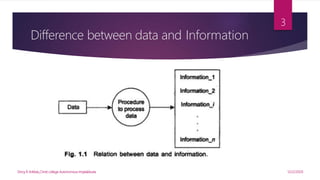
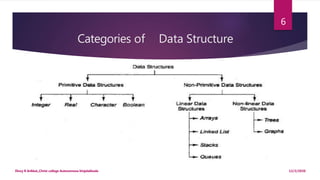
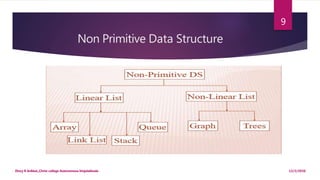
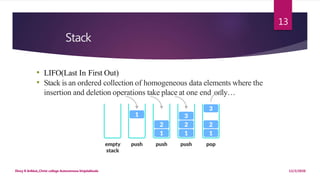
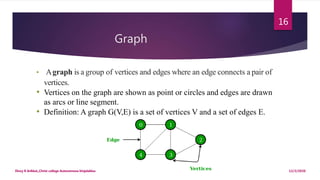
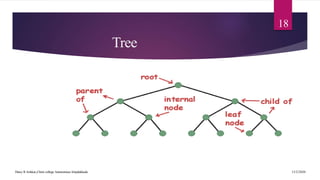
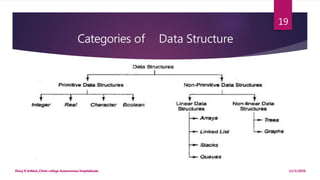
This document provides an introduction to data structures. It defines data as a set of values and information as processed data. It distinguishes between primitive and non-primitive data structures. Primitive structures are fundamental data types like integers and floats, while non-primitive structures are built from primitive types, such as lists, stacks, queues, trees and graphs. Linear structures like arrays, stacks and queues store elements in a sequential order, while non-linear structures like trees and graphs distribute elements across a plane in a non-sequential way. Common non-primitive structures are described in more detail, including their properties and uses.