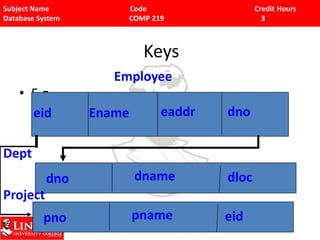
The document discusses key concepts of the relational database model including its basic structure using tables and relations. It describes how relations are represented by schemas and instances. It defines the different types of keys like primary keys, foreign keys, and composite keys. It also introduces relational algebra and calculus as procedural and non-procedural query languages for retrieving data in a relational database.


![Subject Name Code Credit Hours
Database System COMP 219 3
Relational Model:
• To denote the value of attribute ‘a’ on second
tuple, then it can be denoted as t2[a]=value.
• E.g..
• t2[ename]=“bbb”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbmschaptervii-140731025718-phpapp02/85/Dbms-chapter-vii-5-320.jpg)