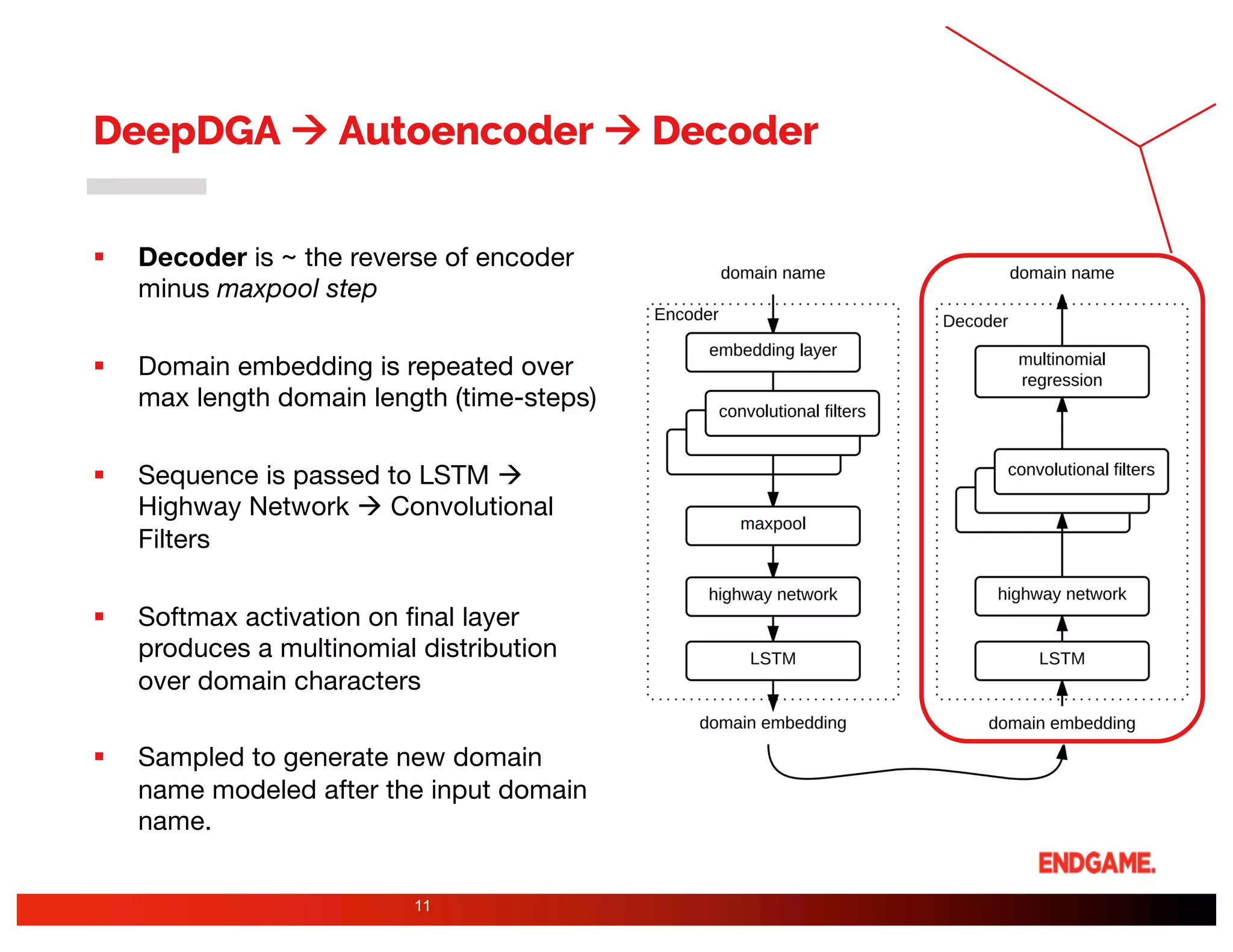
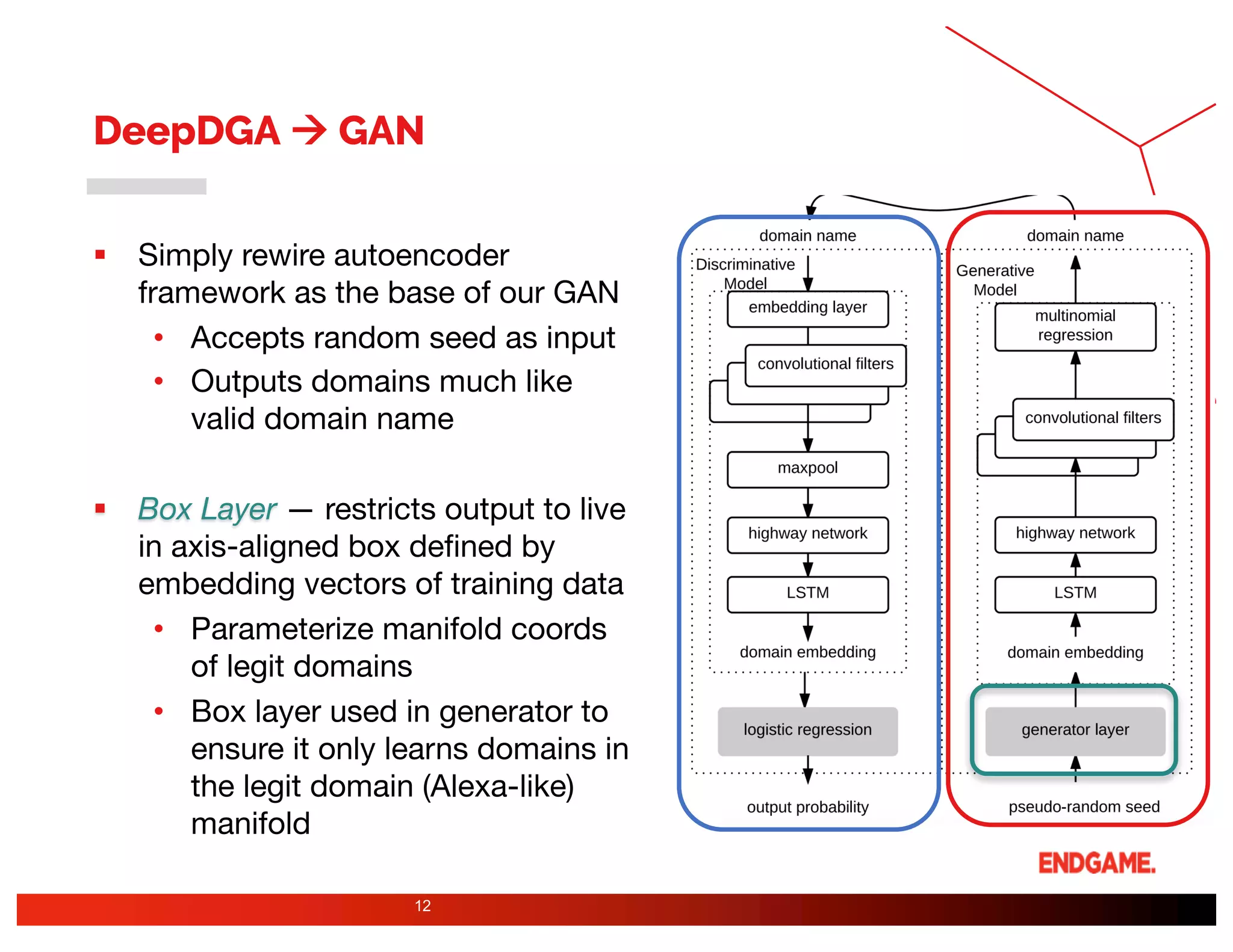
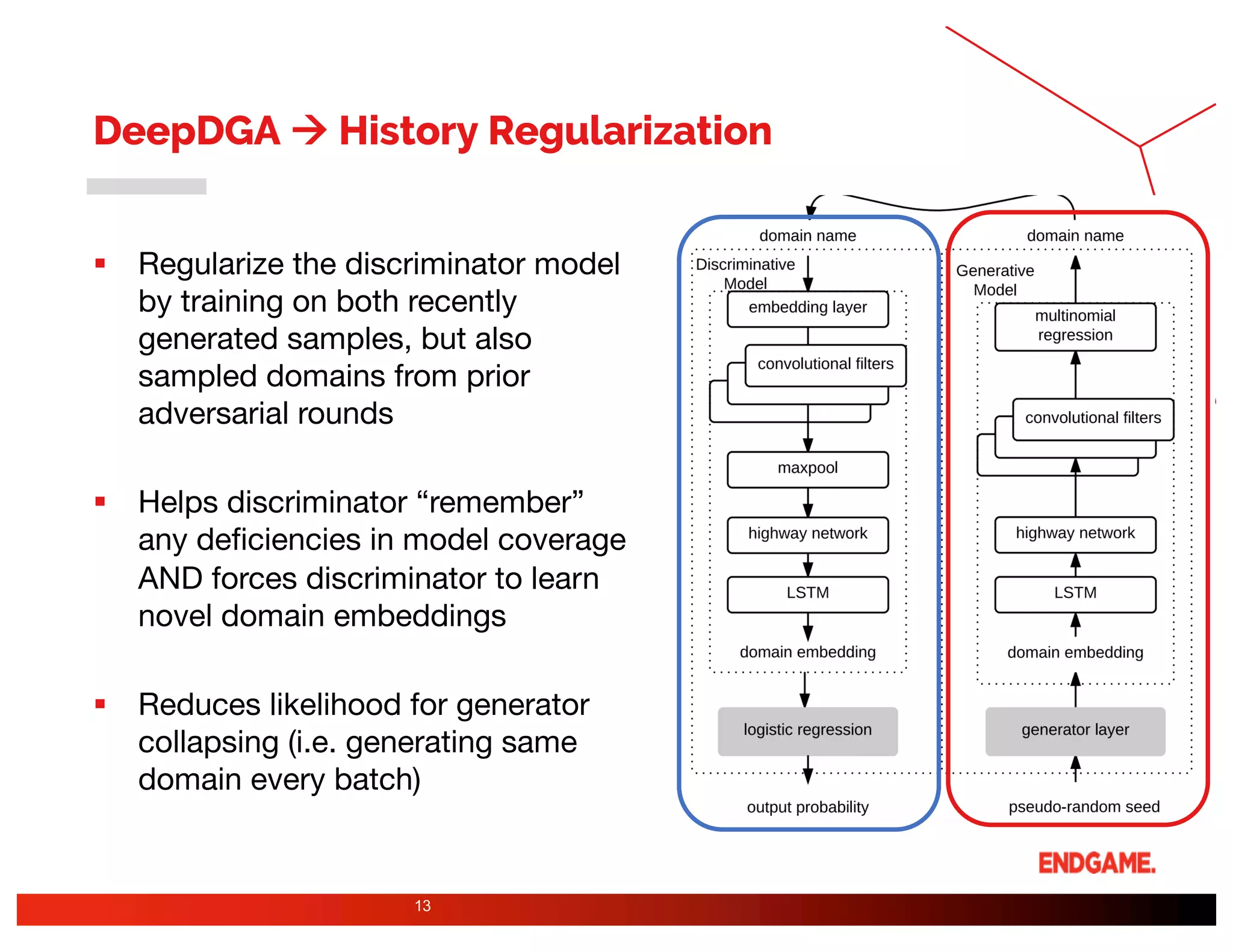
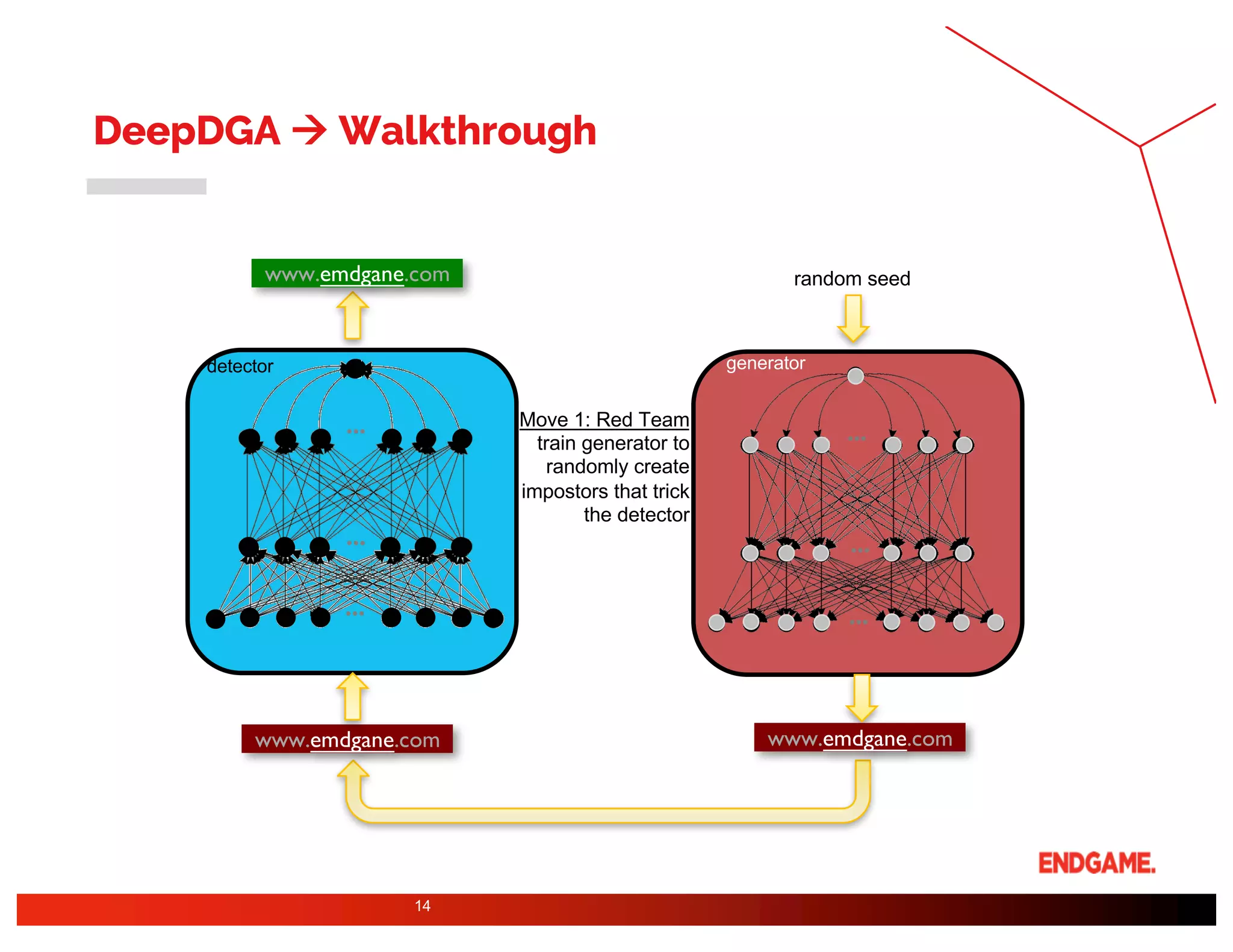
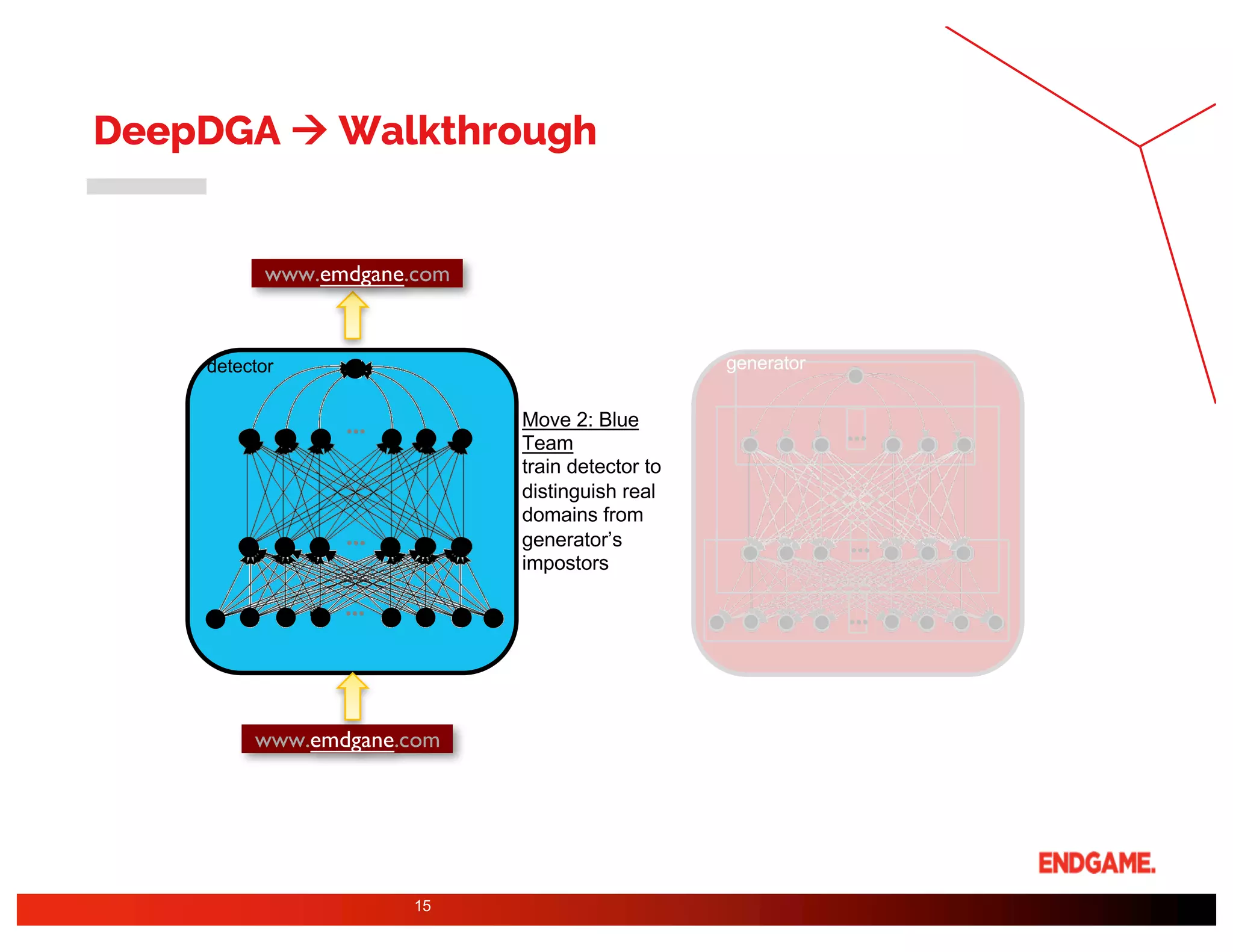
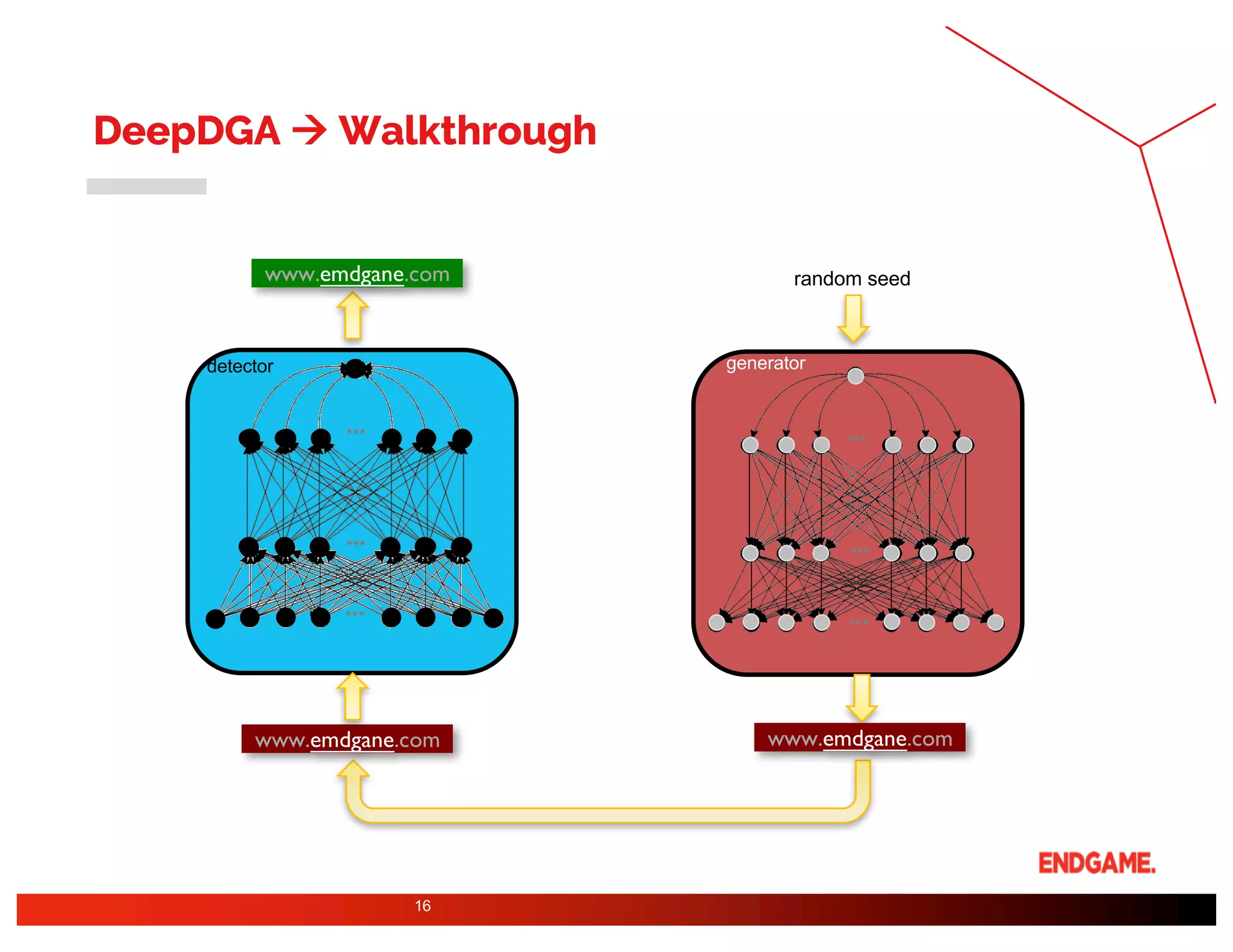
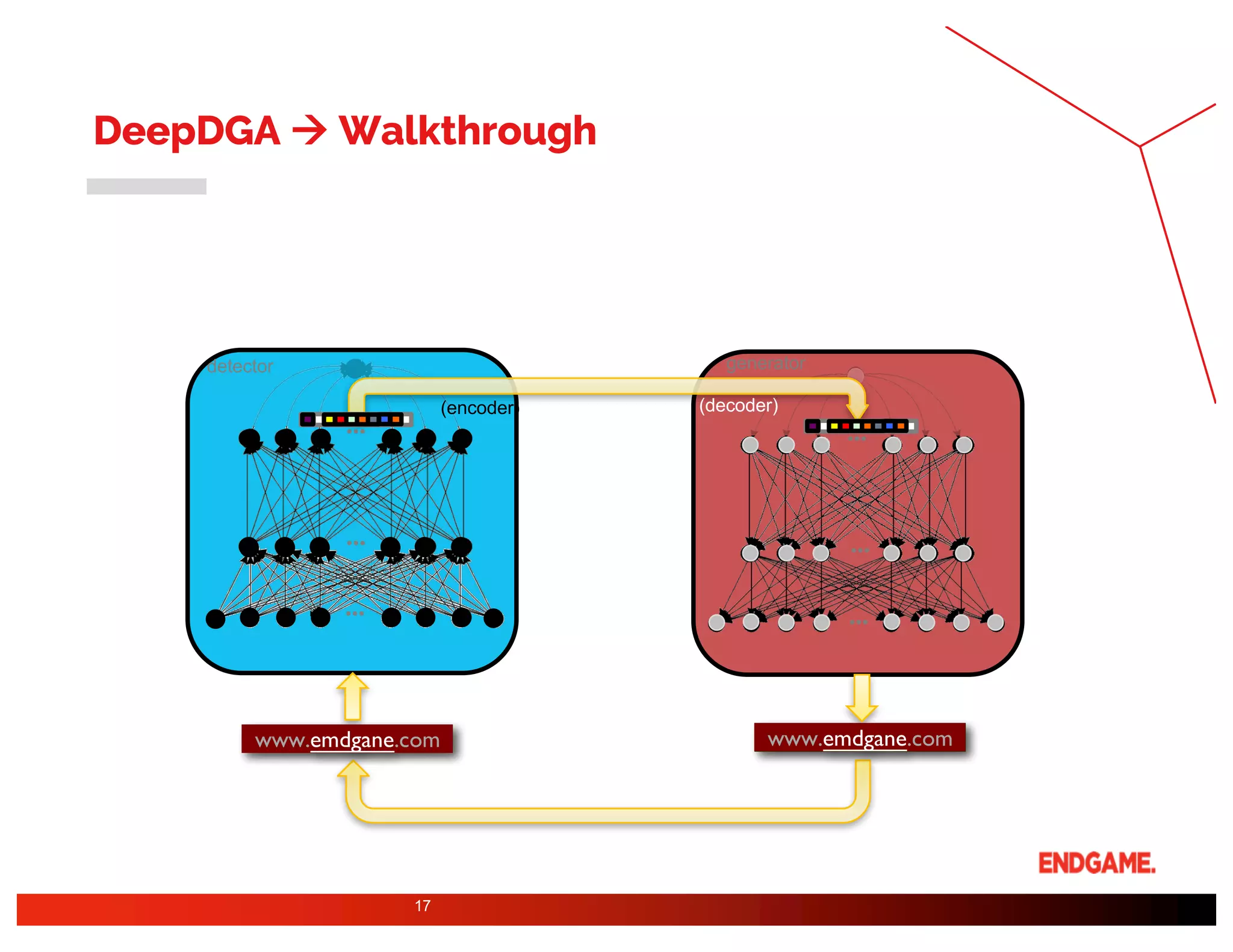
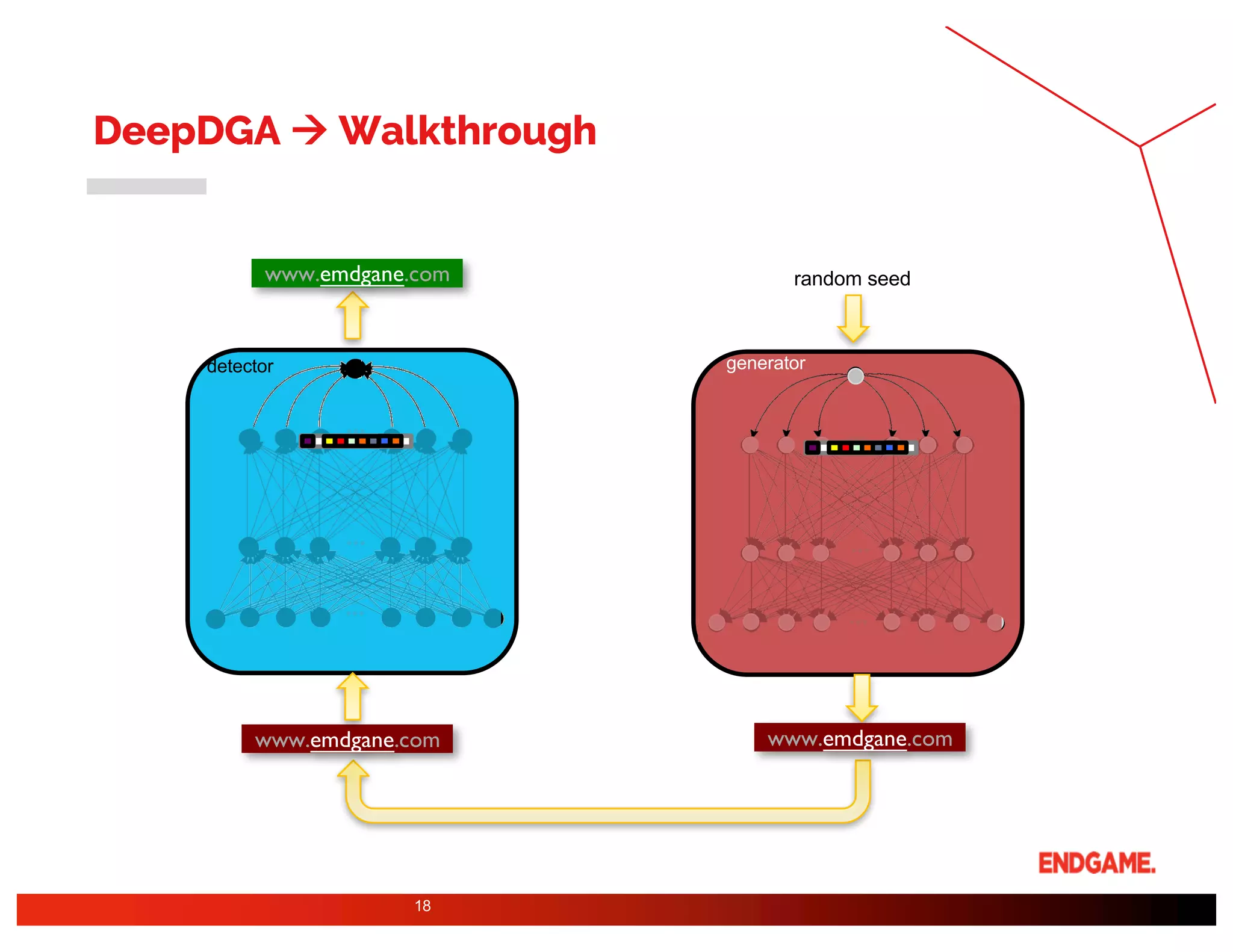
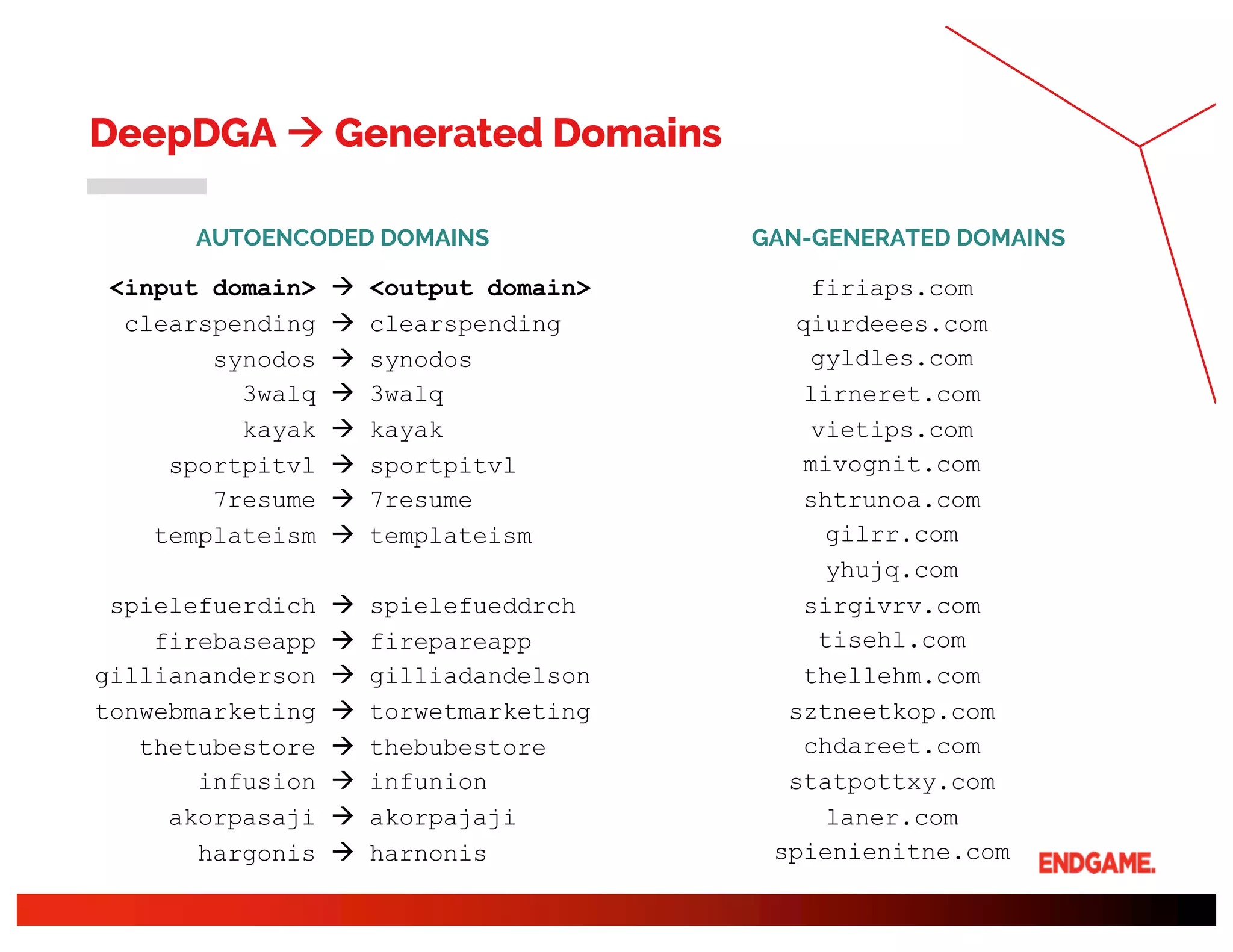
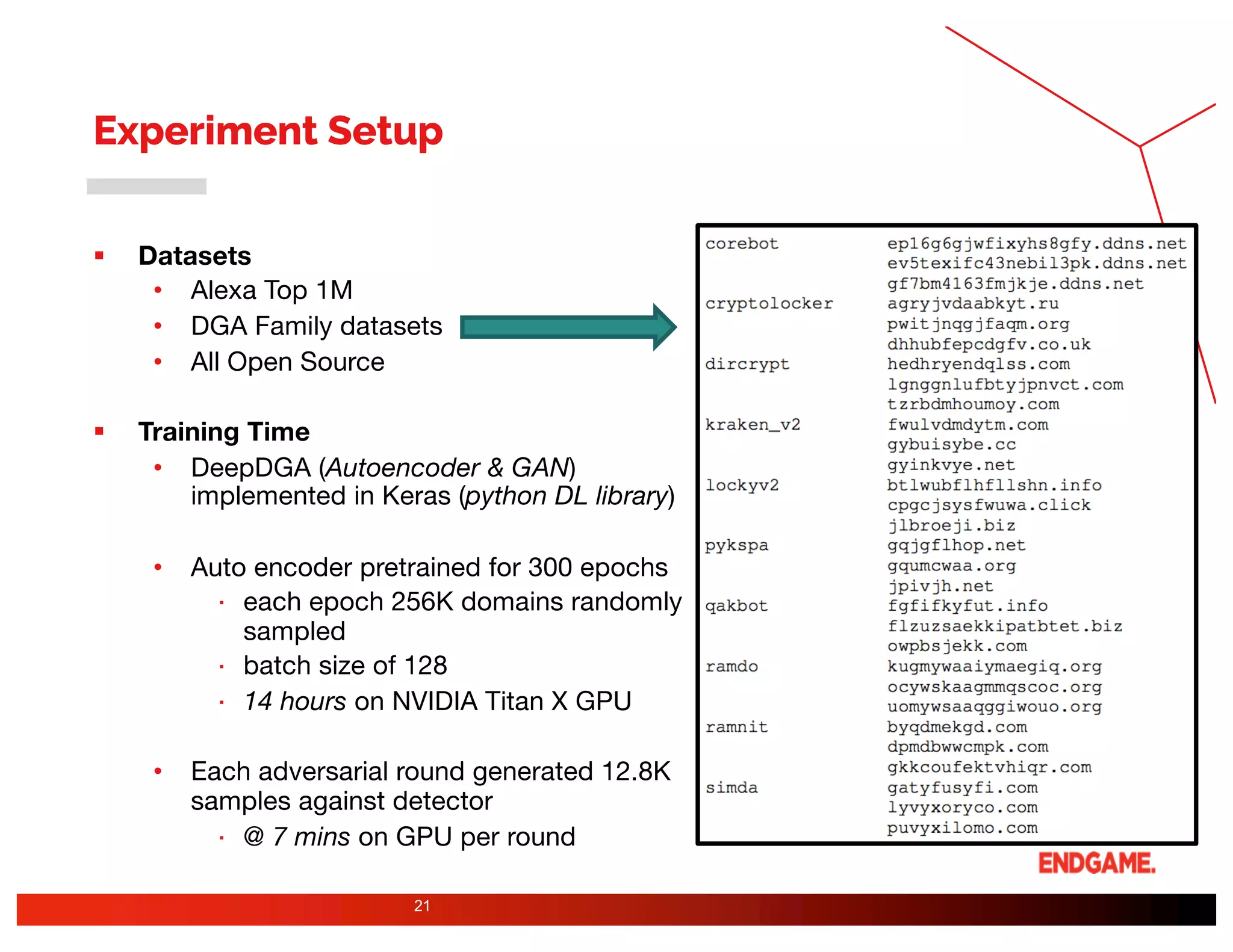
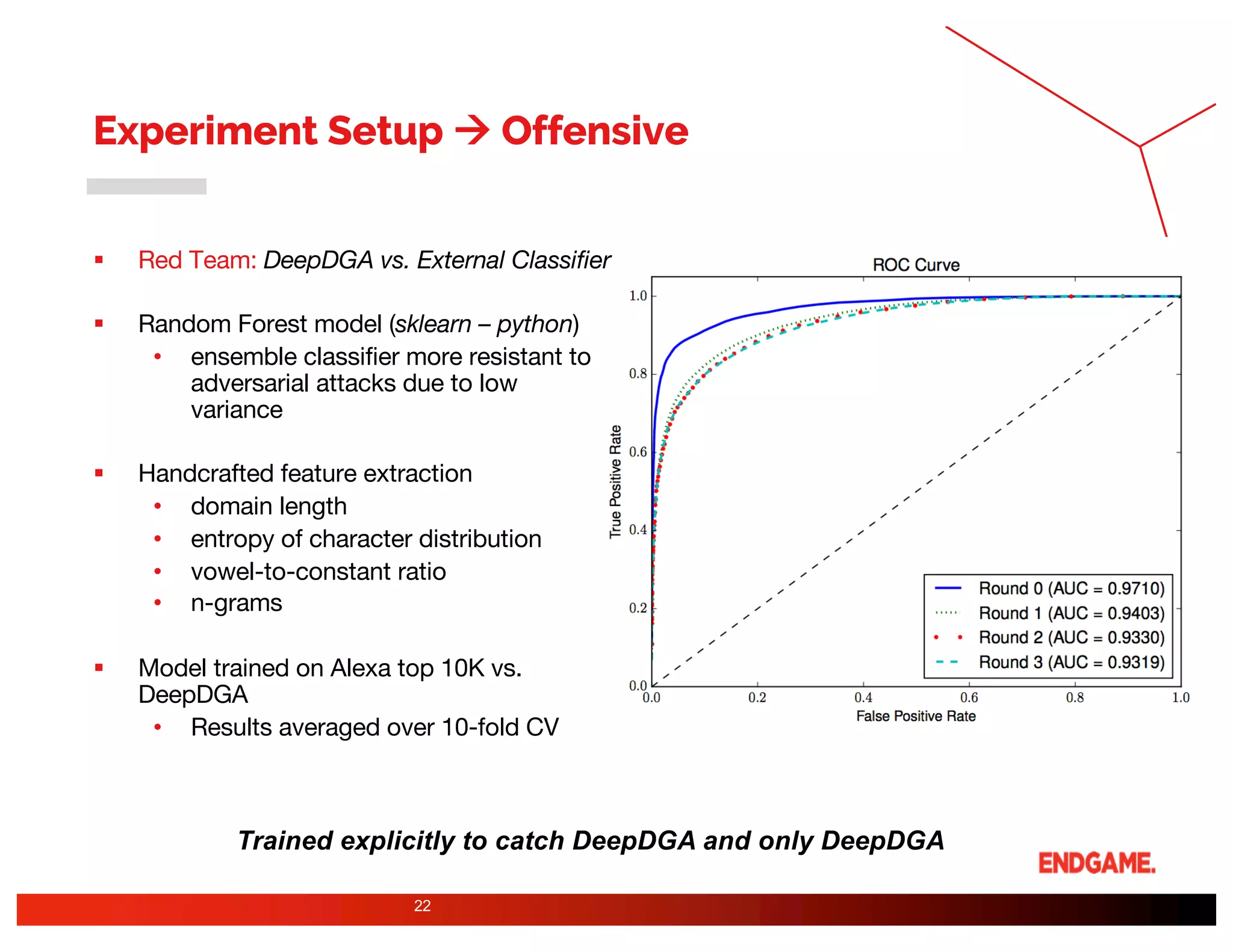
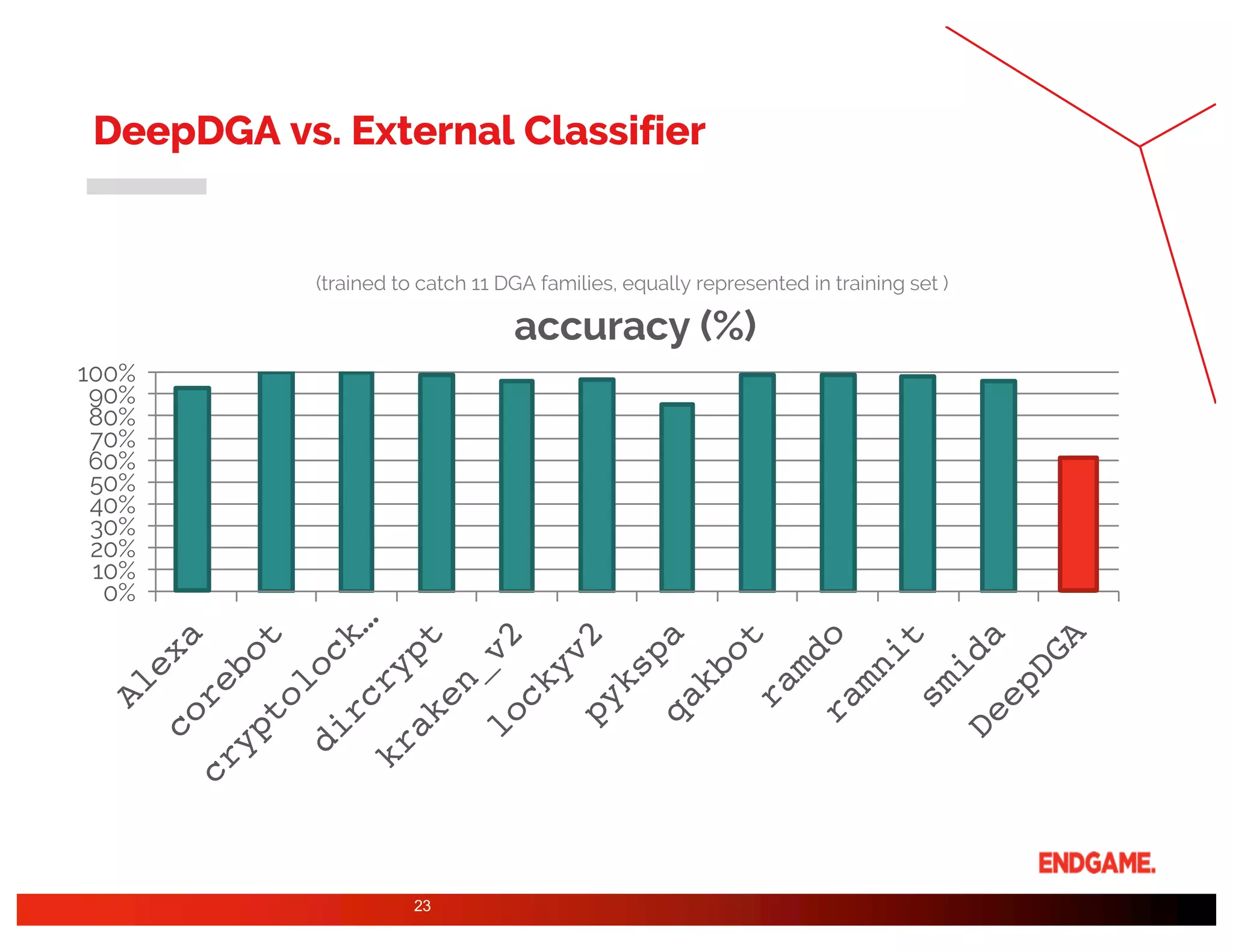
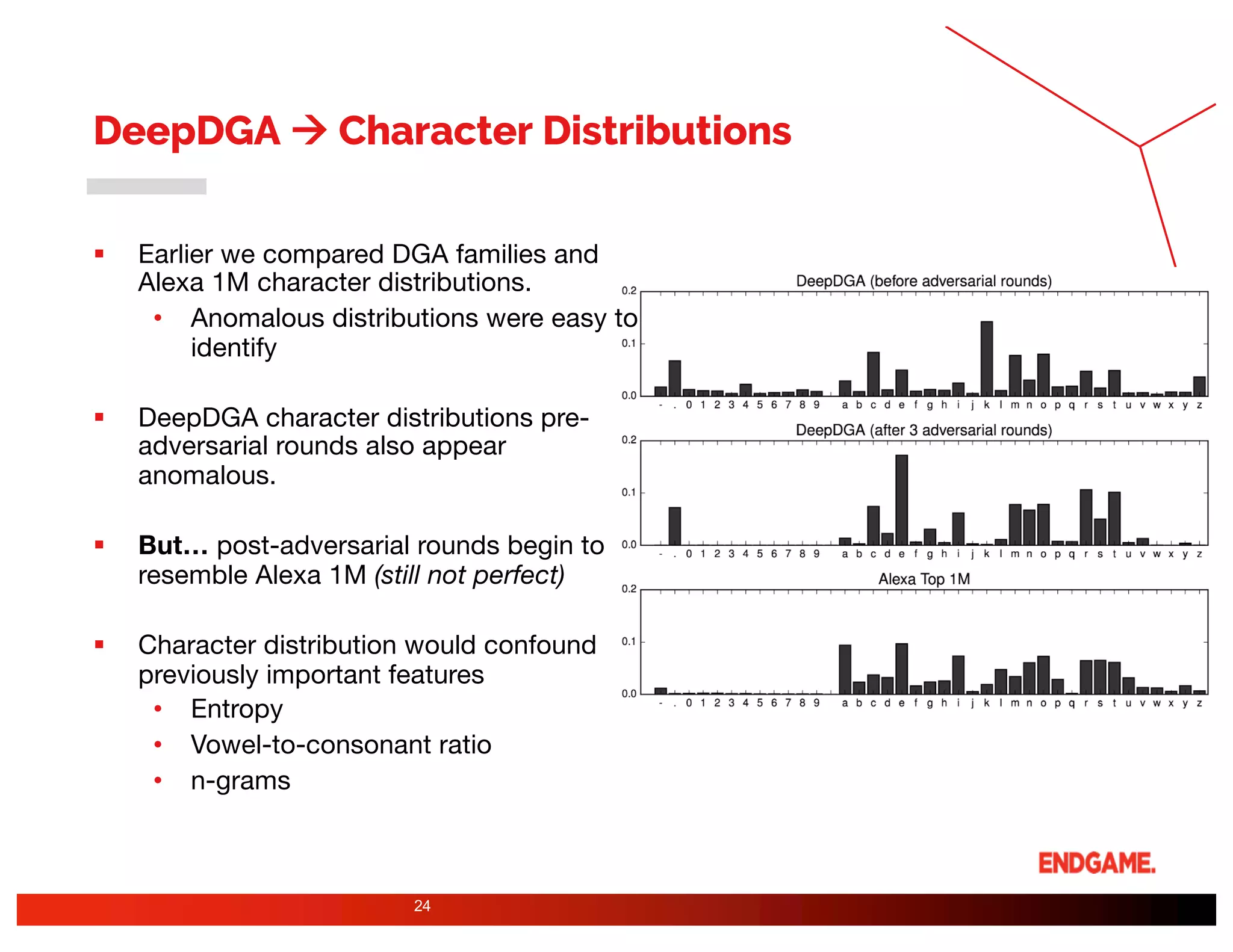
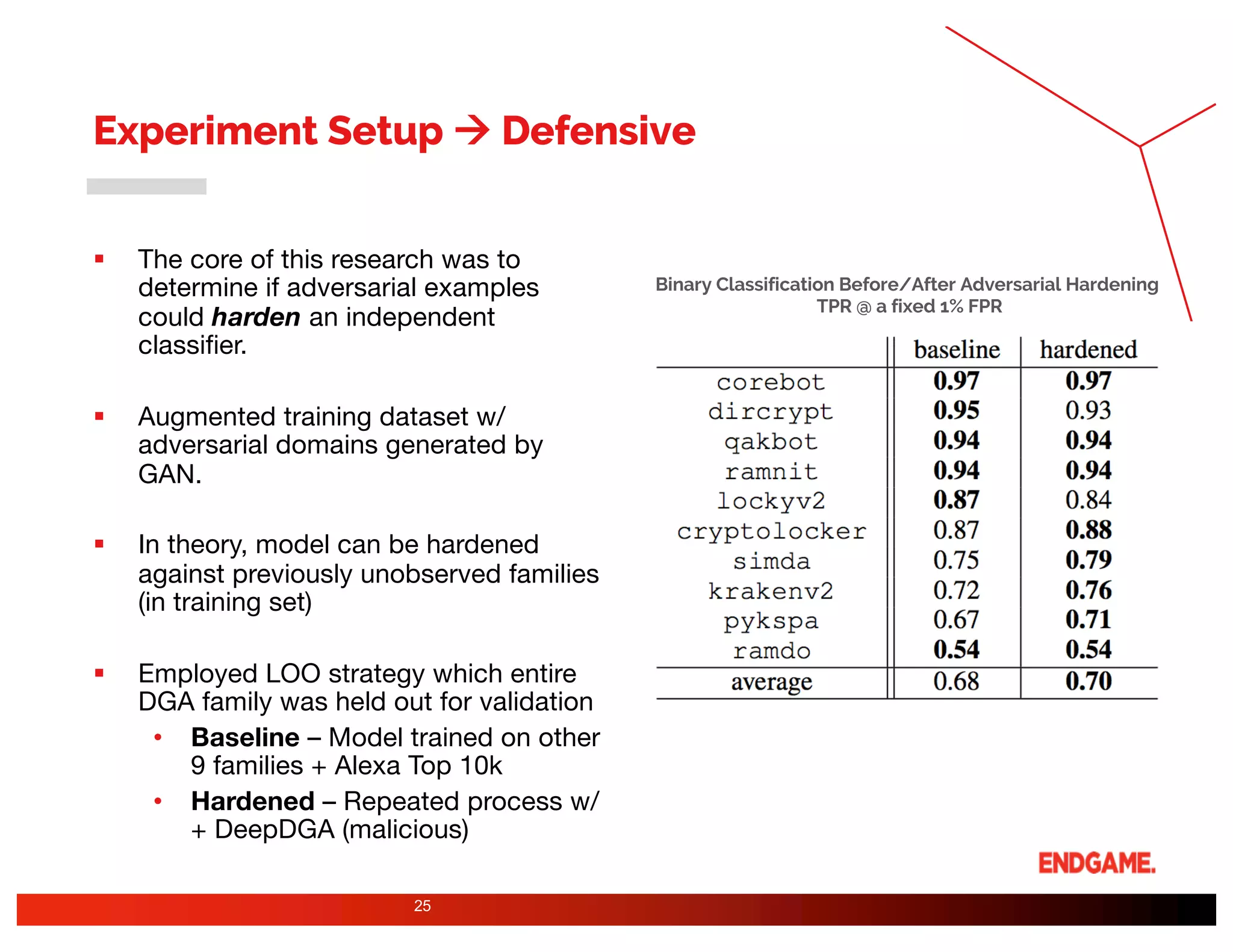
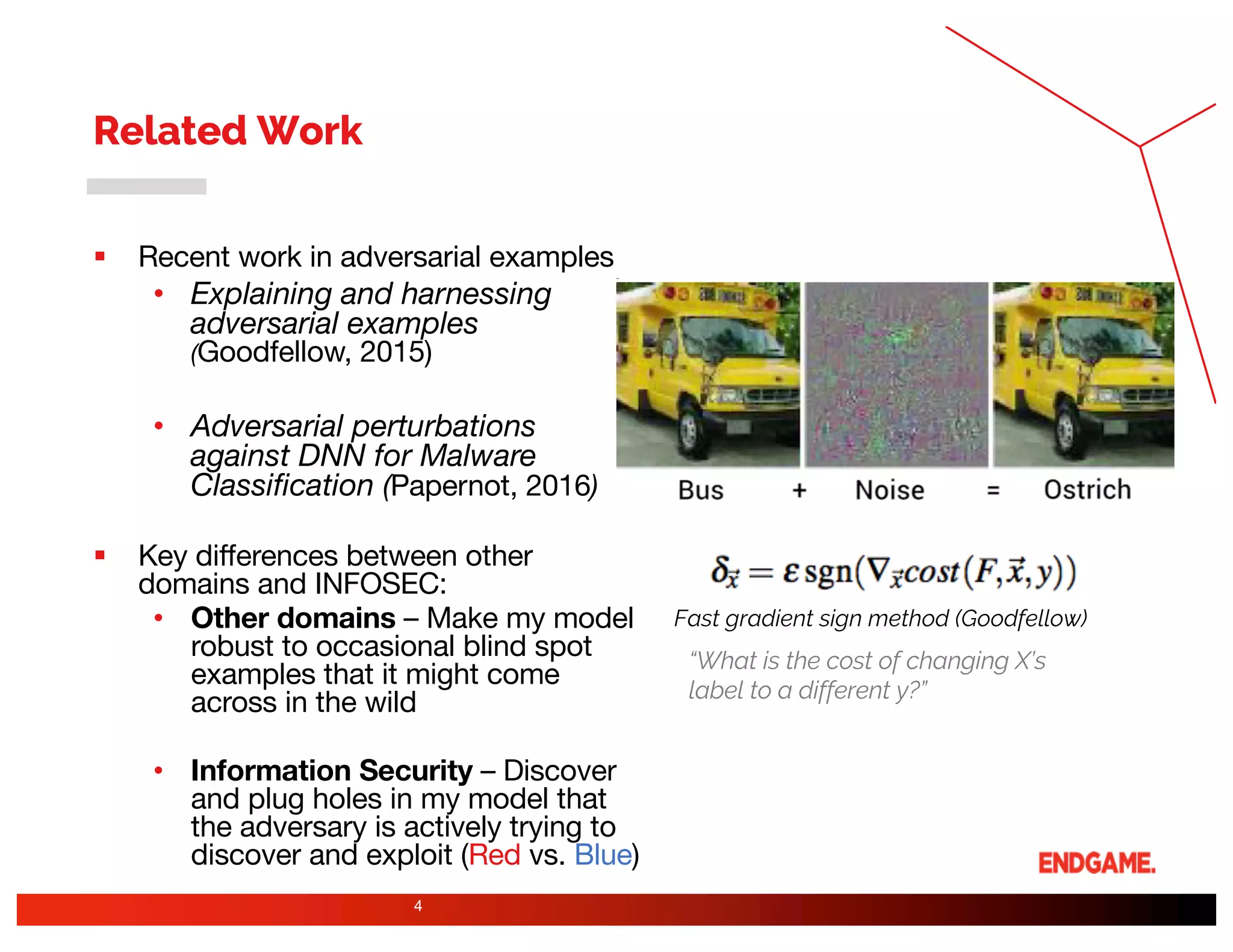
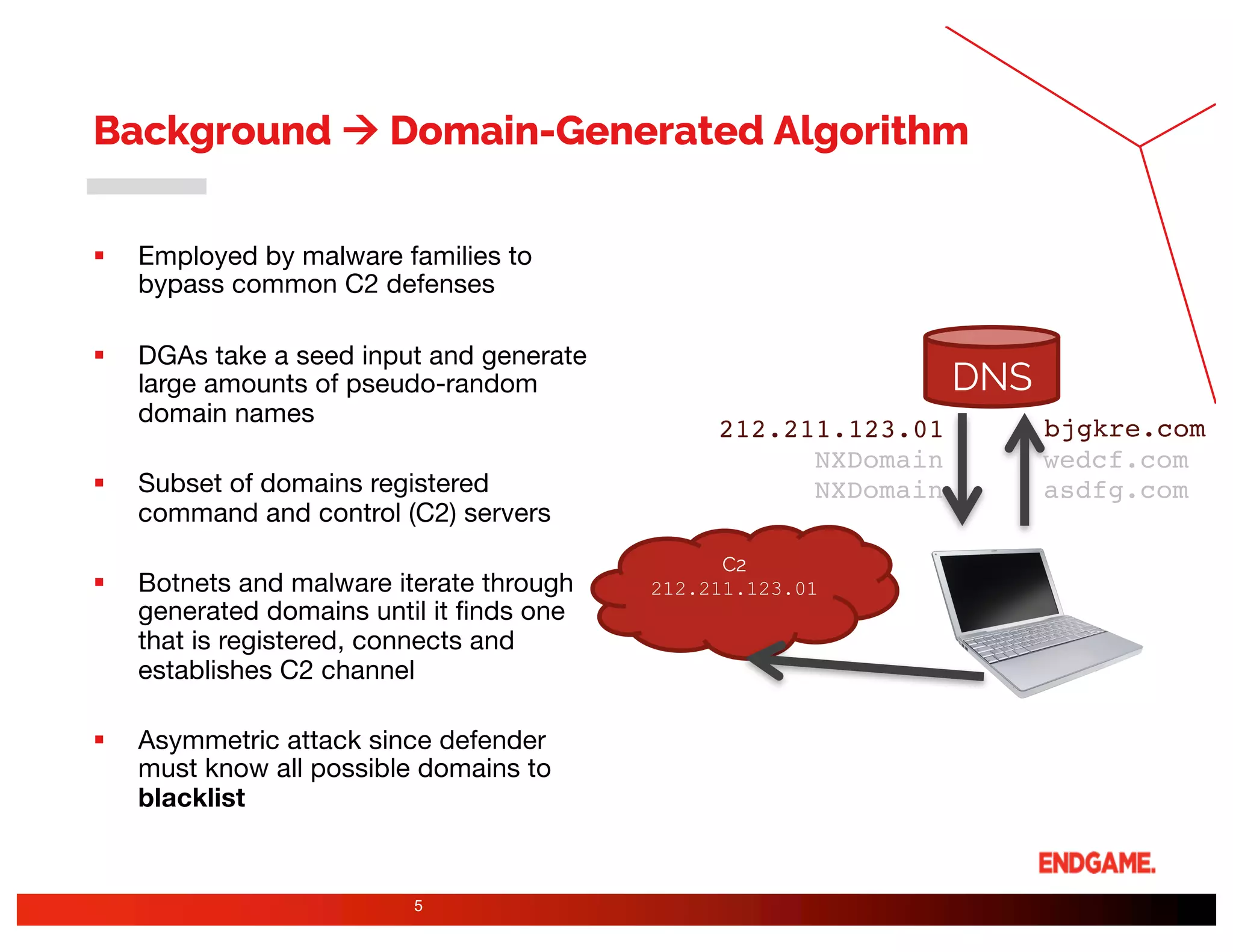
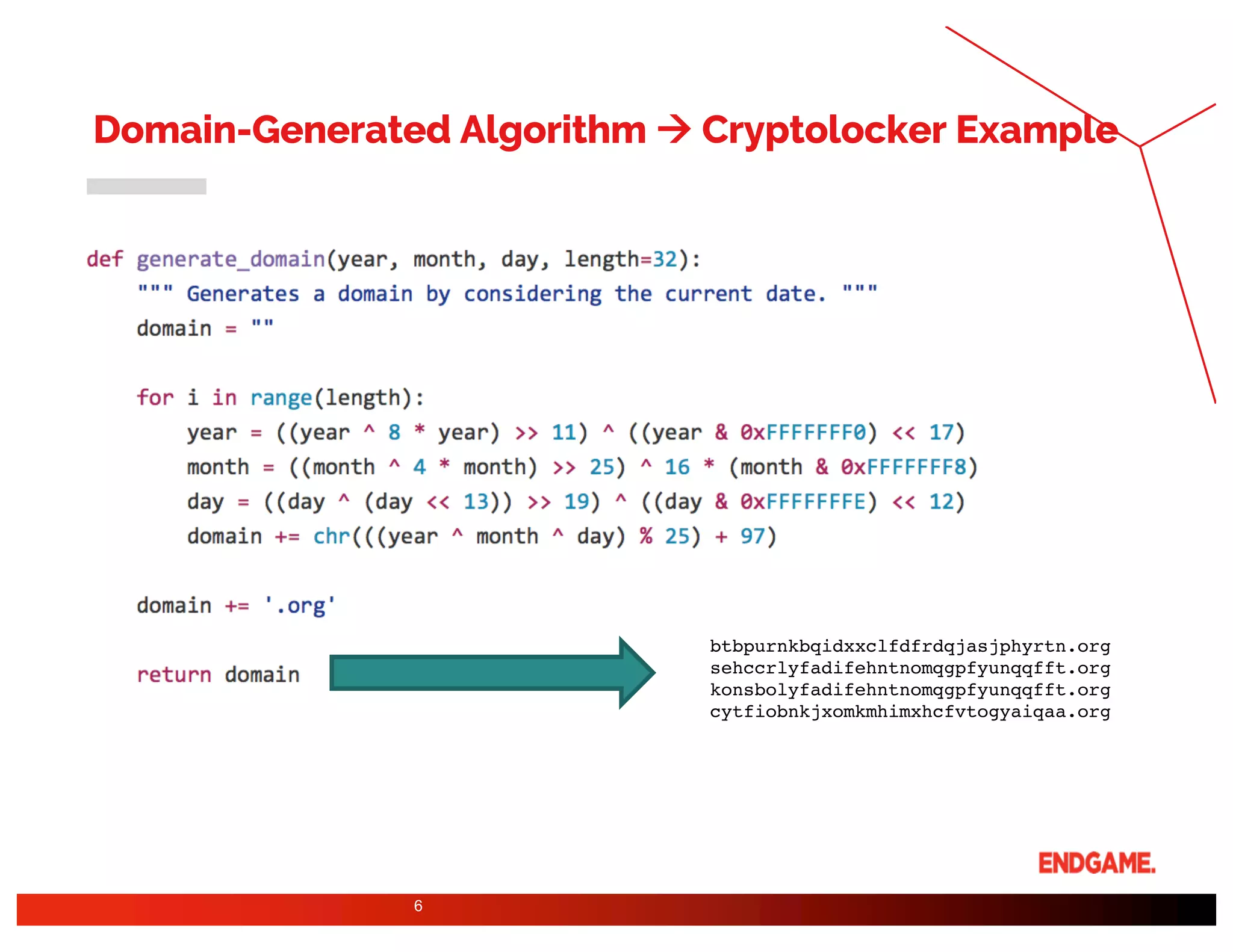
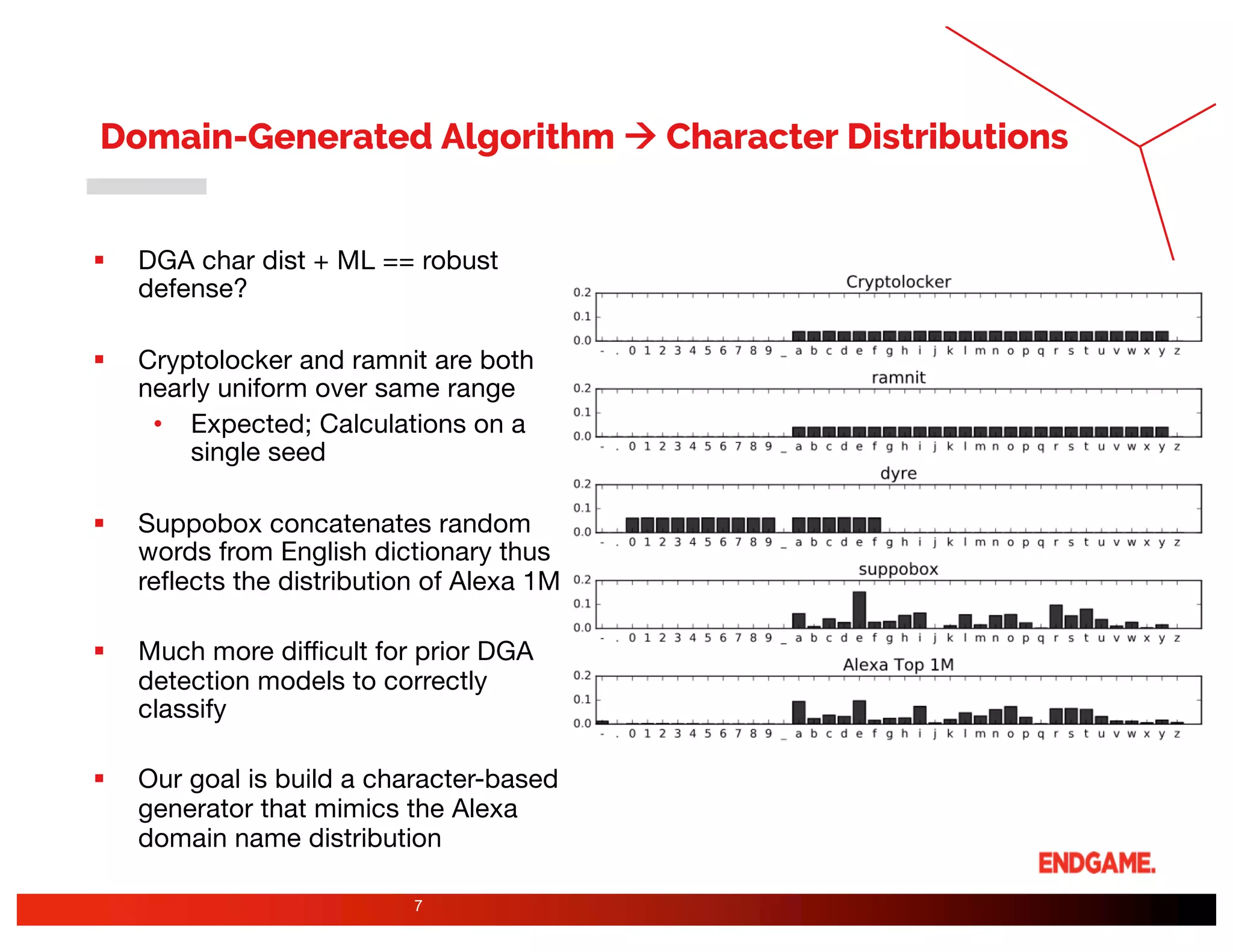
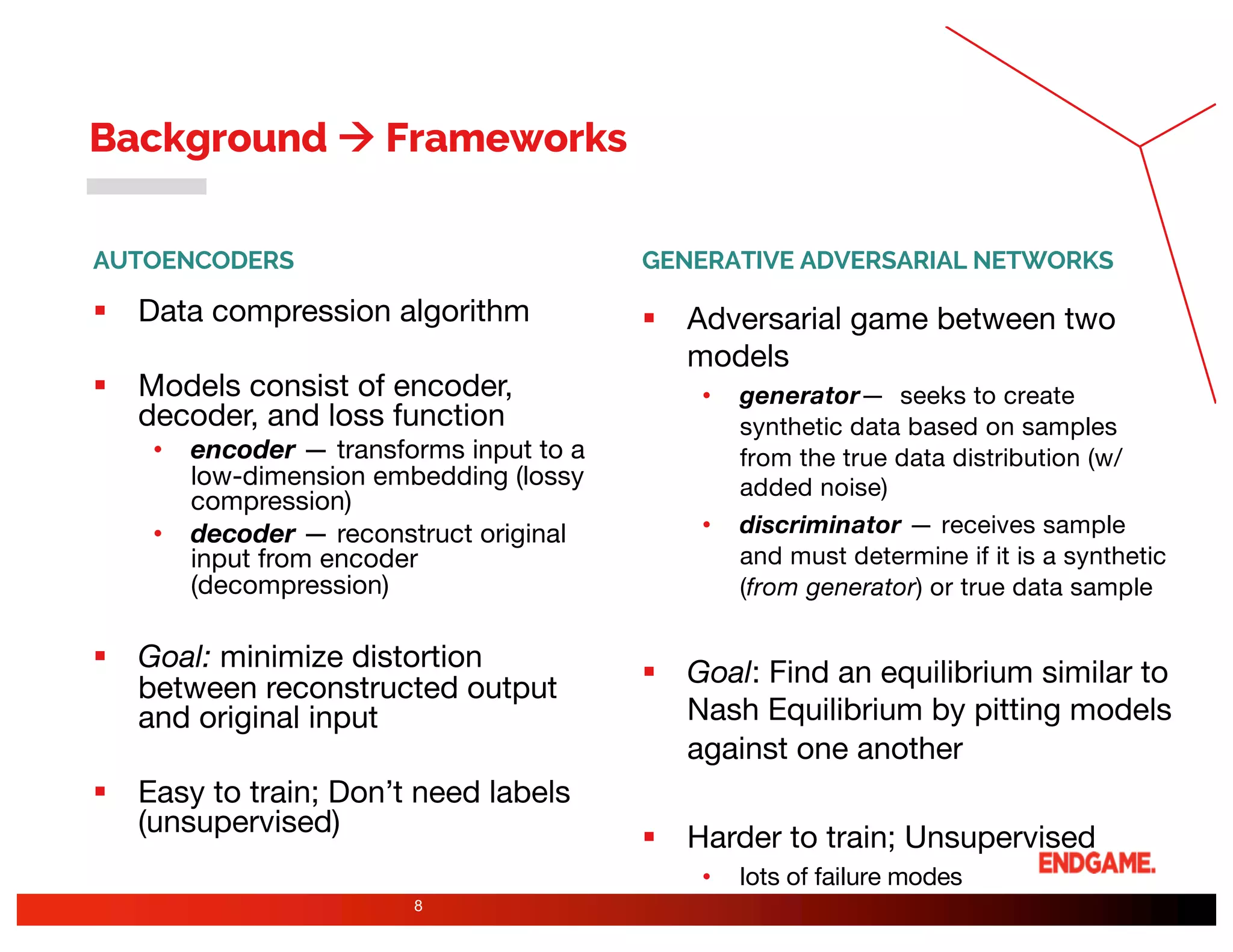
The document presents a study on DeepDGA, a deep learning architecture using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to generate domain names for countering Domain Generation Algorithms (DGAs) in cybersecurity. It explores the dual-use of GANs, both for offensive tactics to bypass classifiers and defensive tactics to enhance training data for classifiers. The findings suggest that adversarially crafted domain names can be effective in augmenting and strengthening classification models against DGAs.




![DeepDGA à Autoencoder à Encoder
§ Encoder architecture taken from [Kim et
al, 2015], found useful in character-level
language modeling
§ Embedding learns linear mapping for
each valid domain character (20
dimension space)
§ Convolutions filters applied to capture
character combos (bi/trigrams)
§ Max-pooling over-time & over-filter
• Gather fixed-representation
§ Highway Network à LSTM
10
Learn the right representation of Alexa domains](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aisecdeepdga-161108143007/75/Deep-DGA-Adversarially-Tuned-Domain-Generation-and-Detection-10-2048.jpg)