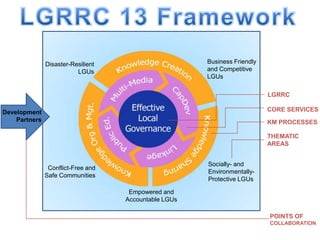
The document outlines the framework of the Local Governance and Regional Resource Center (LGRRC). It aims to contribute to effective local governance through four core services: public education, multi-media development, capacity development, and linkage/networking. These services help local government units through knowledge processes like creation, sharing, and management. The framework also addresses five thematic areas: business friendly and competitive LGUs; disaster resilient LGUs; empowered and accountable LGUs; conflict free and safe communities; and socially and environmentally protective LGUs. Stakeholders from government, private sector, and civil society collaborate within this framework.