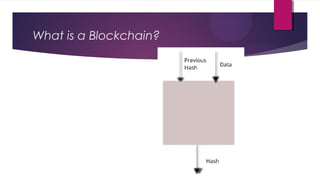
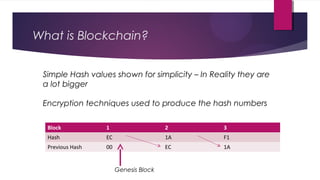
Blockchain is an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and permanently. It works by linking transaction records into blocks secured by cryptography, forming a chain. Tampering with a block would change its hash and break the chain. Blockchains use consensus algorithms like proof-of-work and proof-of-stake to validate transactions without centralization. Smart contracts enable blockchain applications. Supply chain management may be a promising application area due to blockchain's decentralization, immutability, and transparency. Examples include partnerships between IBM/Walmart and Everledger for provenance tracking.