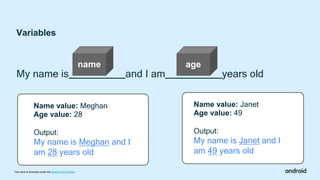
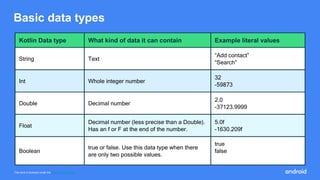
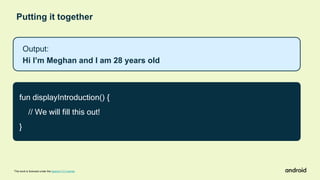
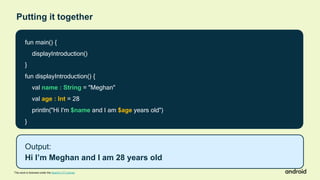
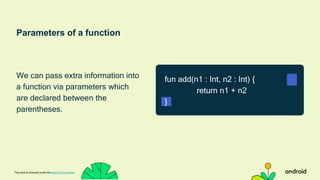
Compose Camp is an introduction to building Android apps using Jetpack Compose. The document outlines the prerequisites, learning objectives, and structure of Compose Camp. It will teach participants to set up Android Studio, learn Kotlin fundamentals, and build their first Android apps with Compose. The course is divided into units that introduce key Compose concepts and provide interactive exercises to apply the learning.