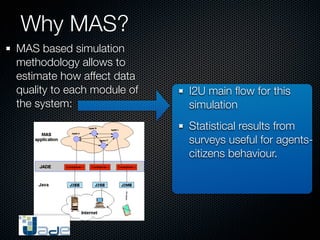
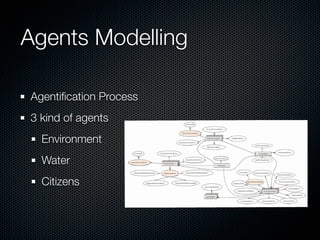
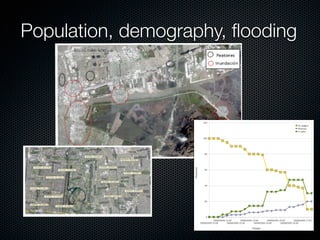
This document discusses using data from the web and internet (I2U flows) to simulate urban dynamics and the extreme impacts of events like hurricanes. It focuses on using available I2U data about New Orleans and Hurricane Katrina in 2005 to design a multi-agent system simulation. Key data sources included the USGS, OpenStreetMap, and Google Maps/Earth. The simulation models environment, water, and citizen agents to estimate how data quality impacts the system and visualize evacuation patterns and group behaviors. The authors conclude I2U data analysis is fundamental for urban cloud computing and simulations, and future work will use complex systems methods to analyze events and detect emergent phenomena in digital cities.