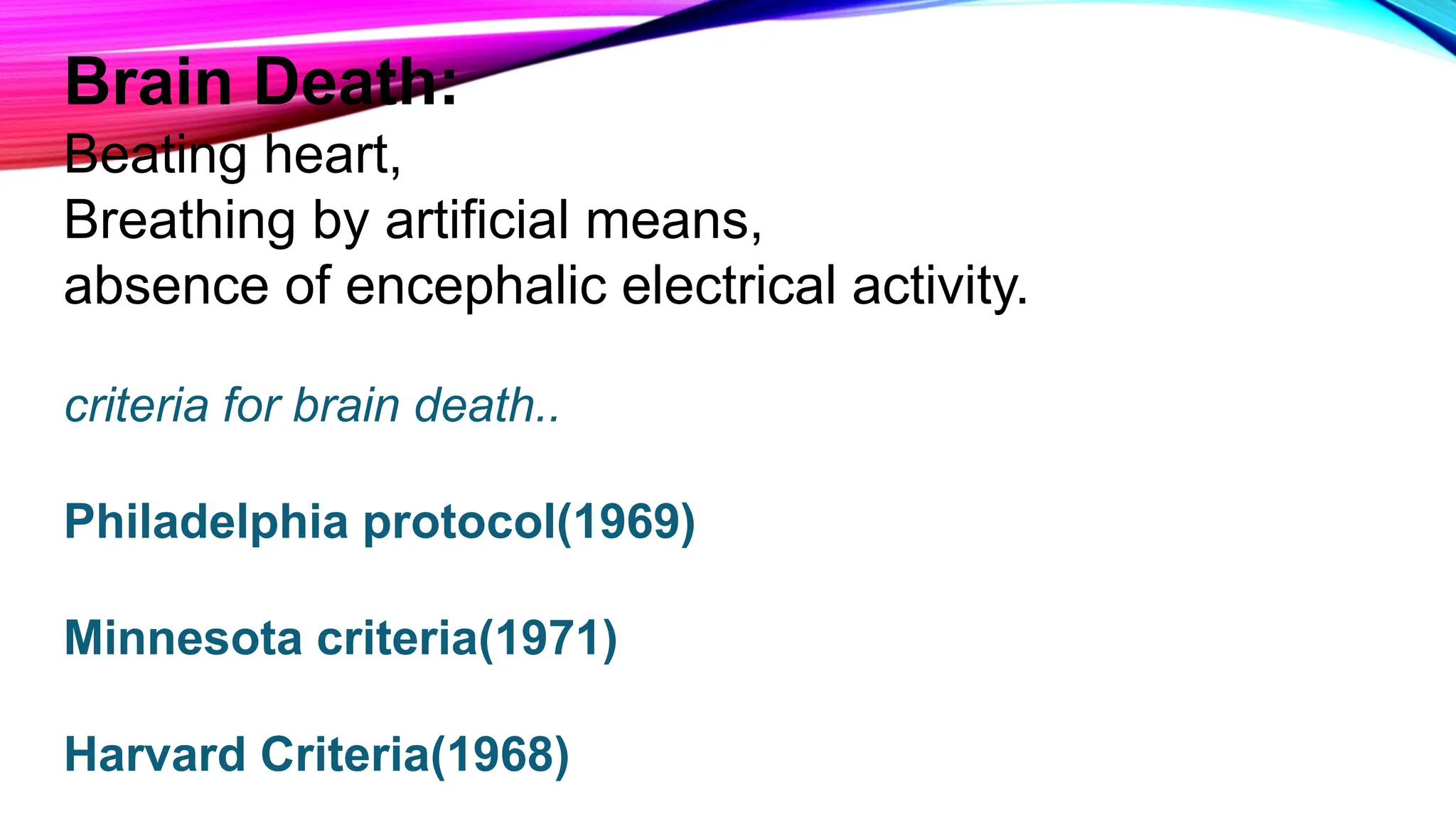
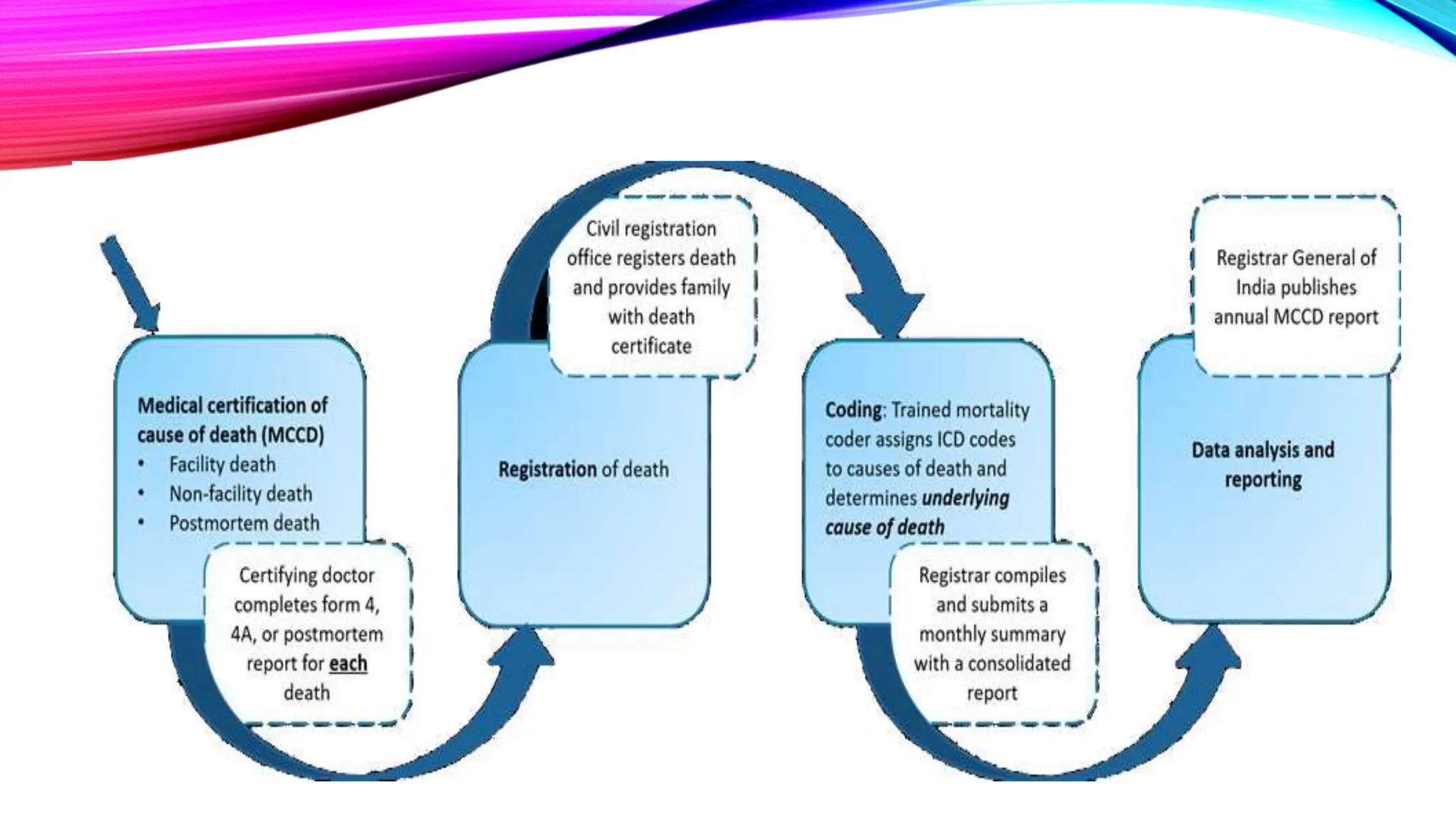
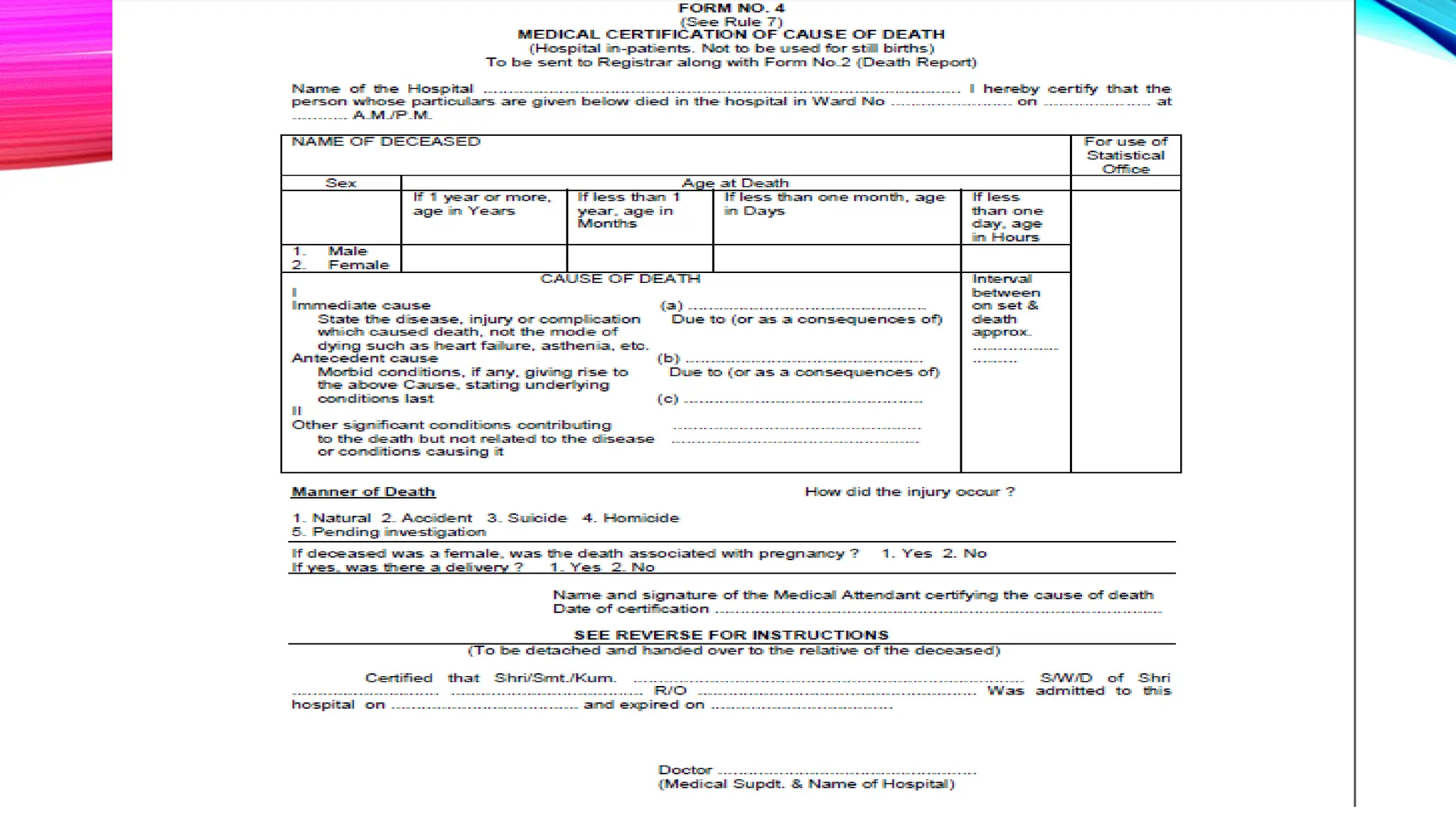
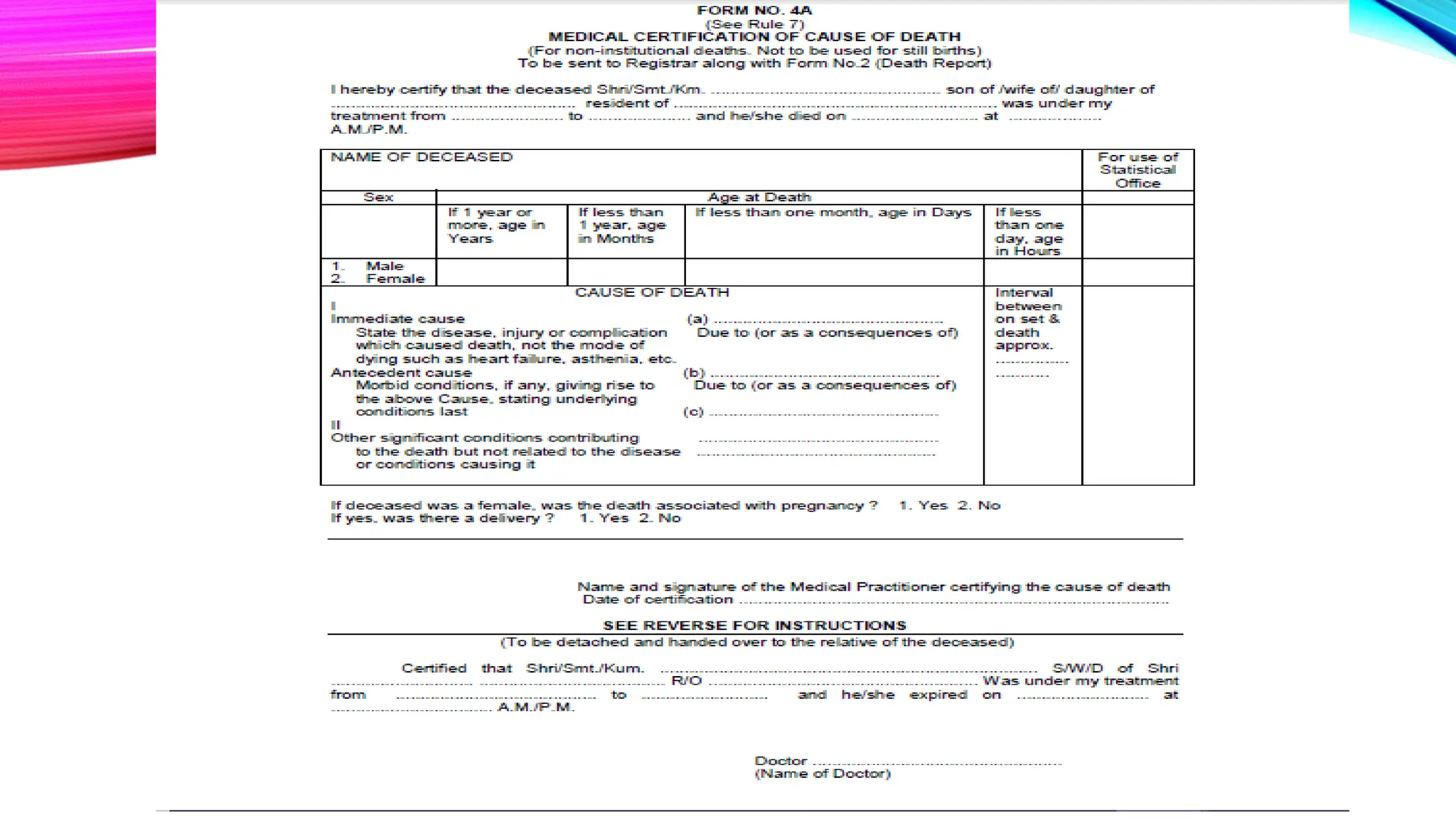
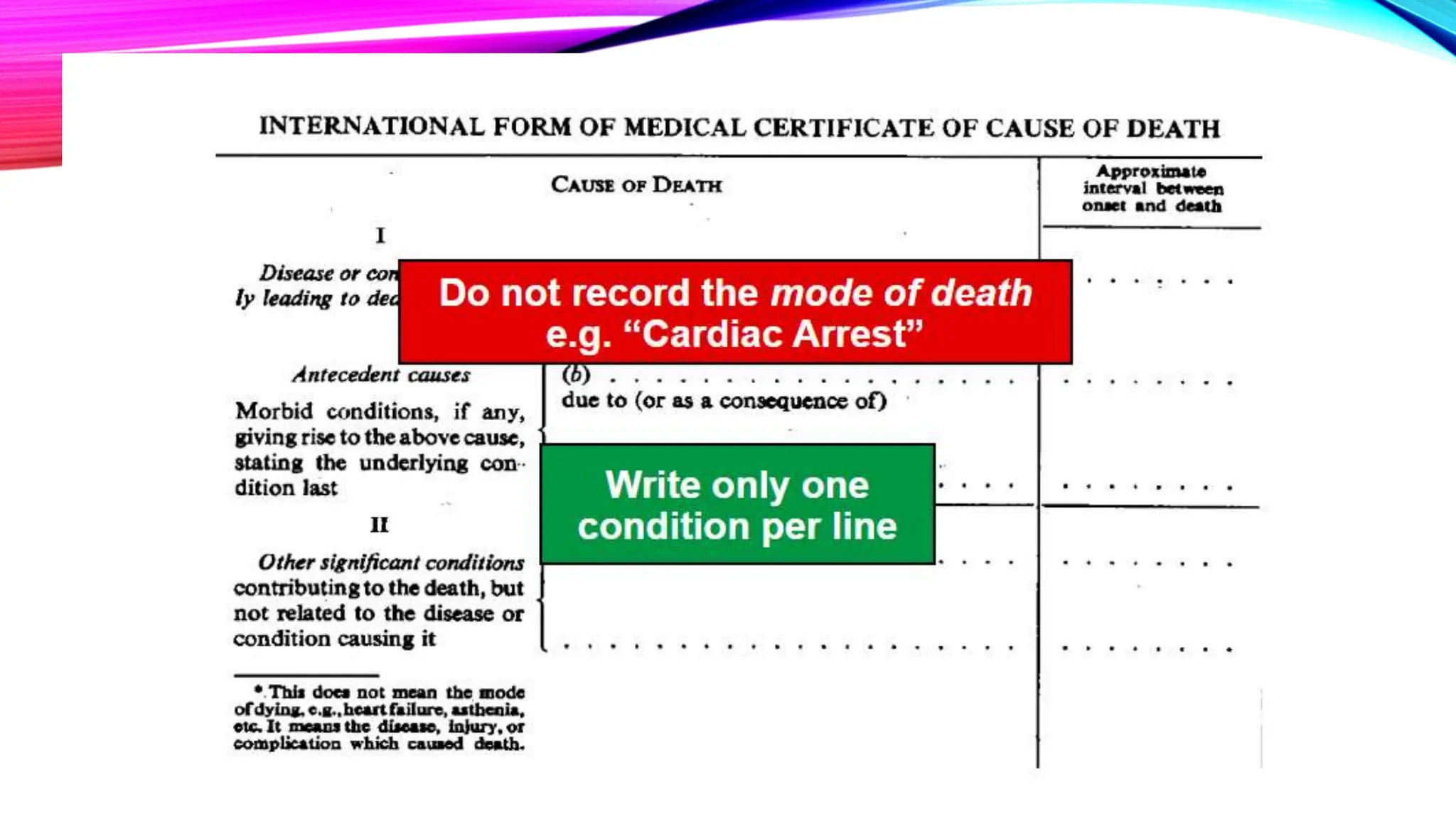
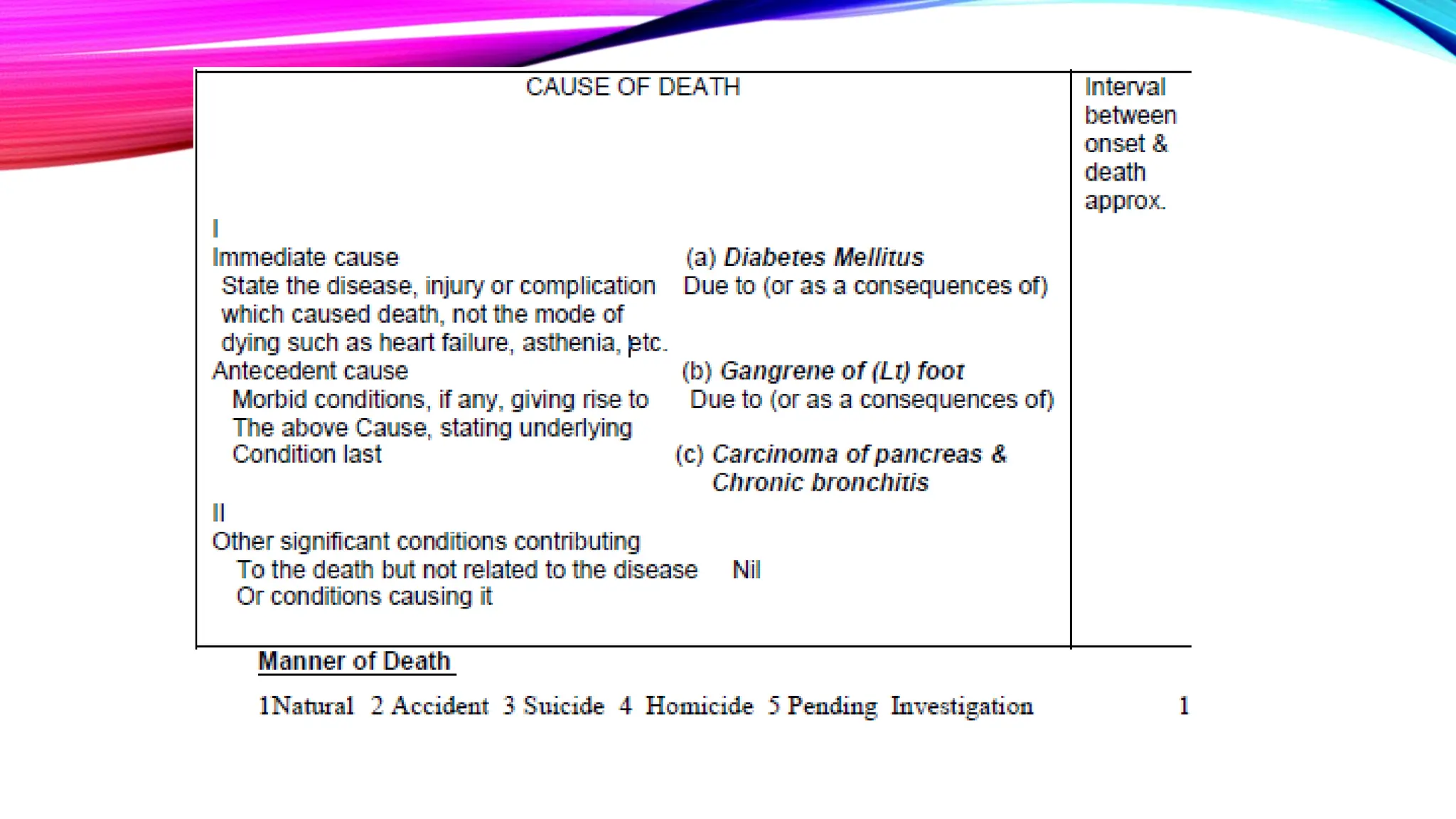
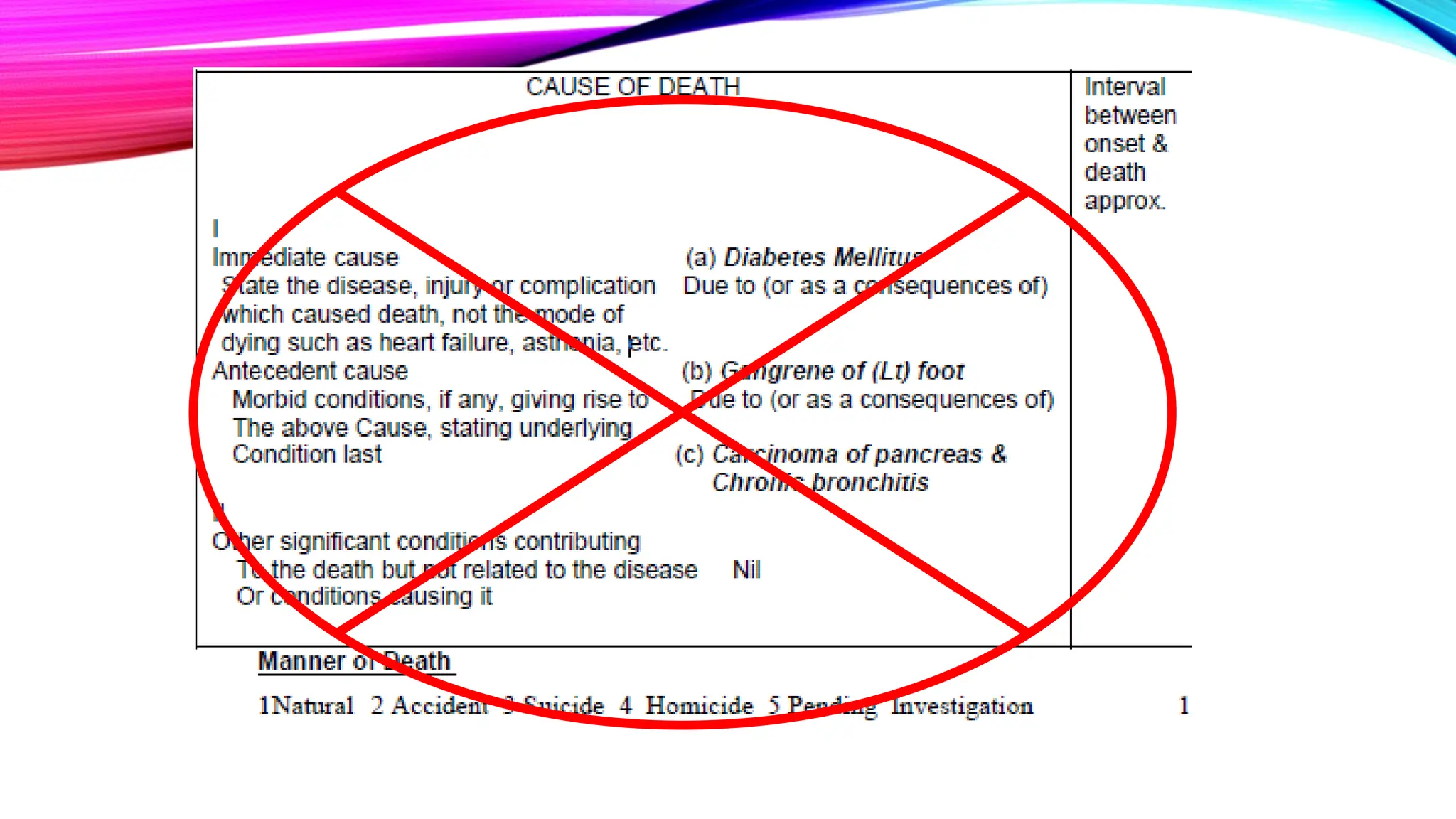
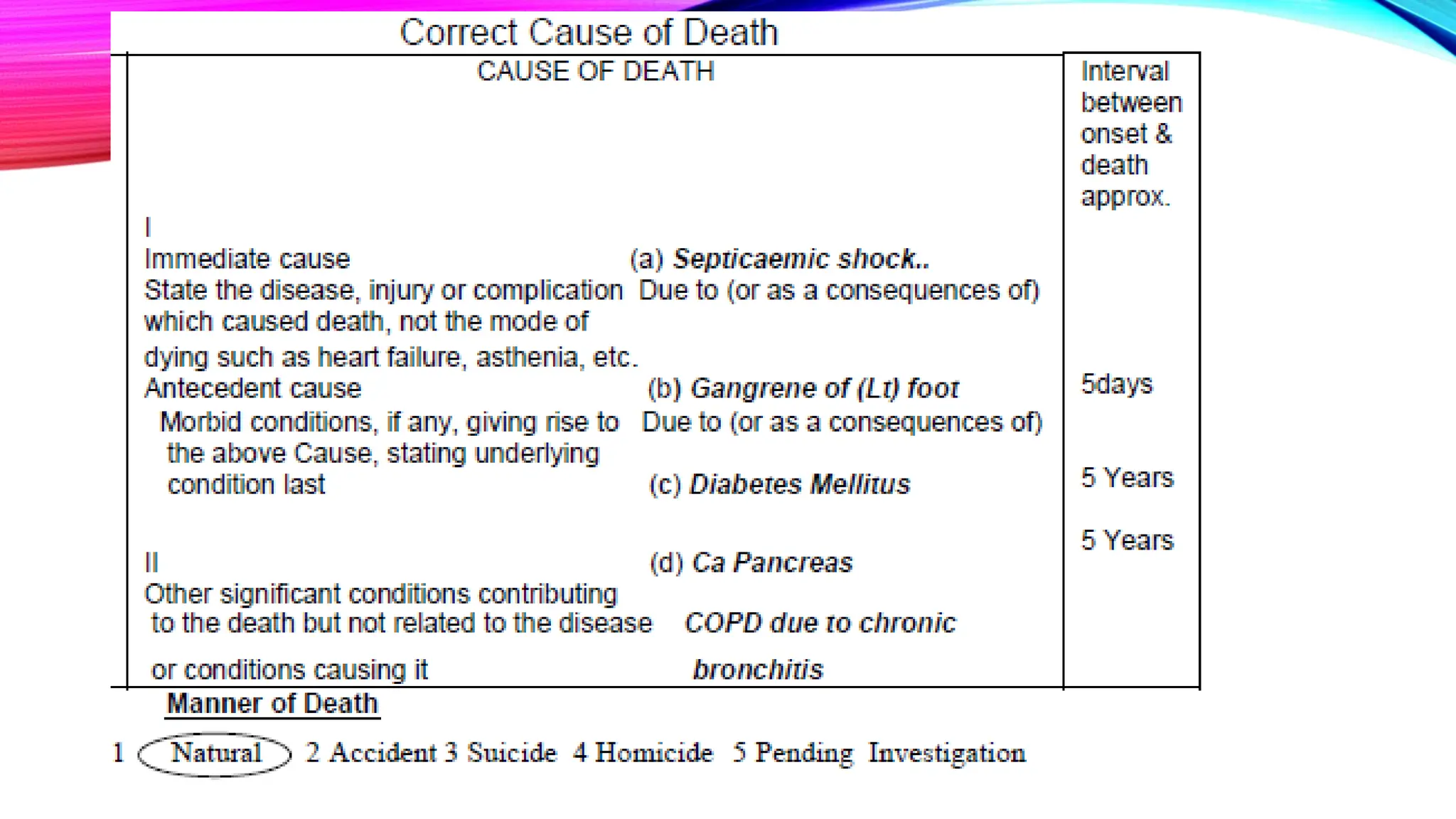
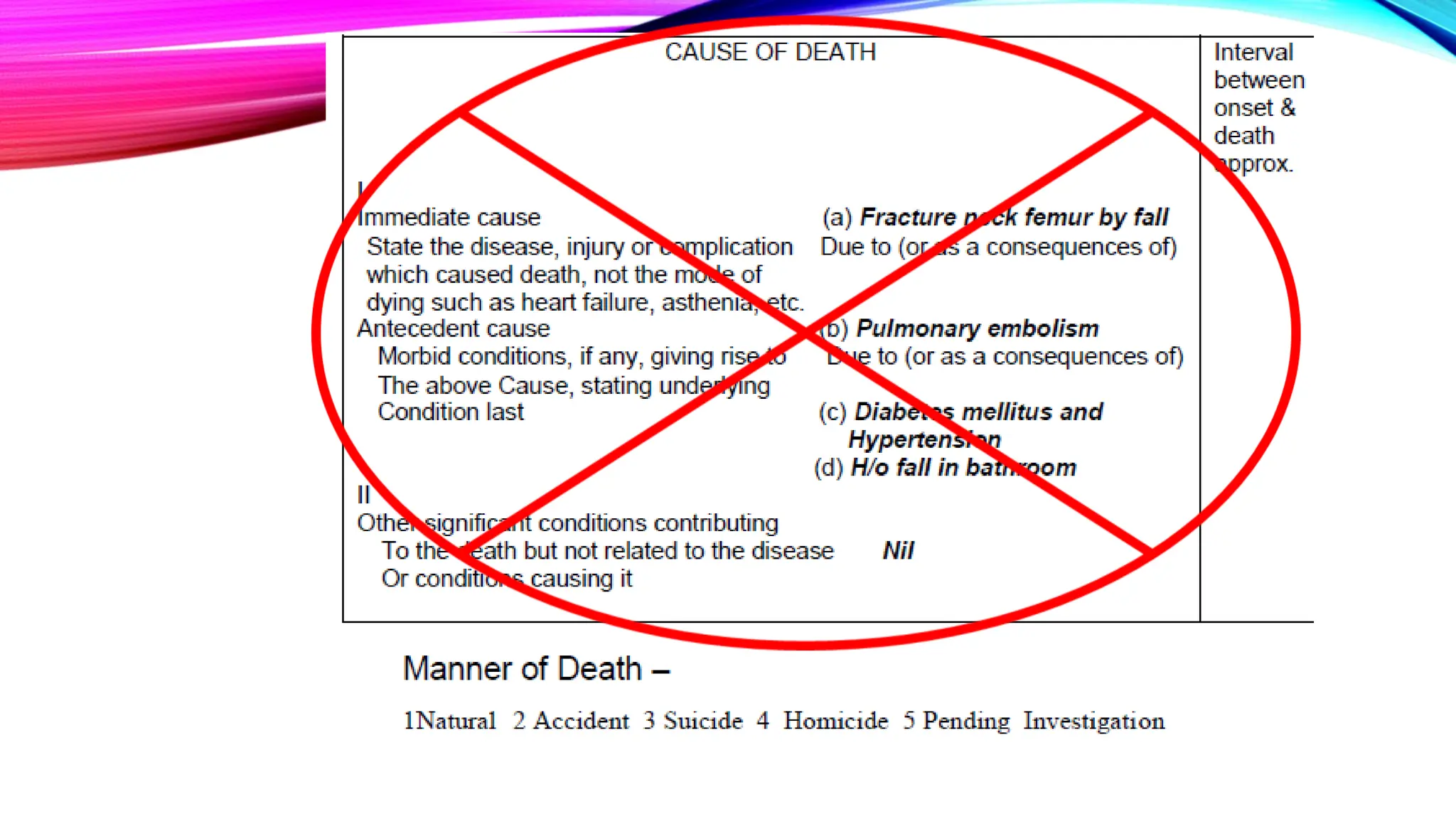
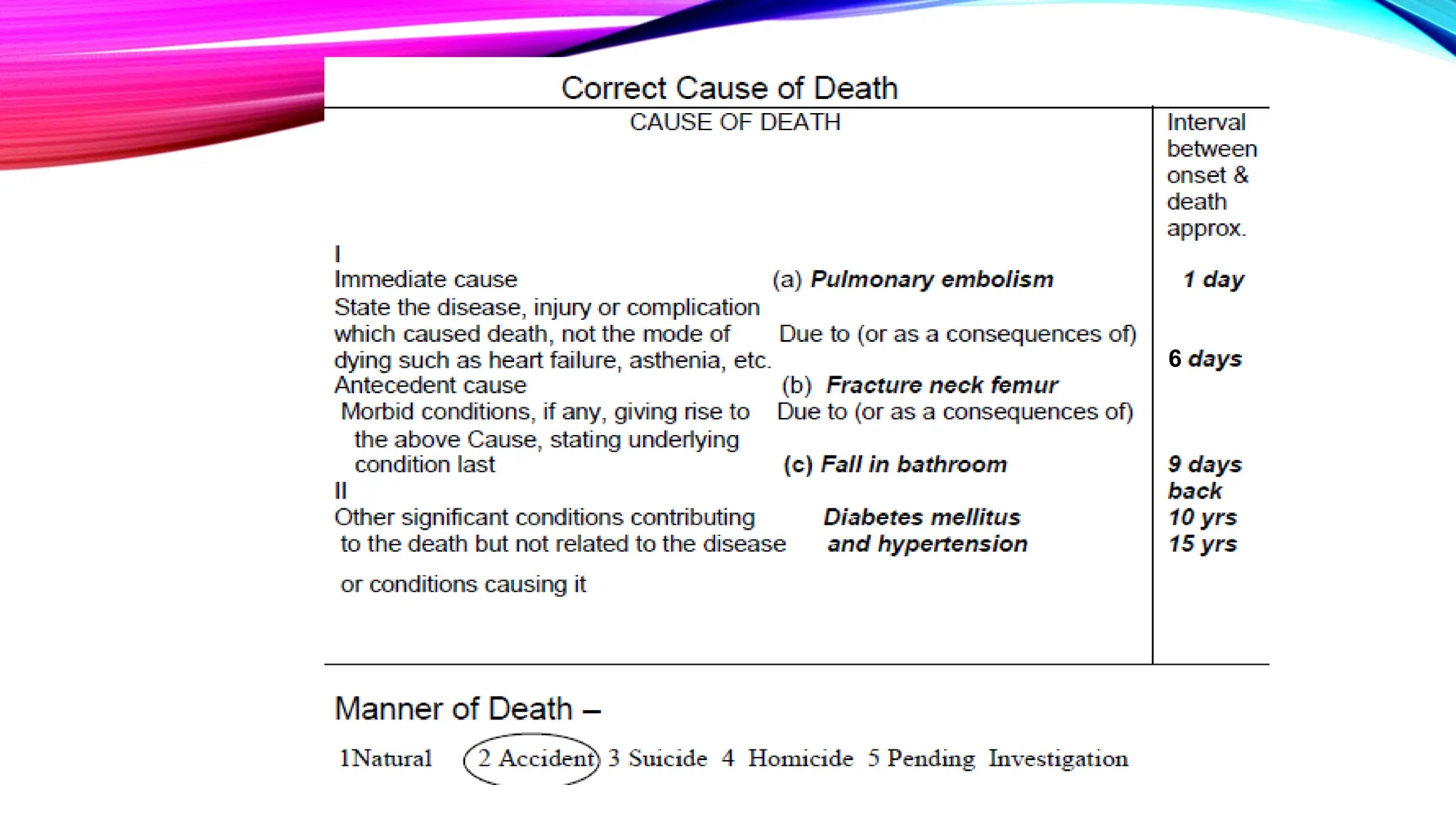
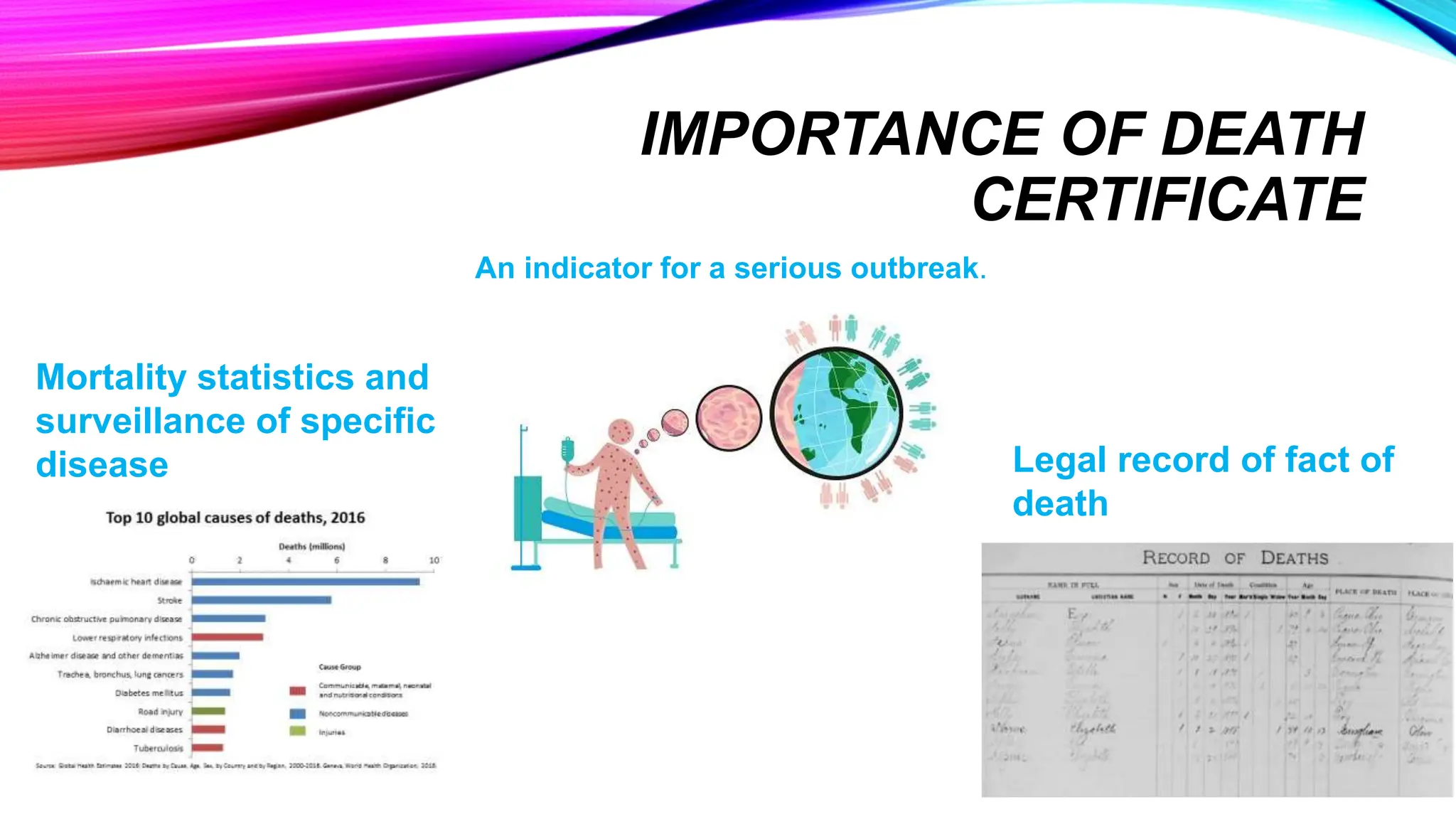
The document outlines the medical certification of cause of death (MCCD), detailing the legal definitions of death and the processes involved in death certification as per relevant laws. It describes the phases of death, criteria for determining brain death, and the essential components required in a death certificate, such as cause, underlying cause, mechanism, and manner of death. It also emphasizes the responsibilities of medical practitioners in death certification and the importance of accuracy in documenting the cause of death for legal, statistical, and protective purposes.