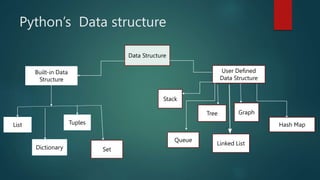
This document discusses data structures in Python. It introduces common data structures like lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets. Lists are described as ordered containers that can hold elements of different data types and be accessed by index. Lists are mutable and dynamic. The document provides examples of list usage, like storing employee data in a list of dictionaries or tweets in a list. It also covers list methods for adding, removing, sorting and accessing elements. The goal of data structures is to organize data for efficient storage and computation.




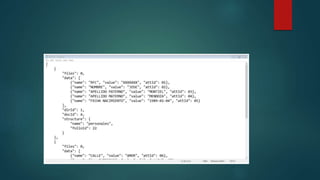




![Examples
city_list=['Newyork','chicago', 'Los Angeles', 'Houston', 'Philadelphia',
'Dallas']
squares = [‘1’, ‘4, 9’, ’16’]
List with Mixed Data types
My_list = [‘1’ ,”Hello”, ‘3.5’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresinpython-230131173832-abfca358/85/Data-Structures-in-Python-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![Example
data = [{"id": ("1", "2", "3"), "name": ("Dannie", "Williams"),
"department": ("HR", "IT")},
{"id": ("4", "5", "6"), "name": ("jhon", "smith"),
"department": ("HR", "IT")},
{"id": ("7", "8", "9"), "name": ("Allen", "polard"),
"department": ("finance", "IT")},
{"id": ("10", "11", "12"), "name": ("Reema", "Ferguson"),
"department": ("business", "IT")},
{"id": ("13", "14", "15"), "name": ("patrick", "Donald"),
"department": ("business", "IT")}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresinpython-230131173832-abfca358/85/Data-Structures-in-Python-pptx-12-320.jpg)
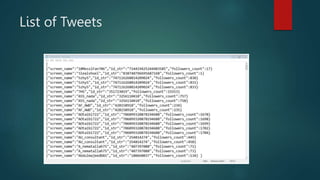

![Lists
Syntax
List_variables = [ val1,val2,val3…….]
My_list = [1,2,3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresinpython-230131173832-abfca358/85/Data-Structures-in-Python-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![List Indices
my_list =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresinpython-230131173832-abfca358/85/Data-Structures-in-Python-pptx-16-320.jpg)
