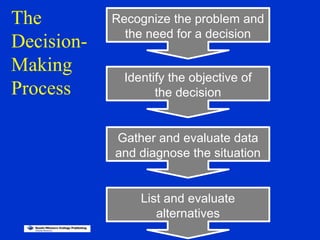
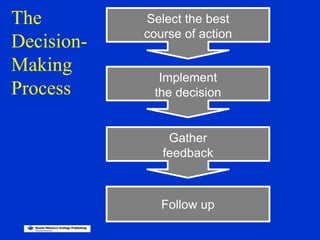
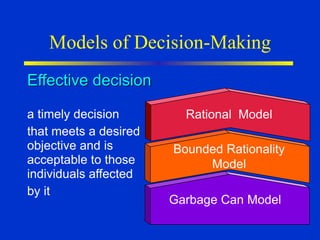
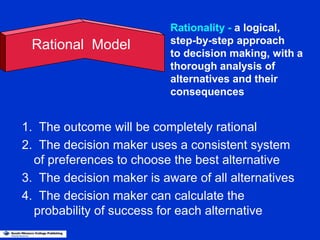
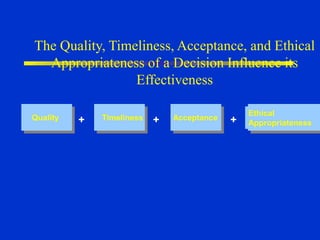
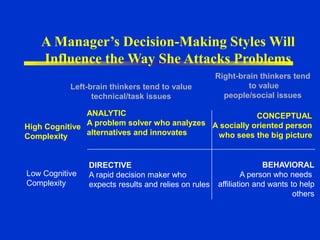
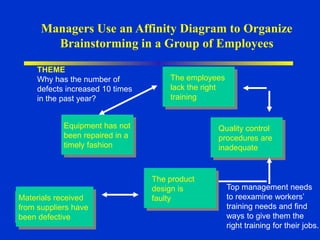
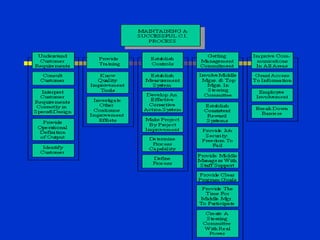
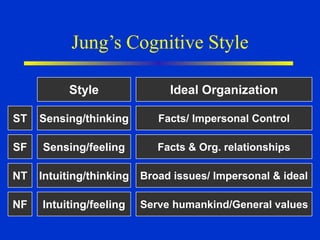
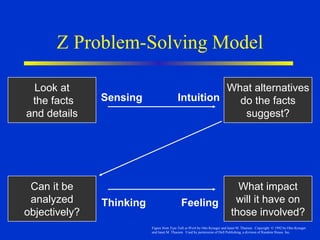
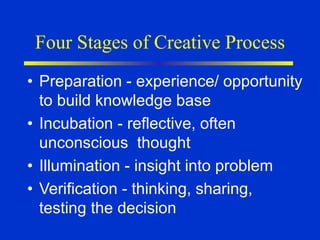
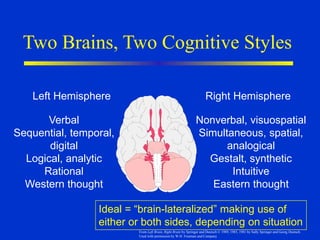
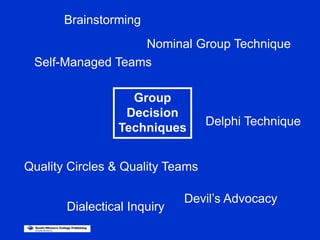
The document discusses models of decision making including the rational model, bounded rationality model, and garbage can model. It describes the decision making process which involves recognizing a problem, identifying objectives, gathering data, listing alternatives, selecting a course of action, implementing, and gathering feedback. Effective decision making considers quality, timeliness, acceptance and ethics. Managers have different cognitive styles that influence how they approach problems and make decisions. The document provides tips for techniques to aid decision making like brainstorming, affinity diagrams, and the nominal group technique.