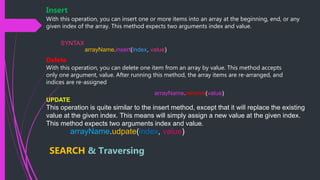
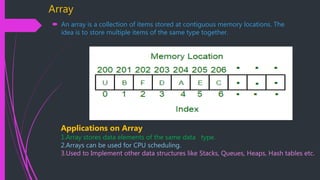
The document discusses data structures and algorithms. It begins with an example of an even/odd number checking algorithm. It then defines arrays as a collection of items stored in contiguous memory locations that can store multiple items of the same type together. It provides examples of declaring and initializing single-dimensional arrays. It also discusses two-dimensional arrays and provides a code example. Finally, it briefly discusses common array operations like insertion, deletion, updating, and searching/traversing arrays.


![Even / odd Algorithm
Step 1: Start
Step 2: [ Take Input ] Read: Number
Step 3: Check: If Number%2 == 0 Then
Print : N is an Even Number.
Else
Print : N is an Odd Number.
Step 4: Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-220221073806/85/Data-structures-Lecture-5-3-320.jpg)
![int arr[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int arr[5];
Declaration & initialization
int values[5];
printf("Enter 5 integers: "); // taking input and storing it in an array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
scanf("%d", &values[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-220221073806/85/Data-structures-Lecture-5-5-320.jpg)
![Array Types
Single Dimensional Array / One Dimensional Array
single dimensional arrays are used to store list of values of same
datatype. In other words, single dimensional arrays are used to store a
row of values. In single dimensional array, data is stored in linear form.
Single dimensional arrays are also called as one-dimensional arrays,
Linear Arrays or simply 1-D Arrays.
int rollNumbers [60] ;
int marks [6] = { 89, 90, 76, 78, 98, 86 } ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-220221073806/85/Data-structures-Lecture-5-6-320.jpg)
![2D Array
A two-dimensional array can be
thought of as a matrix with rows and
columns. The general syntax used to
declare a two-dimensional array is
int my_array[5][3];
int main()
{
int my_array[5][3] = {
{1, 2, 3}, //row 1
{4, 5, 6}, //row 2
{7, 8, 9}, //row 3
{10, 11, 12}, //row 4
{13, 14, 15} //row 5
};
Initializing two-dimensional arrays
int main()
{
int my_array[5][3] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8,9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15};
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-220221073806/85/Data-structures-Lecture-5-7-320.jpg)
![Array Operations
Here, we have accessed the
second value of the array using
its index, which is 1. The output
of this will be 200, which is
basically the second value of
the balanced array.
printf(balance[1])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-220221073806/85/Data-structures-Lecture-5-8-320.jpg)