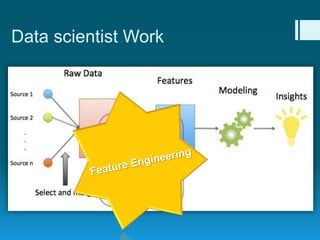
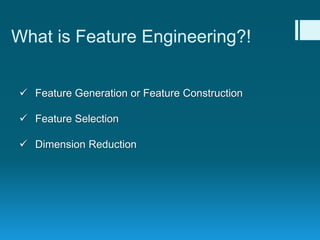
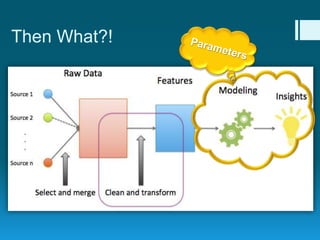
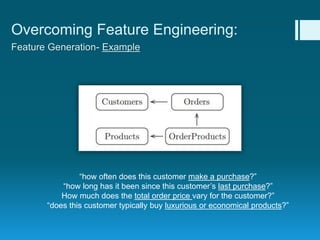
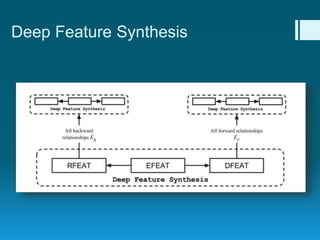
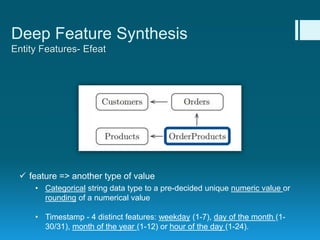
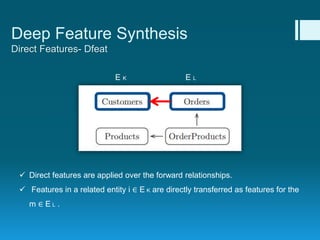
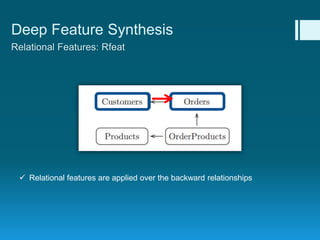
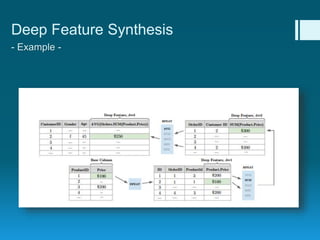
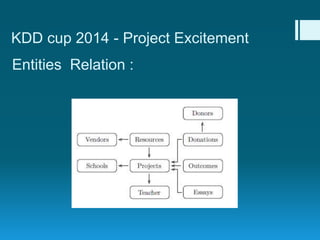
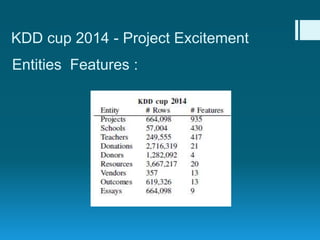
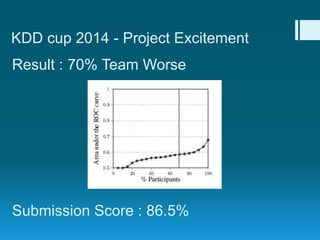
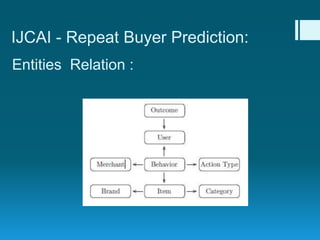
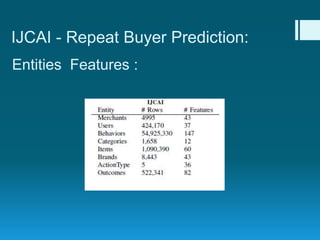
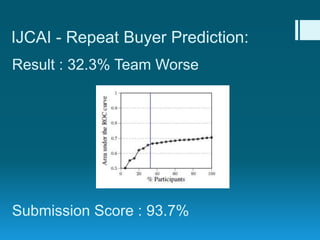
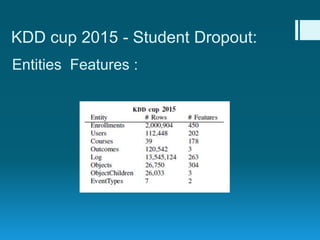
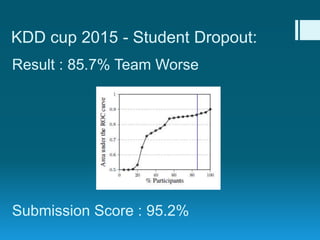
Deep feature synthesis is an approach to automate feature engineering for relational and human behavioral data. It generates features from entities and their relationships using entity features, direct features from related entities, and relational features. This overcomes the iterative and time-consuming nature of traditional feature engineering. The approach is demonstrated on three predictive tasks, generating features from entities and relations and achieving substantially better results than other teams.