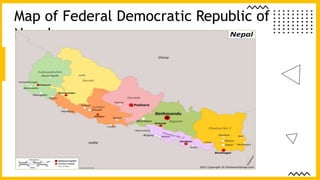
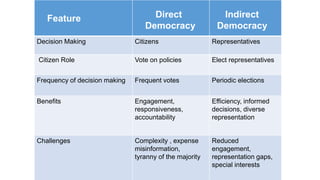
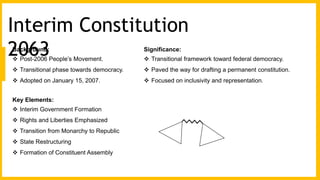
This document discusses democracy, constitutions, and their development in Nepal. It begins by defining democracy as a system of government where citizens have power through elections. It then outlines key features of democracy like elections, transparency, and citizen participation. The document traces Nepal's path to democracy, from its monarchy through a 1990 democracy movement and the 2008 establishment of a federal democratic republic. It also differentiates between direct and indirect democracy, and discusses advantages and disadvantages of democracy. The document defines a constitution as the foundational legal framework that establishes a nation's governance structure and citizen rights. It highlights elements of Nepal's constitutions like federalism, rights, and amendments. In conclusion, it identifies political instability and diversity as causes for Nepal's