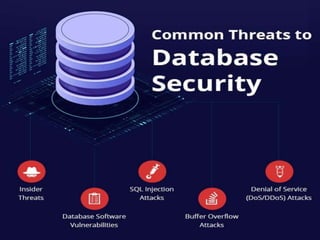
The document outlines the essential measures for database security and integrity, highlighting threats such as SQL injection, unauthorized access, malware attacks, insider threats, and denial-of-service attacks. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining data integrity through validation, removing duplicate data, regular backups, and implementing access controls. The conclusion underscores the need for organizations to educate staff on security practices to protect sensitive information and ensure data reliability.