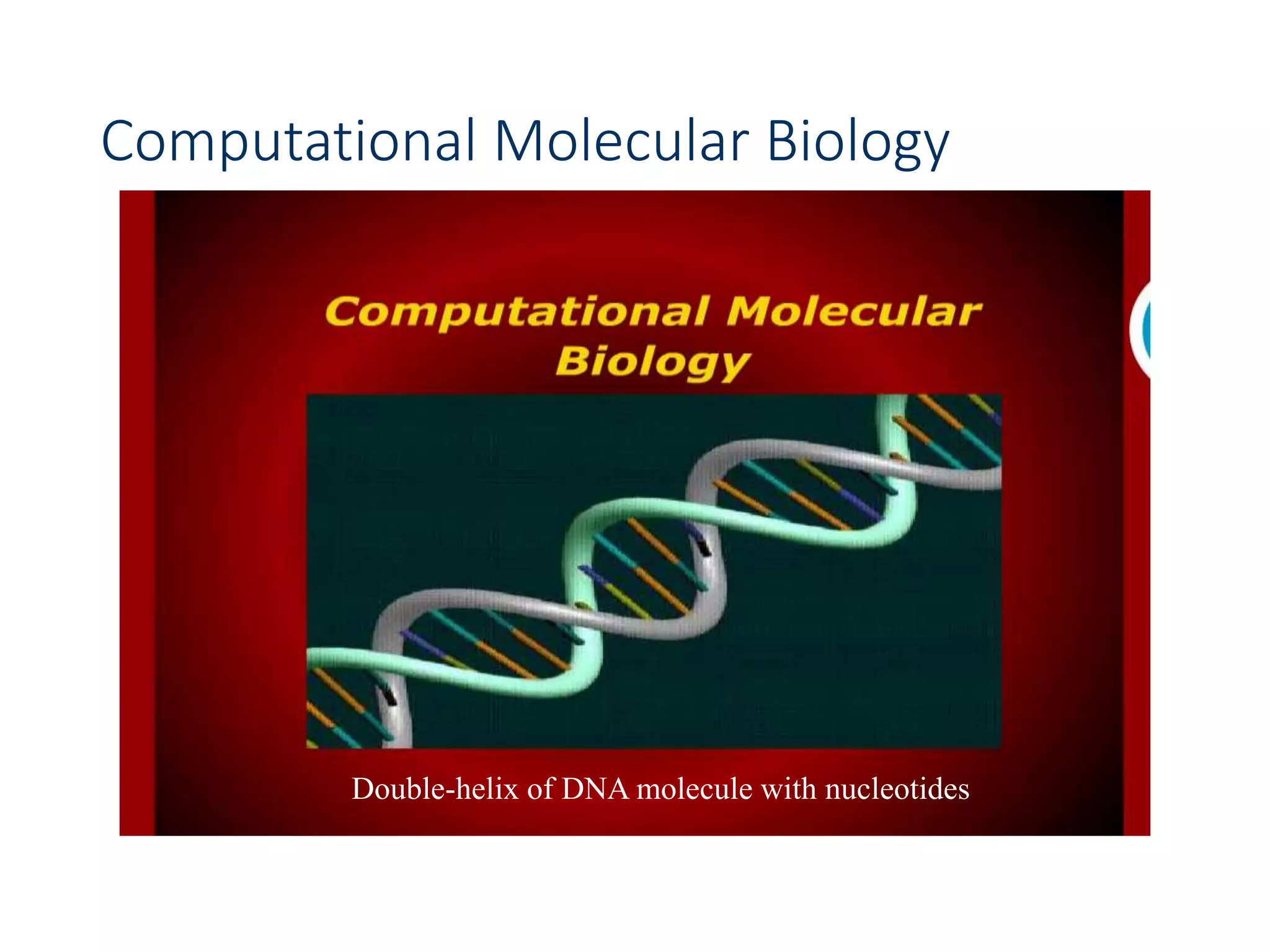
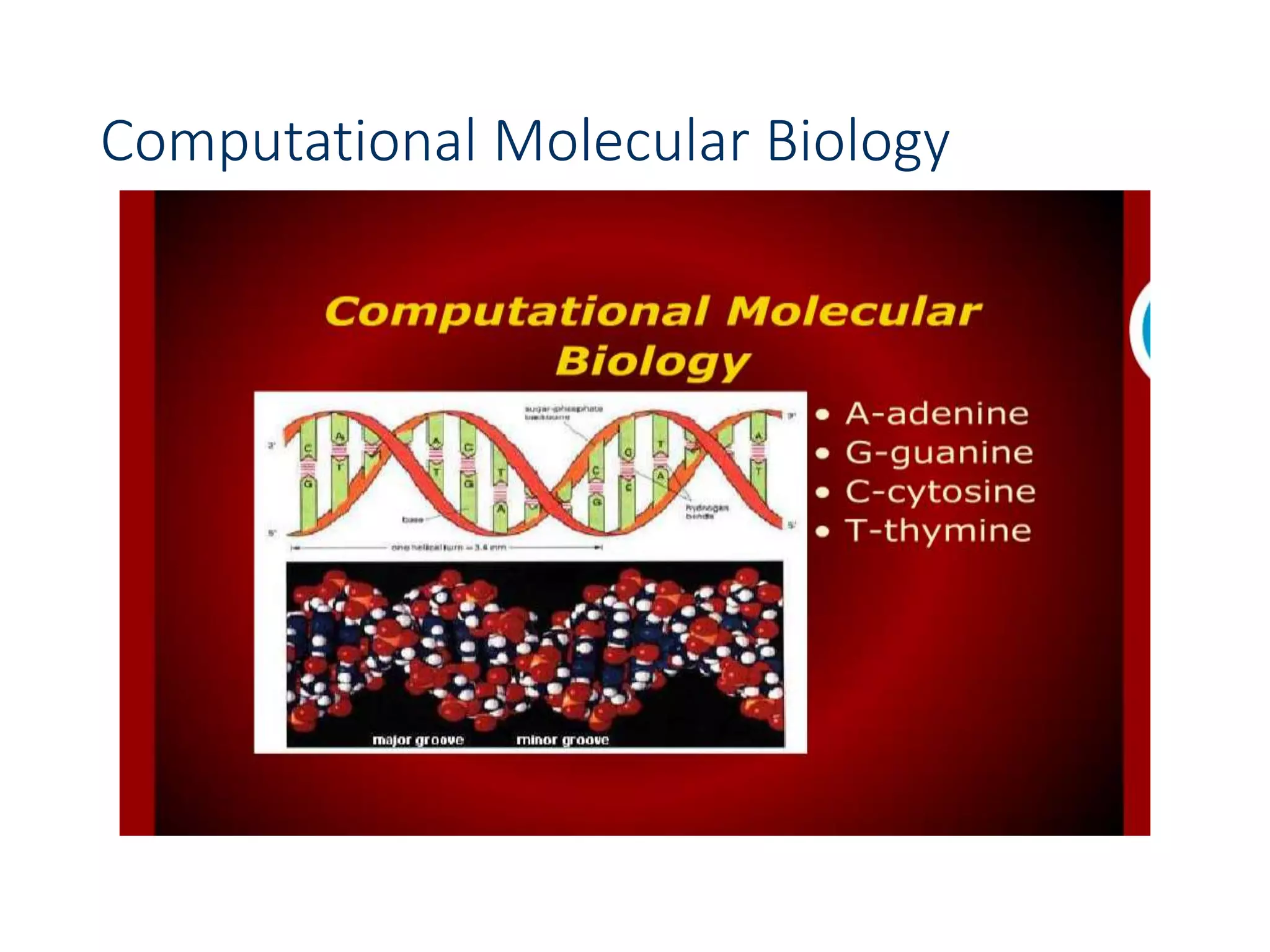












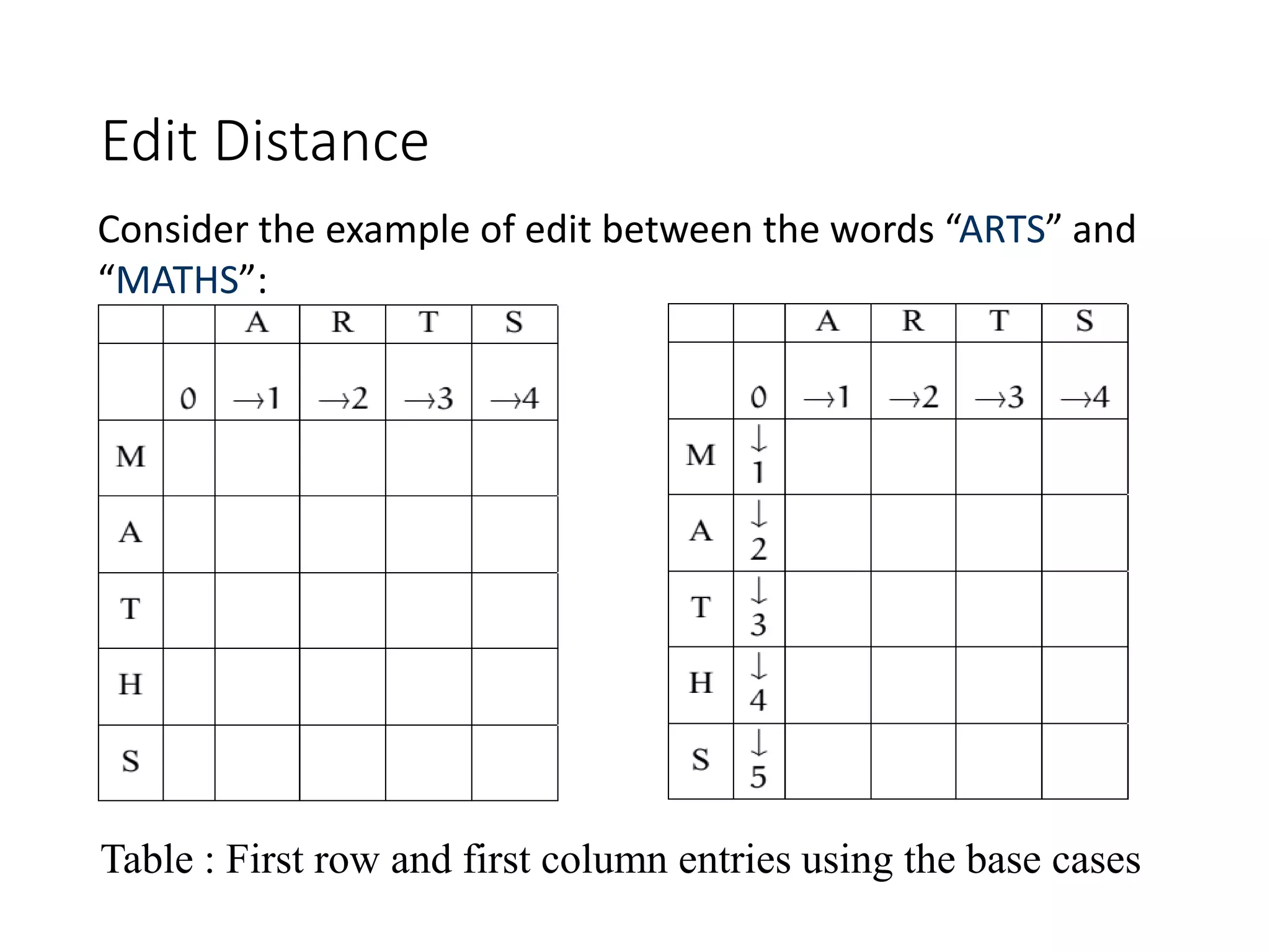
![Edit Distance
Table : Computing E[1, 1] and E[1, 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-34-2048.jpg)
![Edit Distance
Table : Computing E[1, 3] and E[1, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-35-2048.jpg)
![Edit Distance
Table : The final table with all E[i, j] entries computed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-36-2048.jpg)
![Edit Distance
Table : Possible edit scripts. The red arrows from E[0, 0] to E[4, 5] show the
paths that can be followed to extract edit scripts.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-37-2048.jpg)





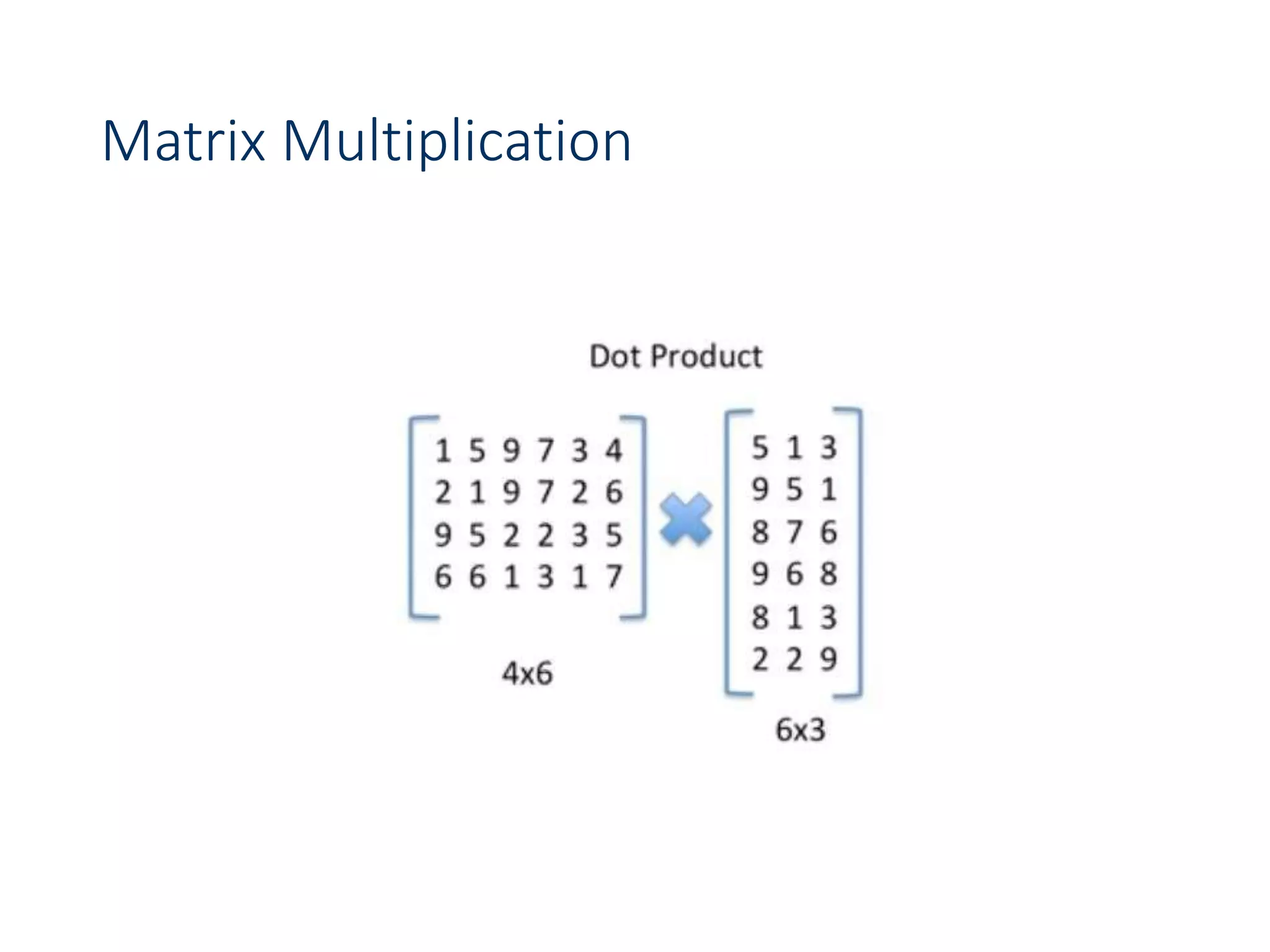
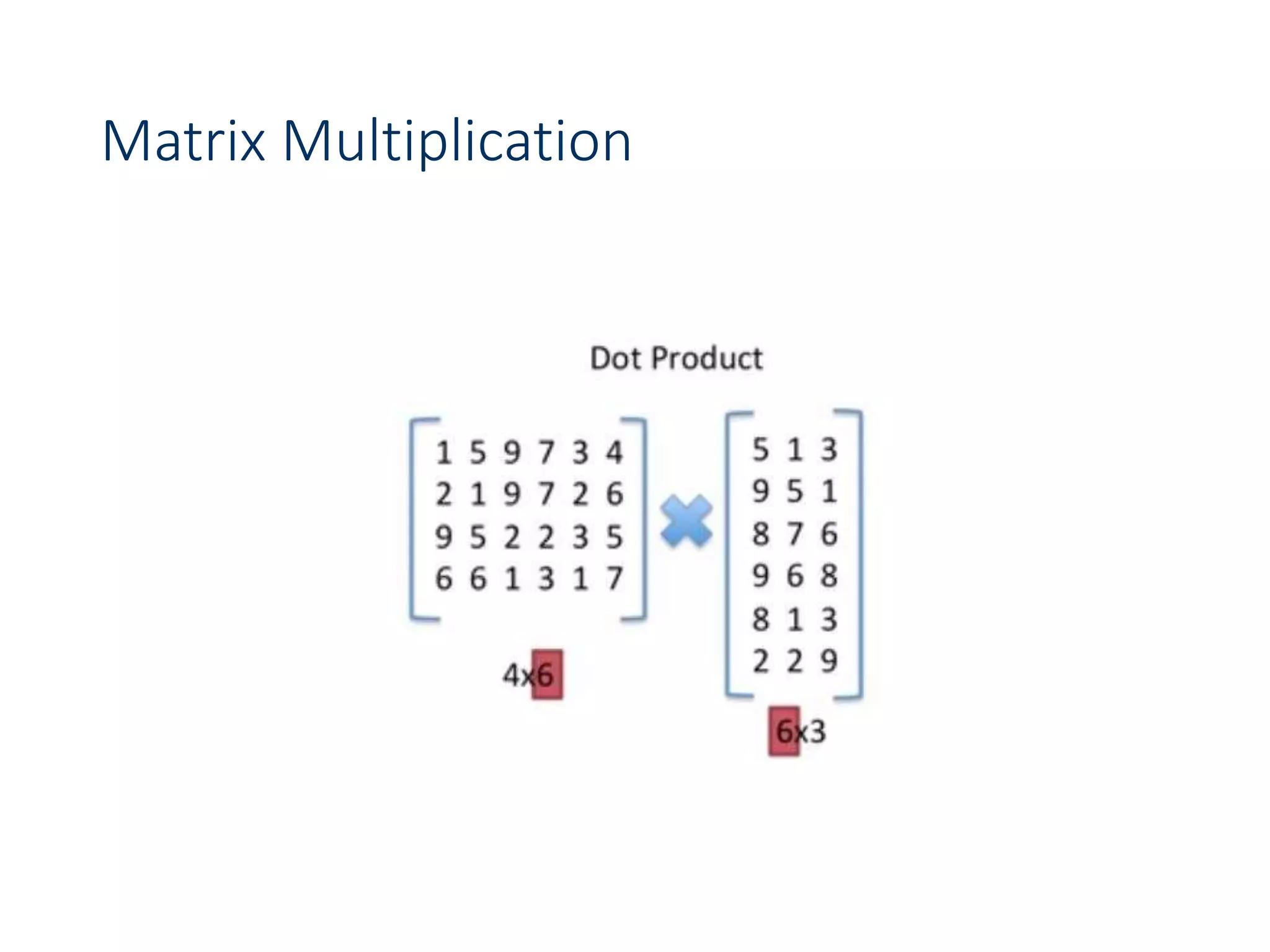
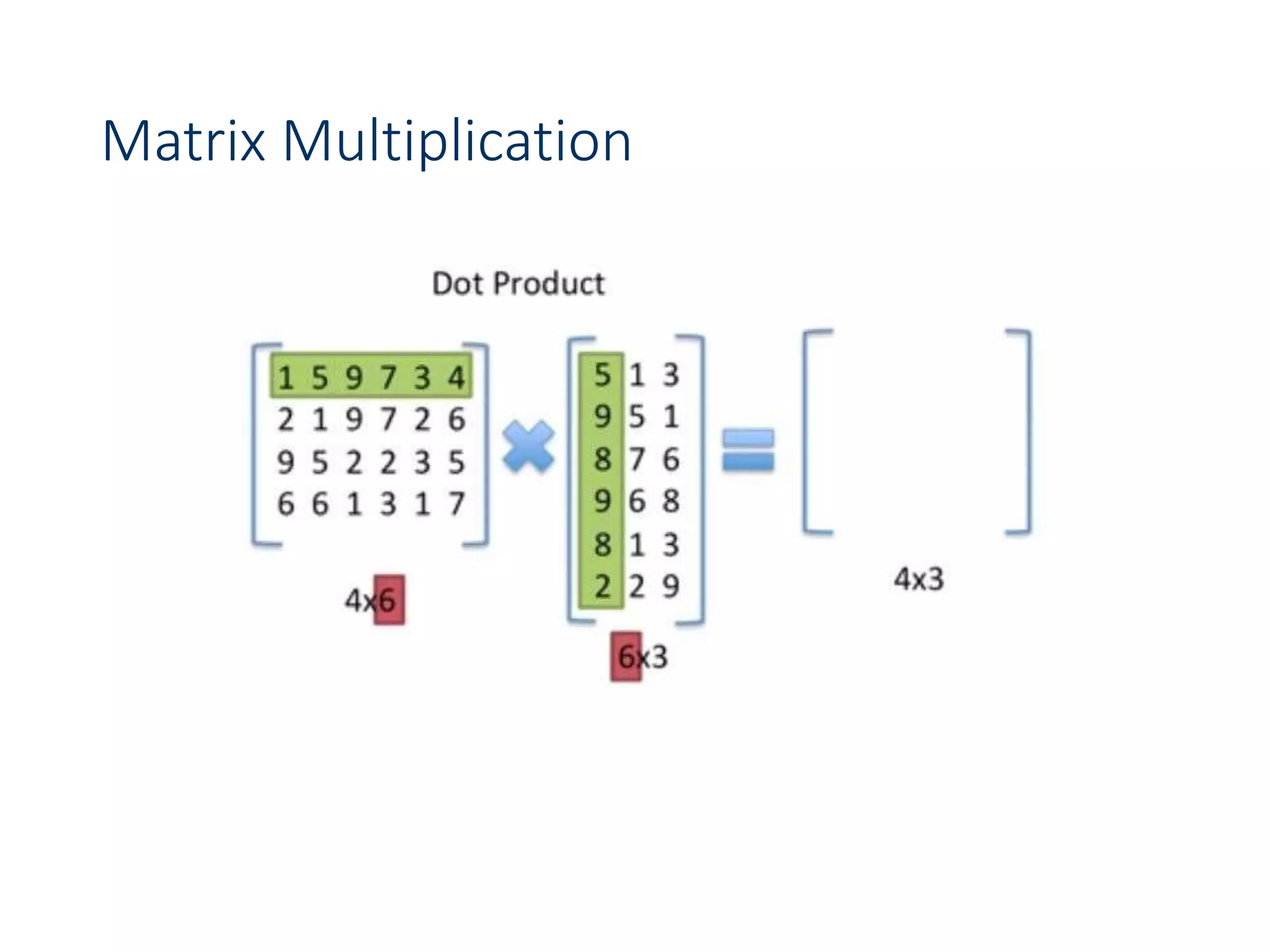
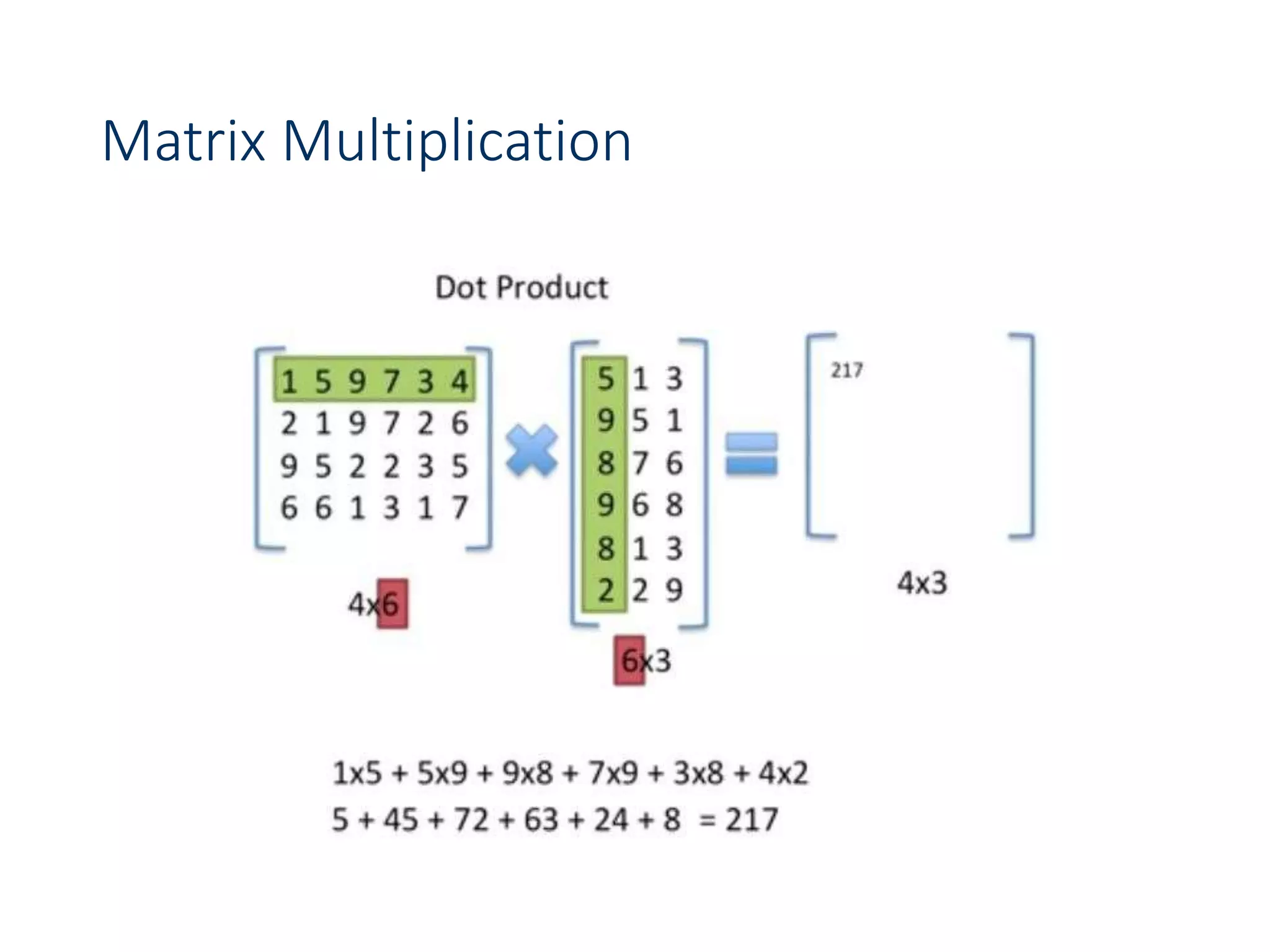
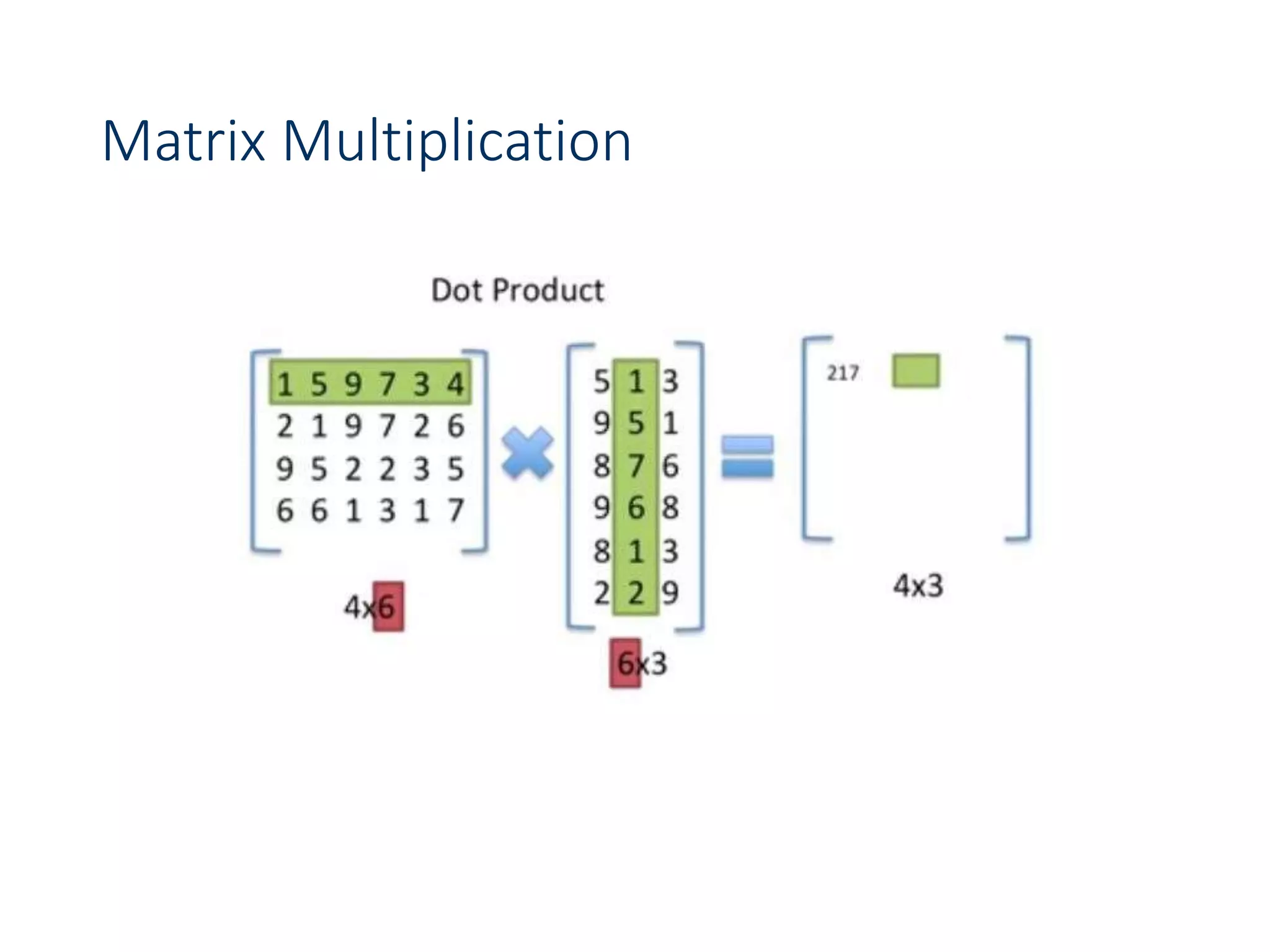
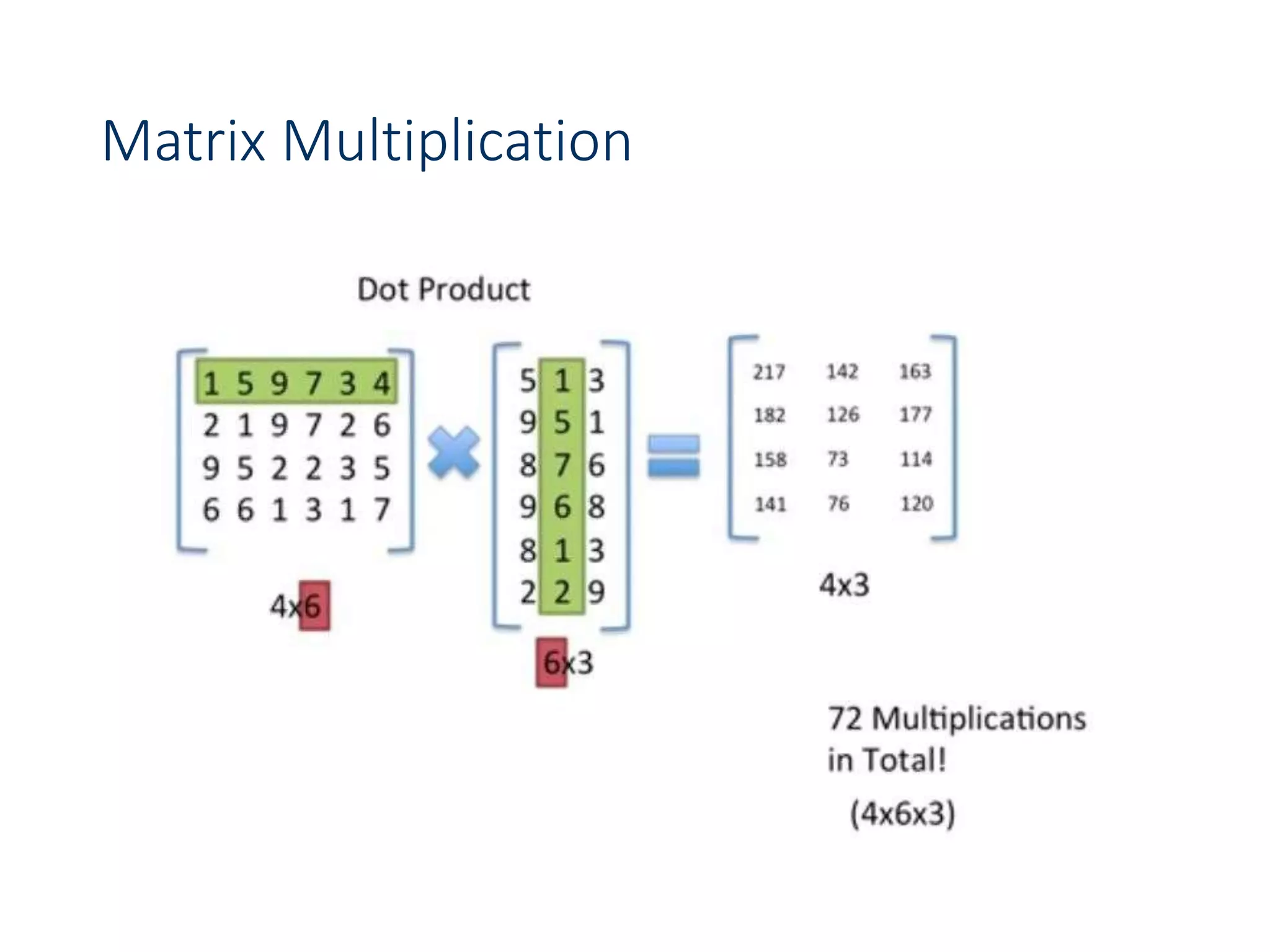
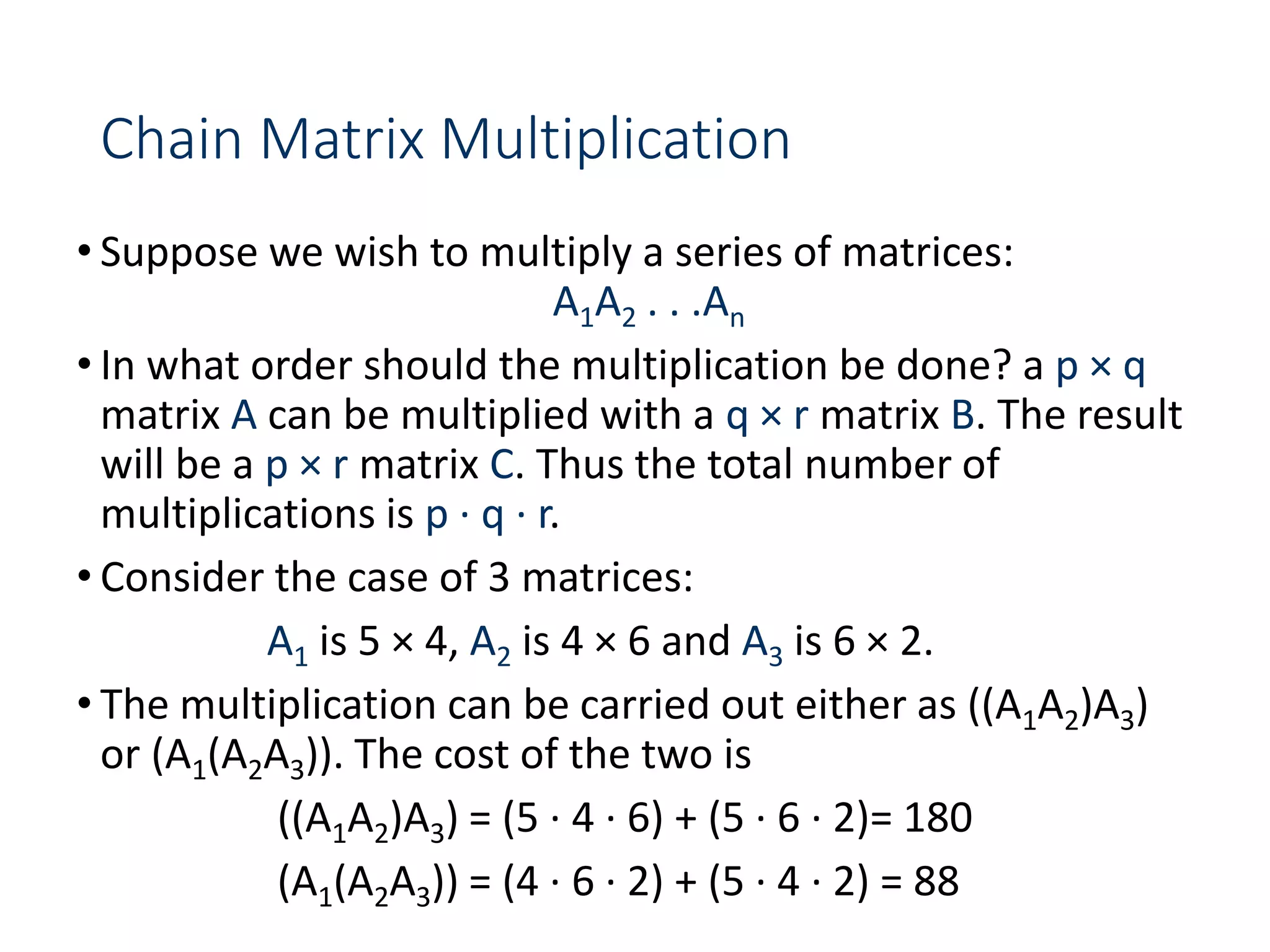




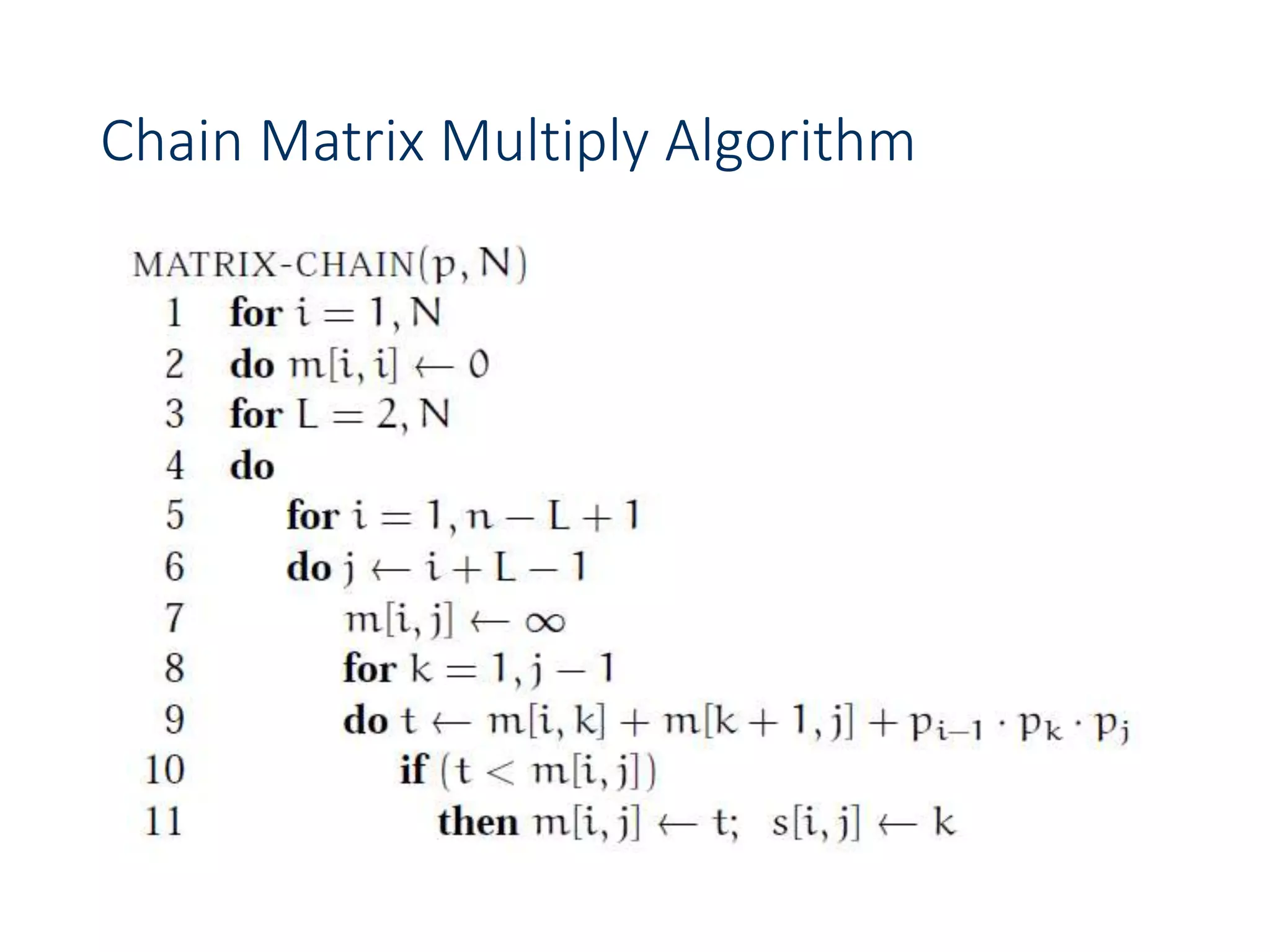
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
•We can not use divide and conquer because we do not
know what is the optimum k. We will have to consider
all possible values of k and take the best of them. We
will apply this strategy to solve the subproblems
optimally.
•We will store the solutions to the subproblem in a
table and build the table bottom-up (why)?
•For 1 < i < j < n, let m[i, j] denote the minimum number
of multiplications needed to compute Ai..j. The
optimum can be described by the following recursive
formulation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-56-2048.jpg)
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
• If i = j, there is only one matrix and thus m[i, i] = 0
(the diagonal entries).
• If i < j, the we are asking for the product Ai..j.
• This can be split by considering each k, i < k < j, as
Ai..k times Ak+1..j.
•The optimum time to compute Ai..j is m[i, k] and
optimum time for Ak+1..j is in m[k + 1, j]. Since Ai..k is a
pi−1 × pk matrix and Ak+1..j is pk × pj matrix, the time to
multiply them is pi−1 × pk × pj.
•This suggests the following recursive rule:
m[i, i] = 0
m[i, j] = mini<k<j (m[i, k] +m[k + 1, j] + pi−1.pk.pj)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-57-2048.jpg)
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
• We do not want to calculate m entries recursively. So how should
we proceed? We will fill m along the diagonals. Here is how. Set
all m[i, i] = 0 using the base condition. Compute cost for
multiplication of a sequence of 2 matrices. These are m[1, 2],
m[2, 3], m[3, 4], . . . , m[n − 1, n].
• m[1, 2], for example is m[1, 2] = m[1, 1] +m[2, 2] + p0 · p1 · p2
• For example, for m for product of 5 matrices at this stage would
be:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-58-2048.jpg)
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
•Next, we compute cost of multiplication for sequences
of three matrices.
•These are
m[1, 3],m[2, 4],m[3, 5], . . . ,m[n − 2, n].
•m[1, 3], for example is
•We repeat the process for sequences of four, five and
higher number of matrices. The final result will end up
in m[1, n].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-59-2048.jpg)



![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
•For example, there are two possible splits for computing
m[1, 3]; we will choose the split that yields the
minimum:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-63-2048.jpg)
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
•Similarly, for m[2, 4] and m[3, 5]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-64-2048.jpg)
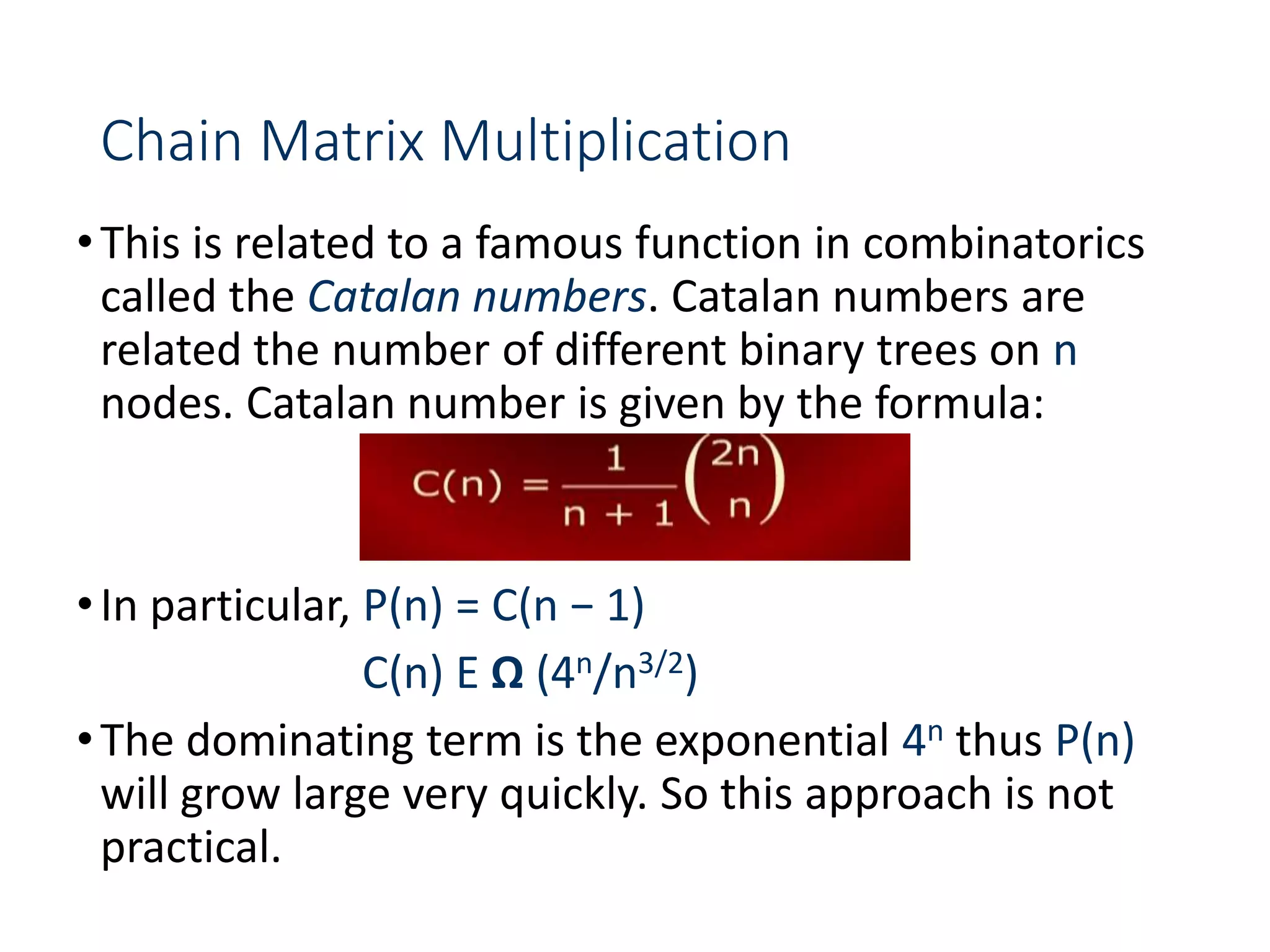
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
•For m[1, 4] and m[2, 5]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-66-2048.jpg)
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
•At this stage (product of 4) the matrix m looks as follow:
•That leaves the m[1, 5] which can now be computed:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-67-2048.jpg)
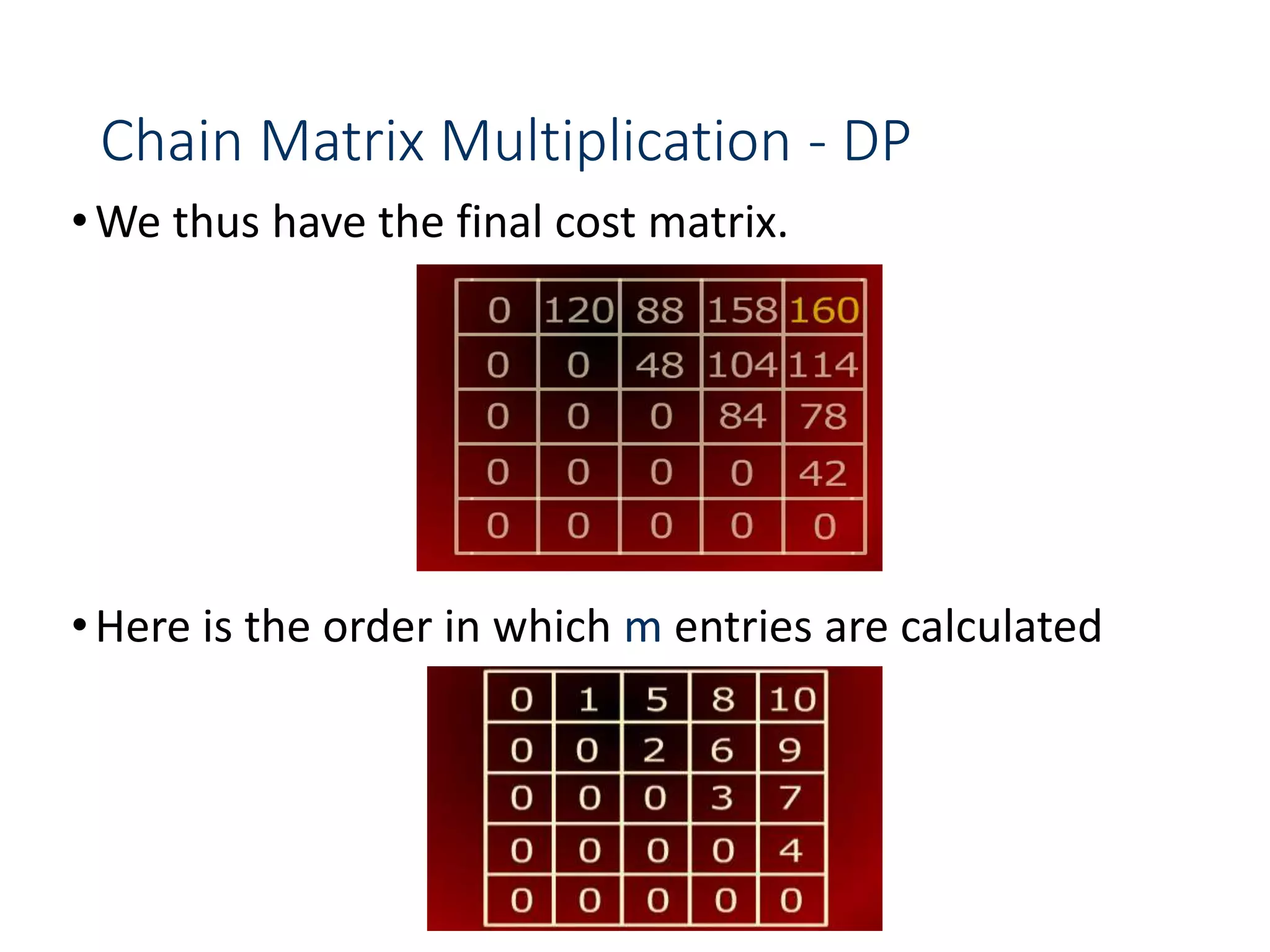
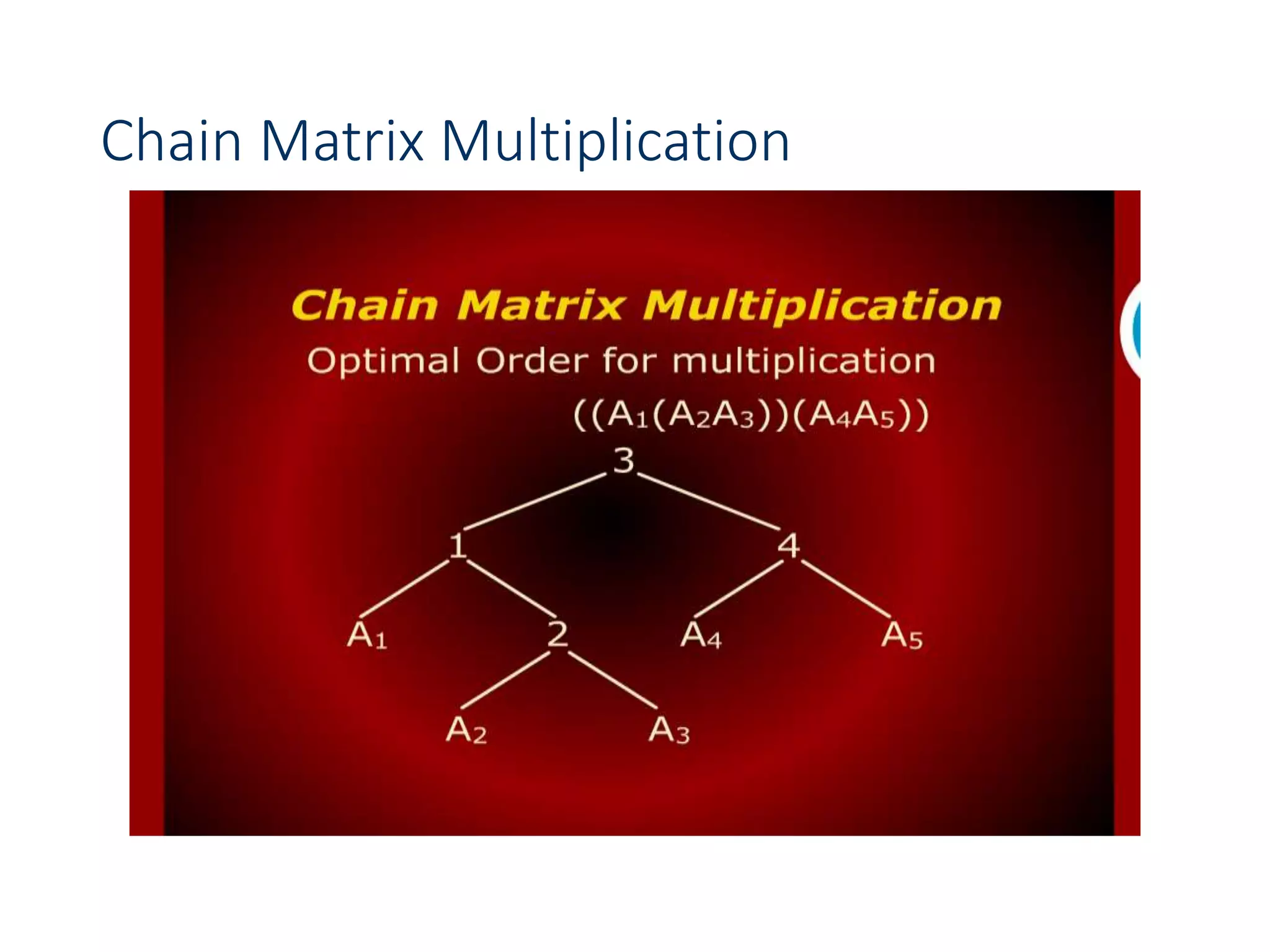
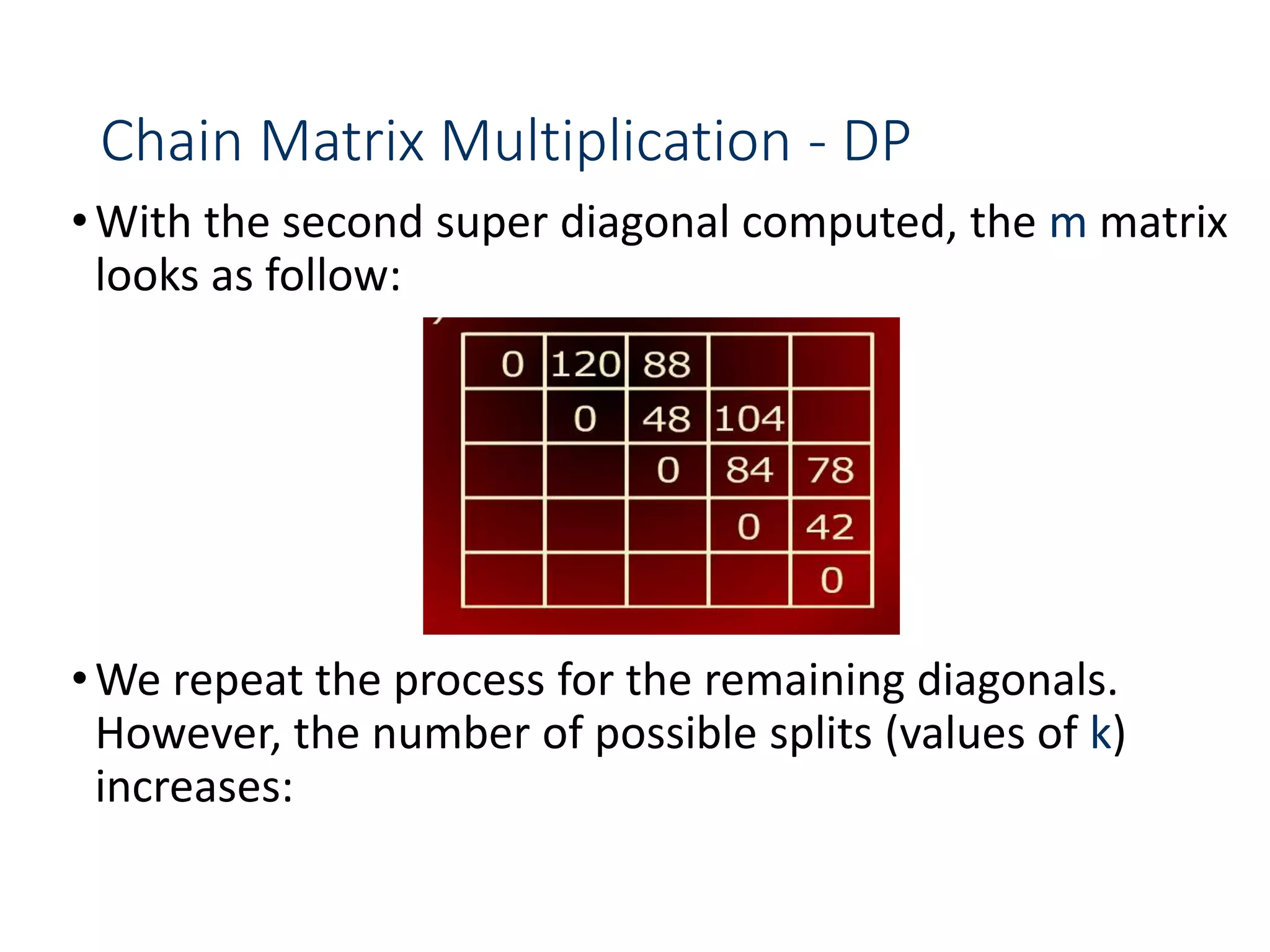
![Chain Matrix Multiplication - DP
•and the split k values that led to a minimum m[i, j] value
•Based on the computation, the minimum cost for
multiplying the five matrices is 160 and the optimal
order for multiplication is:
((A1(A2A3))(A4A5))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designandanalysisofalgorithms-lecture081-230514182933-9e13efc5/75/Design-and-analysis-of-Algorithms-Lecture-08-1-ppt-69-2048.jpg)