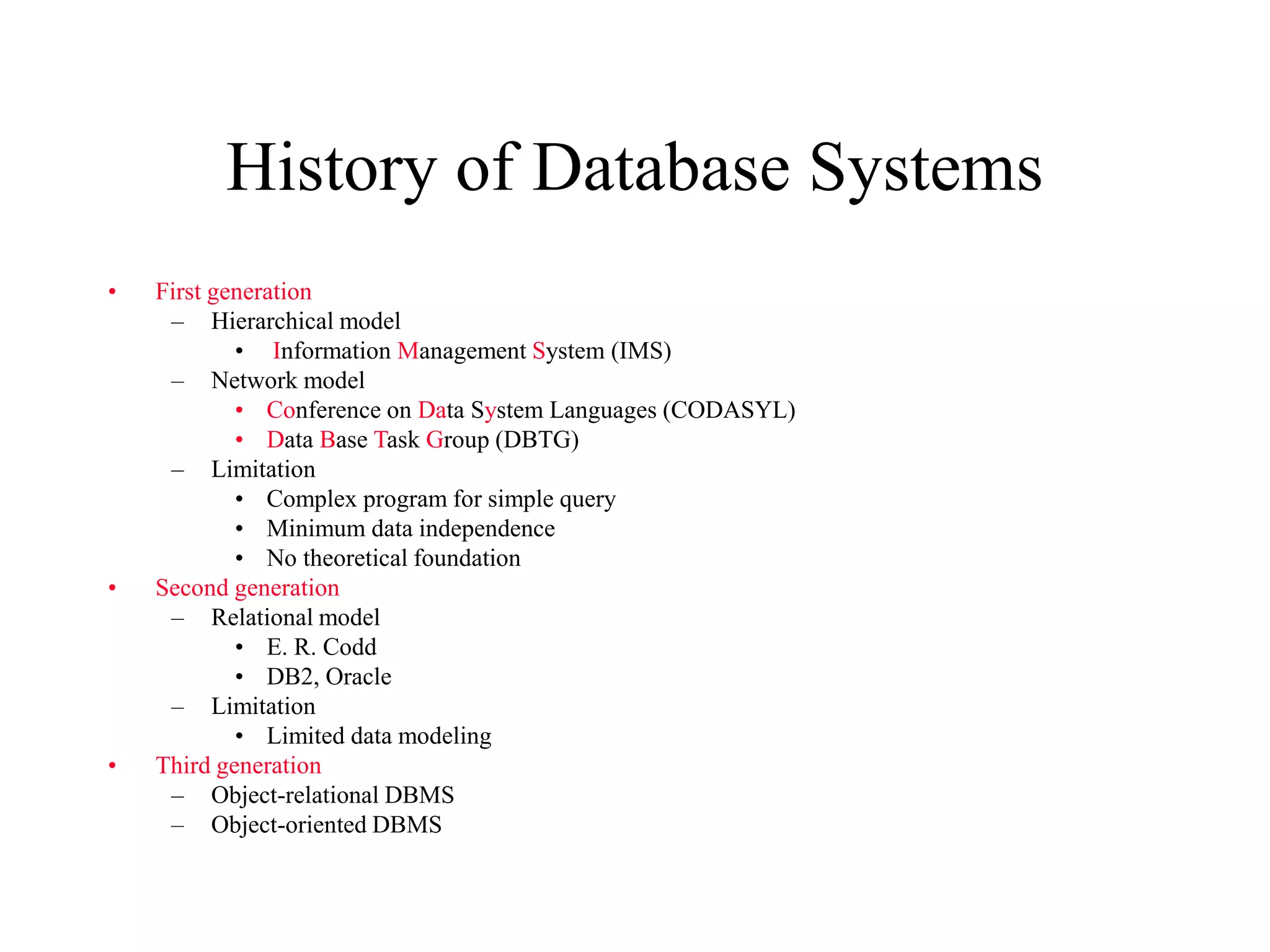
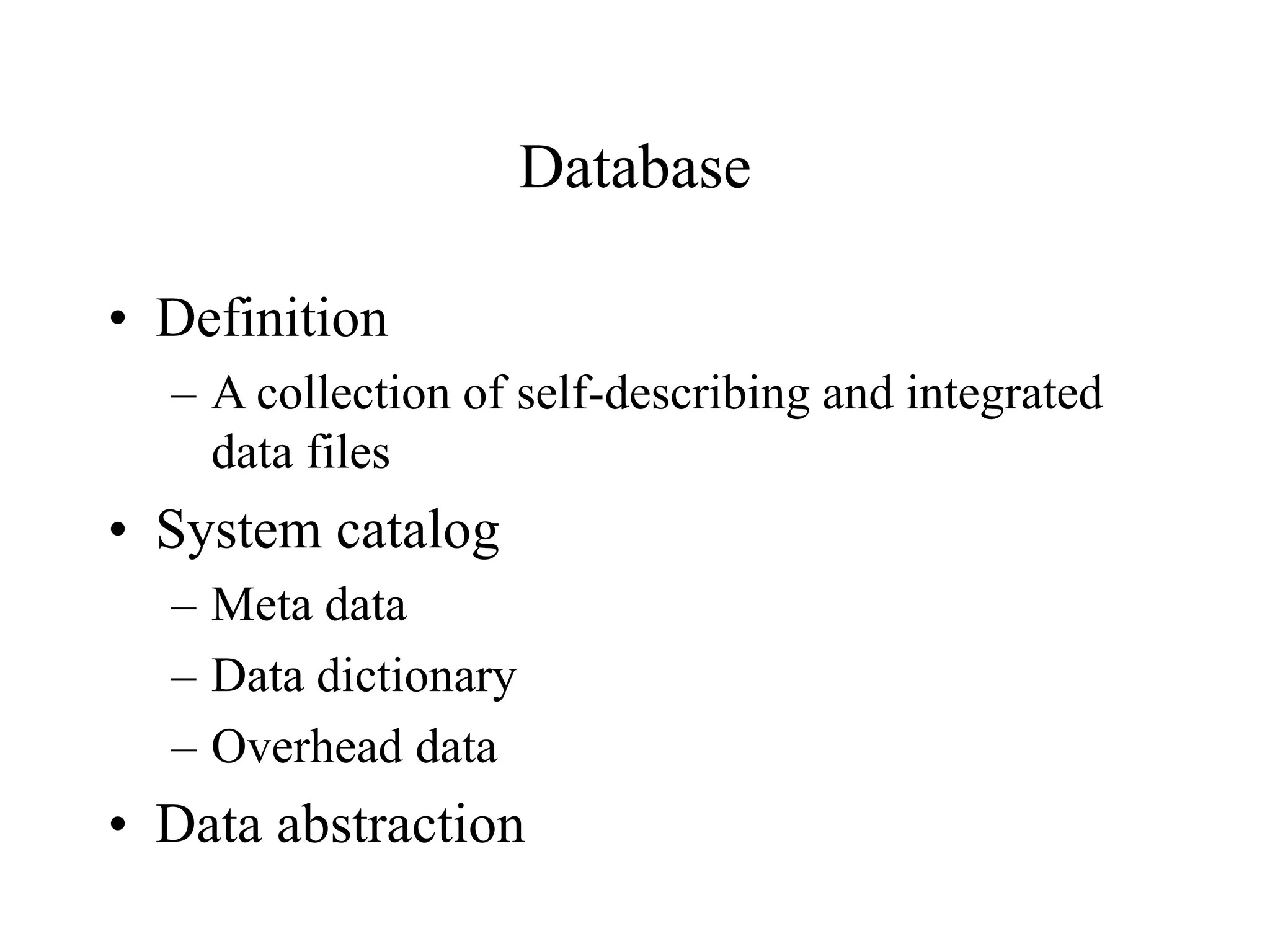
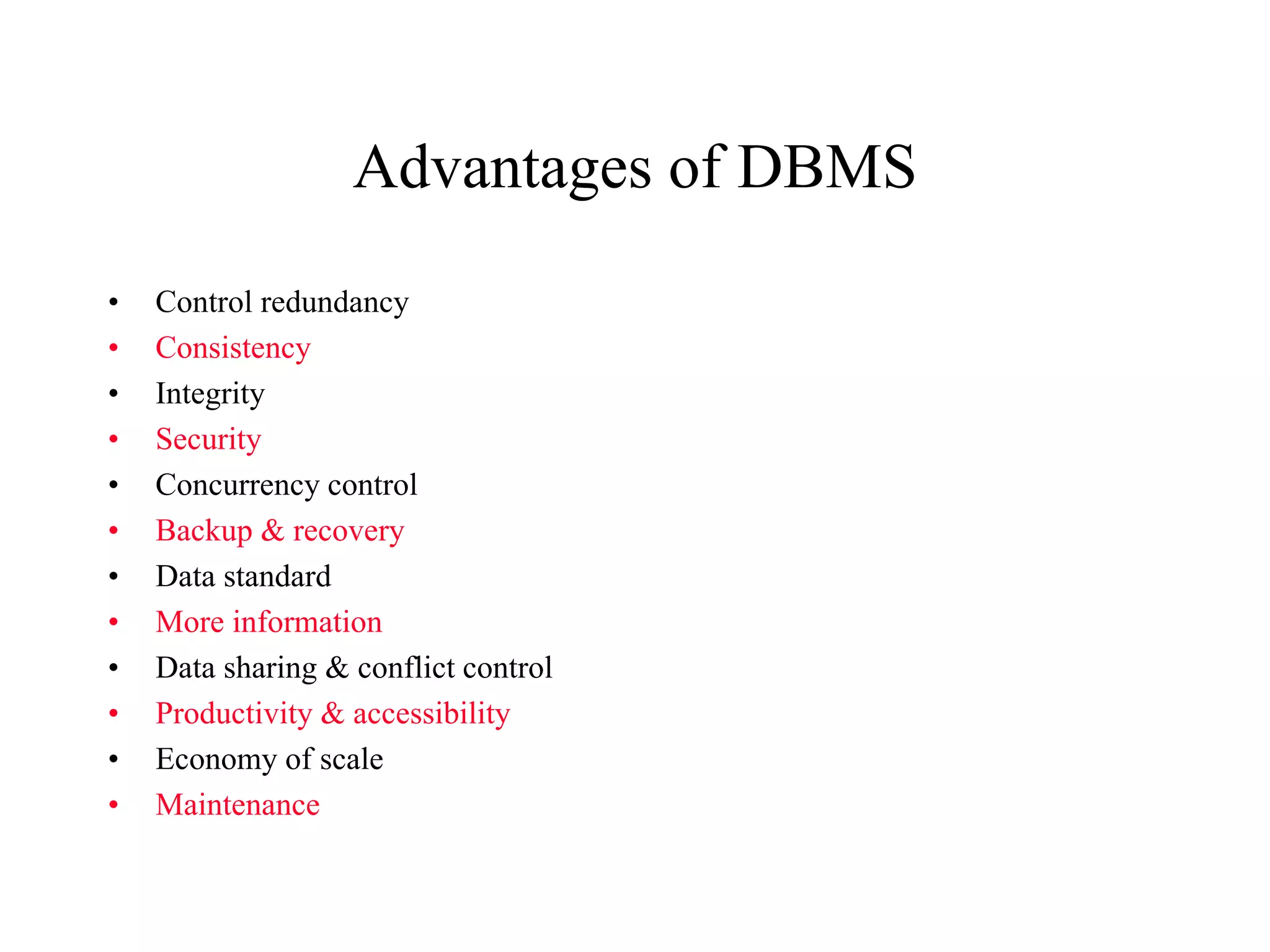
This document provides an overview of databases and database management systems (DBMS). It discusses the history of databases, from early file-based systems to hierarchical, network, and relational models. Key topics covered include the definition of a database, components of a DBMS like SQL and data dictionaries, the roles involved in database administration, and advantages/limitations of DBMS. The document concludes with an assignment asking students to review the chapter, read an appendix, and submit a group list.