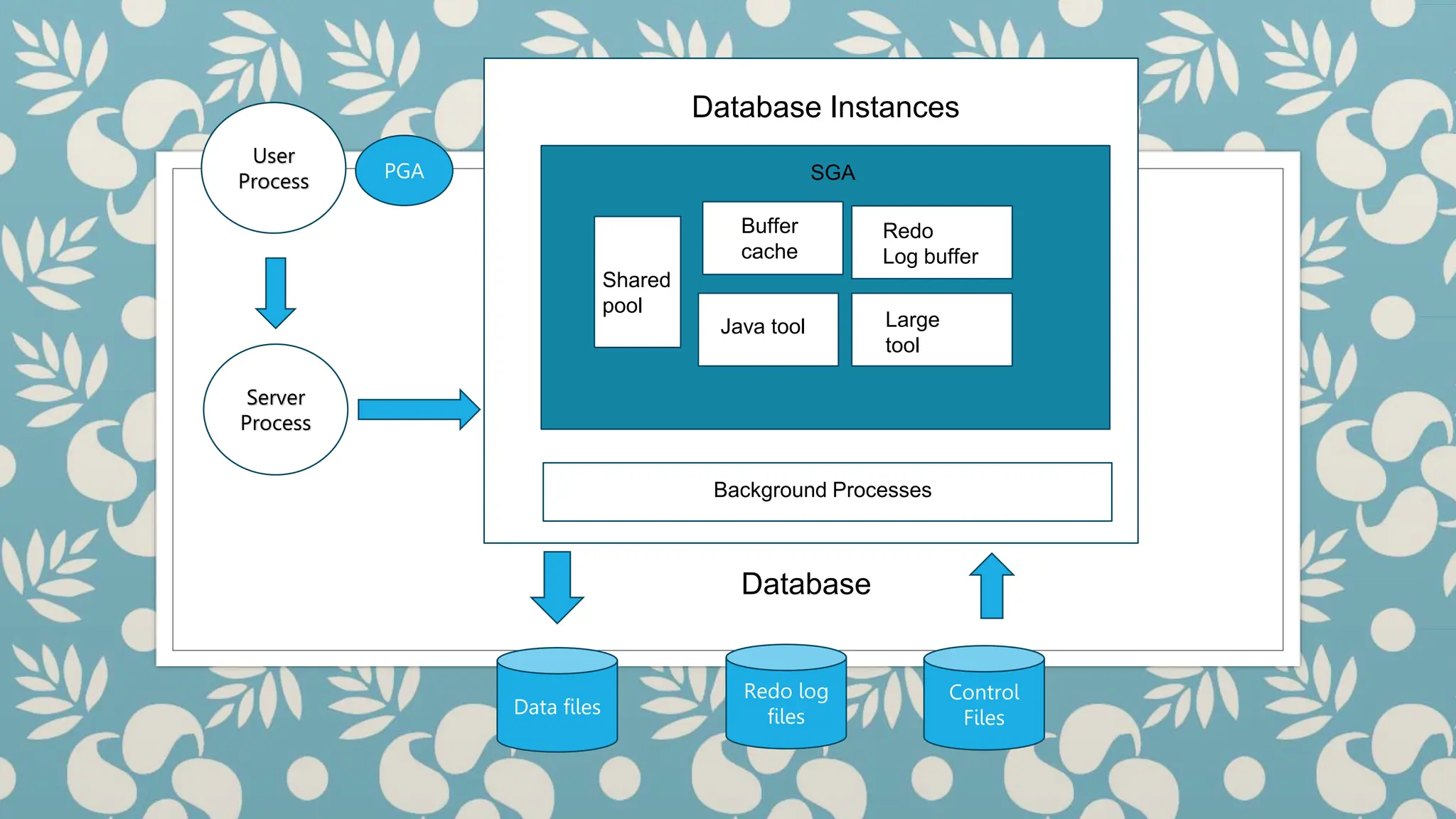
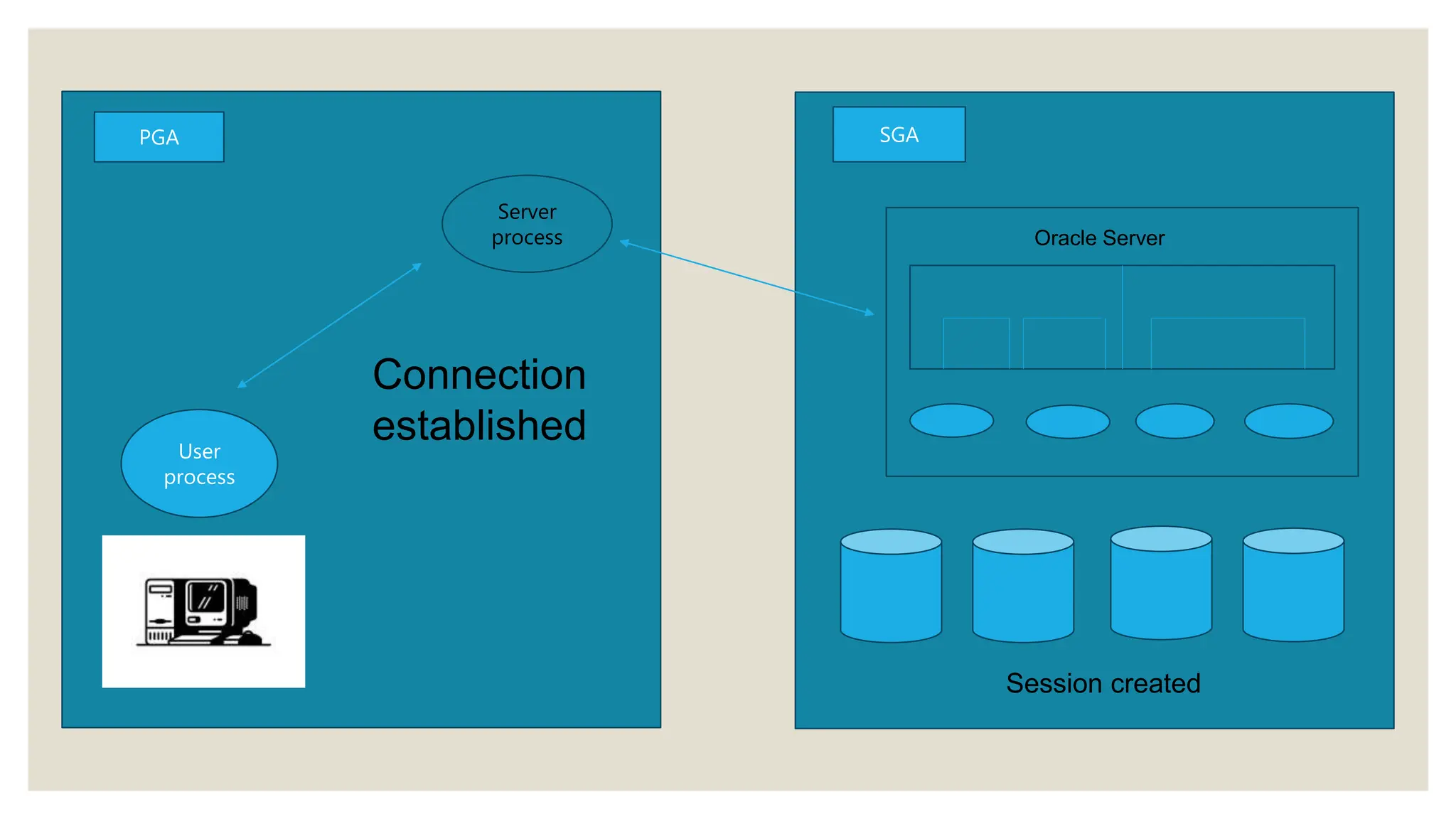
The document describes the architecture of Oracle databases, highlighting the roles of user processes, server processes, and various memory structures such as the System Global Area (SGA) and Program Global Area (PGA). It outlines key components like the shared pool, database buffer cache, and redo log buffer, as well as the function of background processes. Additionally, it explains the organization of databases and the concept of sessions connecting applications to these databases.