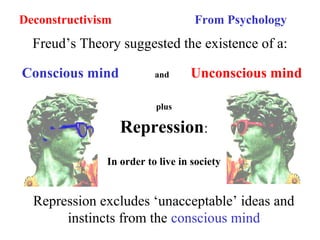
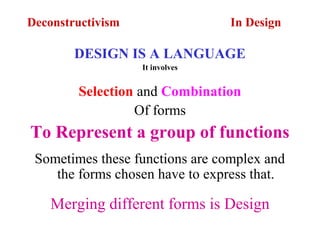
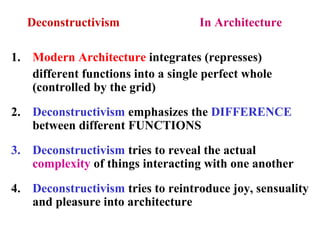
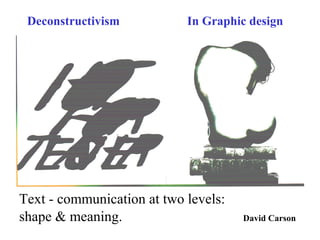
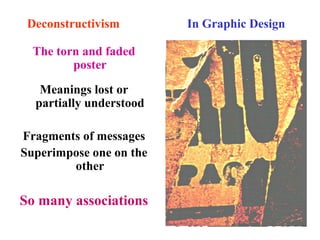
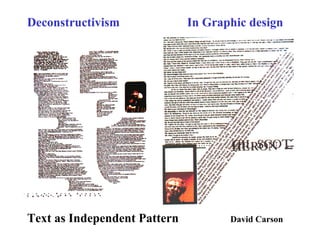
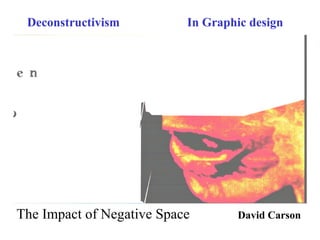
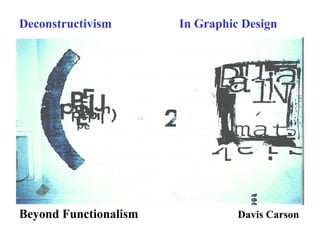
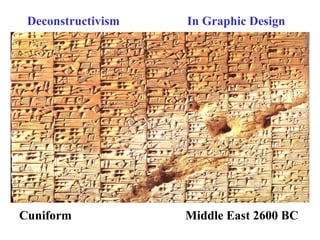
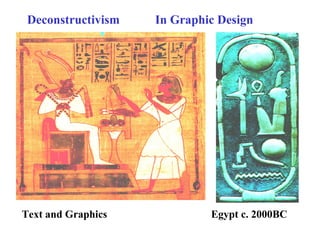
Deconstructivism is a postmodern movement in architecture and design that emerged as a response to the standardized, rational approaches of modernism, emphasizing complexity, diversity, and the multifaceted nature of identity. Originating from psychological concepts by Freud and philosophical ideas by Derrida, it seeks to reveal the underlying complexities and contradictions in forms and texts, challenging the illusion of unity. In both architecture and graphic design, deconstructivism aims to disrupt conventional aesthetics, introducing elements of play, irony, and ambiguity to foster multiple interpretations.