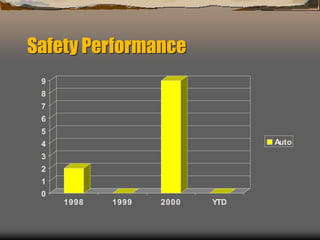
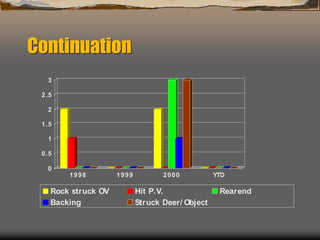
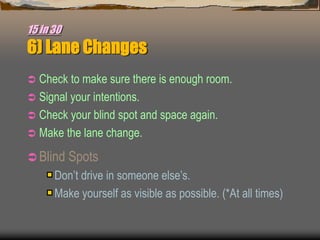
This document provides an agenda and materials for a defensive driving presentation about construction vehicle hazards. The presentation covers: construction vehicle hazards like rollovers, striking workers, and overhead obstructions; prevention techniques; parking hazards; maintenance hazards; and 15 defensive driving safety tips including pre-trip inspections, following distance, backing safely, and winter driving. The goal is to train drivers to operate vehicles and equipment safely and prevent accidents and injuries.