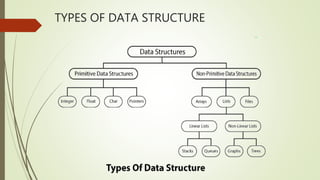
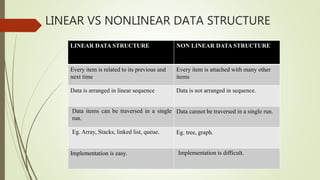
The document provides an introduction to data structures, detailing their definitions, types (primitive and non-primitive), and various operations such as creation, destruction, searching, sorting, and merging. It distinguishes between linear and non-linear data structures, discussing examples like stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Additionally, it covers algorithm efficiency metrics, including time and space complexity, and the analysis of algorithms' performance in worst, average, and best case scenarios.
















![WORST CASE ANALYSIS
In the worst case analysis, we calculate the upper bound on the running
time of an algorithm.
We must know the case that causes the maximum number of operations
to be executed.
For Linear Search, the worst case happens when the element to be
searched is not present in the array.
When x is not present, the search () function compares it with all the
elements of array [] one by one.
Therefore, the worst case time complexity of linear search would be.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructures-introduction-210124070102/85/Data-structures-Introduction-19-320.jpg)

