This presentation explores the critical role of database applications in research and industry, with a focused perspective on Ayurveda, pharmaceutical sciences, and healthcare systems.
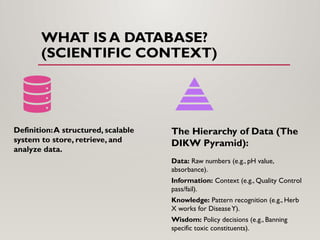
It highlights how modern databases act not merely as data storage systems, but as active engines for scientific discovery, quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and evidence-based decision-making.
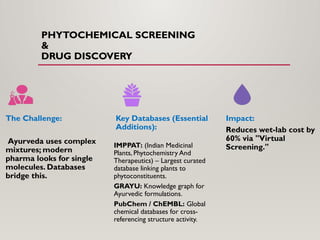
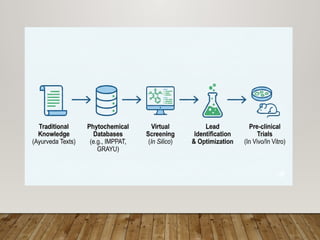
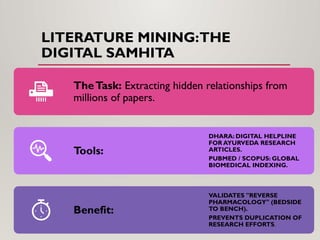
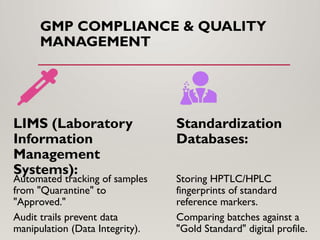
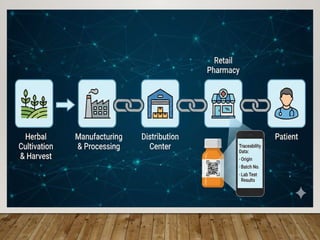
The presentation covers real-world applications of databases in phytochemical screening, drug discovery, omics data integration, clinical trial registries, GMP compliance, supply chain traceability, and intellectual property protection.
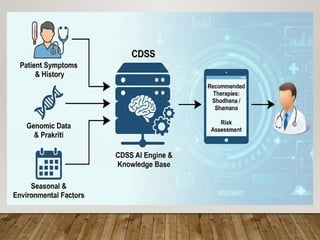
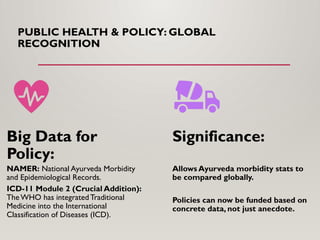
Special emphasis is placed on the role of databases in clinical decision-making and public health policy development, demonstrating how structured data and real-world evidence influence preventive healthcare strategies and integrative medicine frameworks.
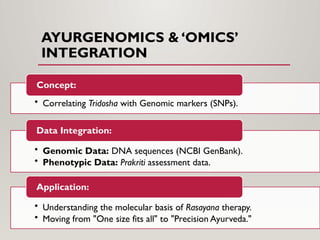
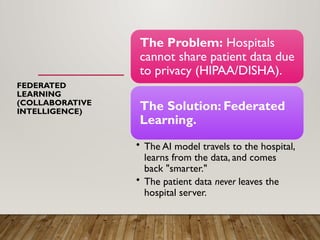
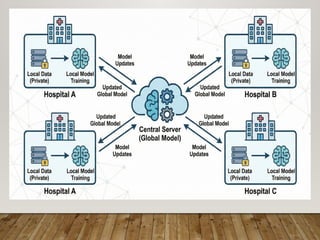
The presentation also discusses future directions in database development, including AI/ML-driven predictive analytics, federated learning, semantic web technologies, cloud-native architectures, distributed databases, and FAIR data principles, highlighting their relevance to next-generation healthcare and pharmaceutical research.
This resource is intended for students, researchers, academicians, healthcare professionals, and policy analysts interested in the intersection of data science, pharmaceutical research, and traditional medicine modernization.
![DATABASE
APPLICATIONS
IN RESEARCH &
INDUSTRY
PRESENTED BY:
DR. AMAN BHARDWAJ
P.G. DEPARTMENT OF RAS SHASHTRA AND BHAISHJYA KALPANA
[M.M.M. GOVERNMENT AYURVEDA COLLEGE, UDAIPUR]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databaseapplicationsinayurvedaresearchindustry-260207053318-5b2f5055/75/Database-Applications-in-Research-and-Industry-Decision-Making-Policy-Development-Emerging-Technologies-pptx-1-2048.jpg)