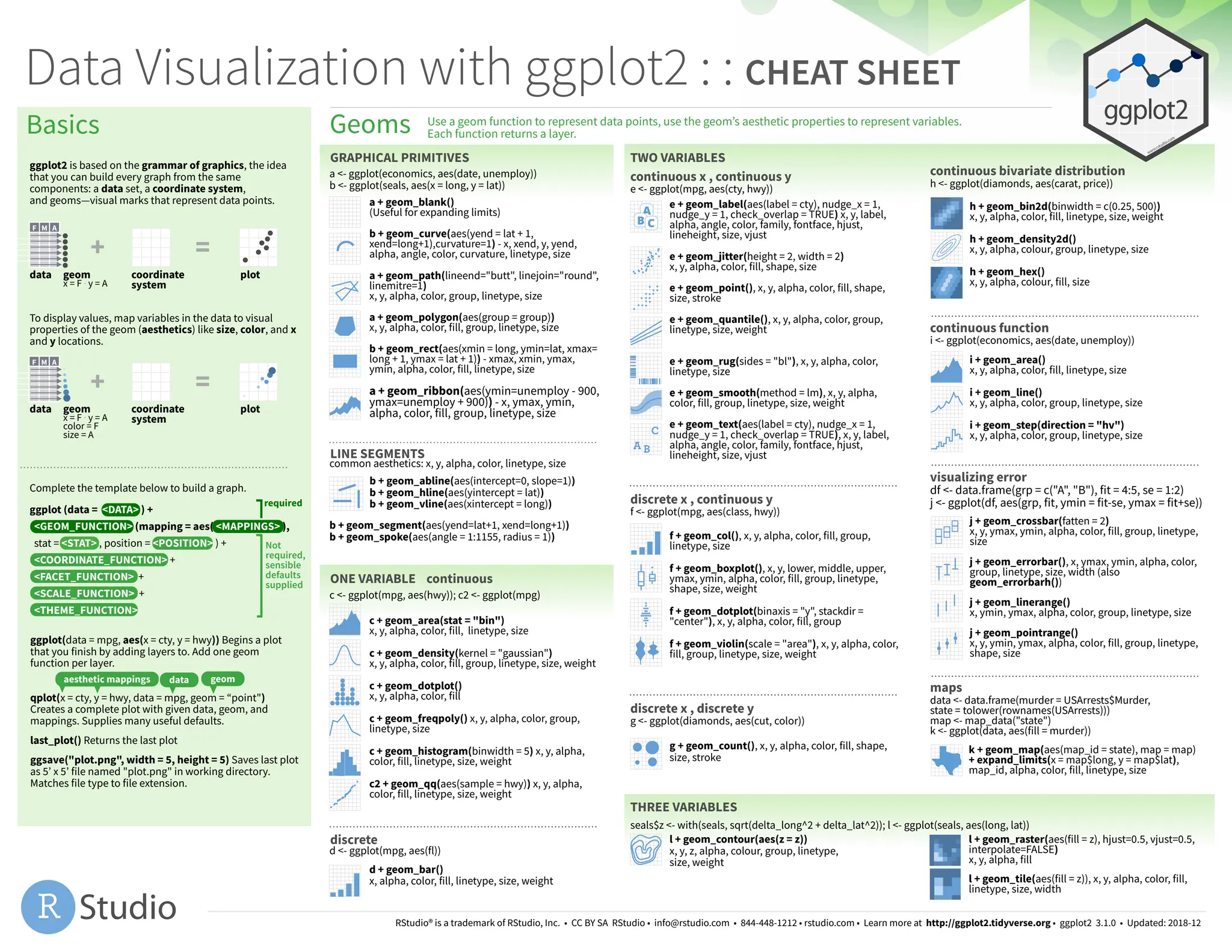
This document is a cheat sheet for data visualization using ggplot2, detailing the core components required to build graphs based on the grammar of graphics, such as data sets, coordinate systems, and visual marks (geoms). It outlines various geometrical functions for plotting different types of data and aesthetics, including layers, mapping, and common adjustments. The document also provides guidance on scales, coordinate systems, and themes to enhance the presentation of visual data.