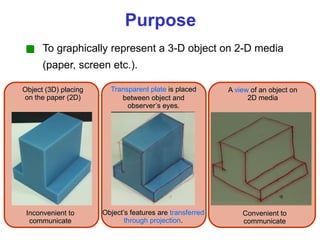
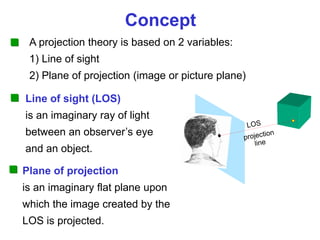
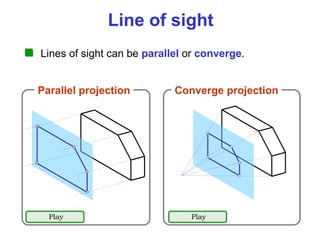
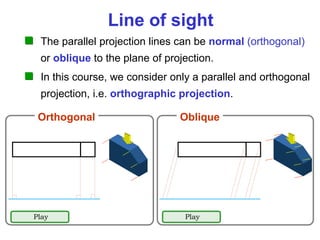
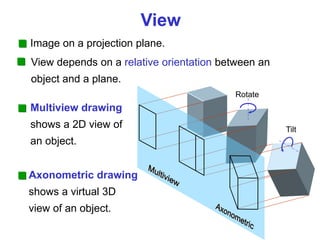
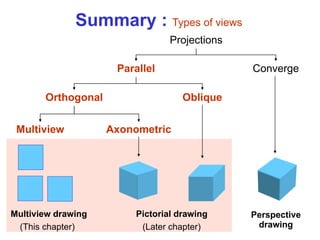
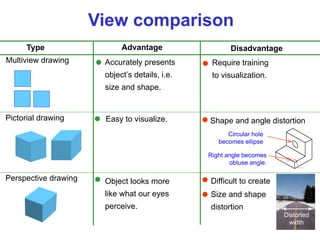
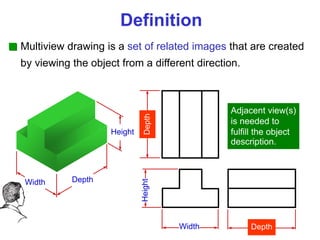
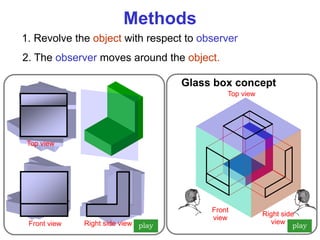
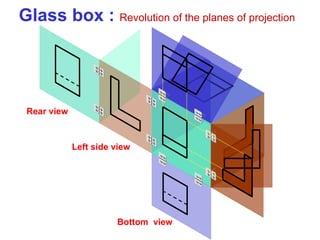
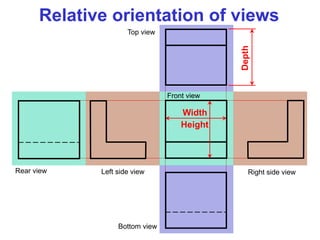
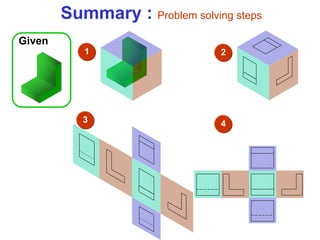
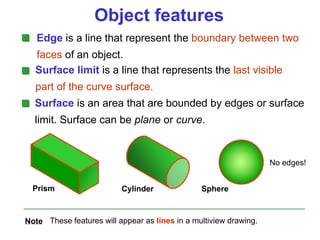
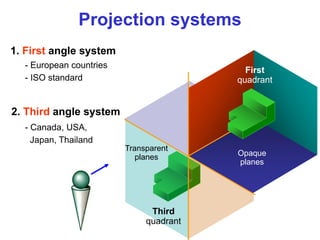
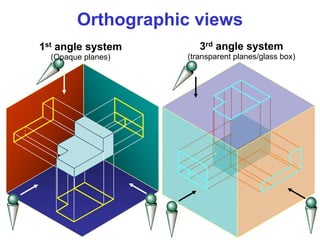
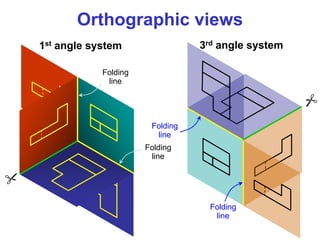
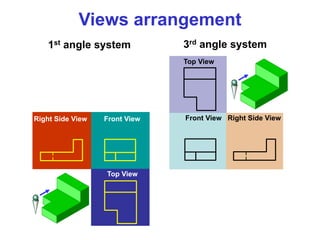
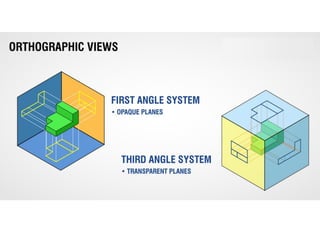
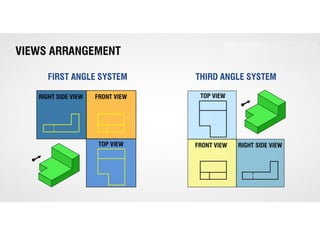
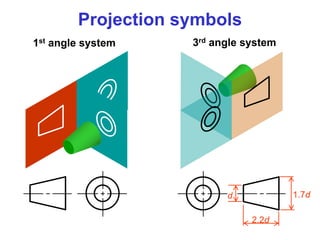
This document discusses orthographic projection and multiview drawings. Orthographic projection uses parallel lines of sight and projection planes to represent a 3D object in 2D. A multiview drawing shows an object through multiple views, such as the front, top, and side views. It accurately depicts an object's size and shape without distortion. The document also explains first and third angle projection systems, which determine the placement of views in a multiview drawing.