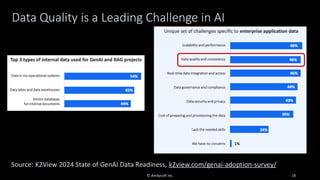
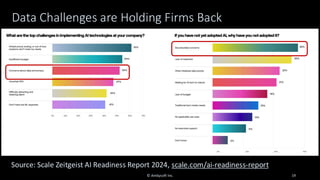
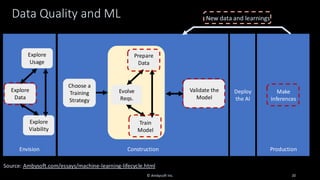
Organizations want to apply artificial intelligence (AI) to increase their business agility, but are struggling to do so. One of the fundamental challenges for AI development teams is data quality, or more accurately the lack of data quality. Your AI solution is only as good as the data that you train it on, and therein lies the rub: Is your data of sufficient quality to train a trustworthy system? If not, can you improve your data so that it is?
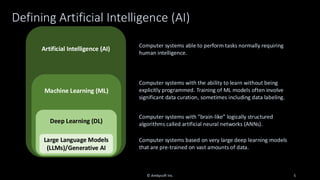
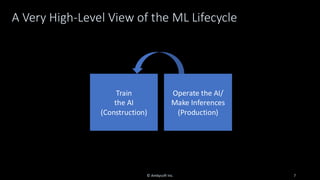
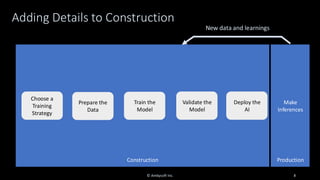
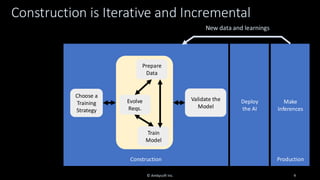
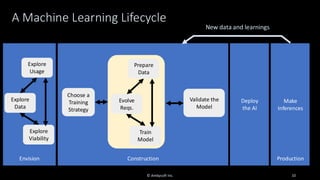
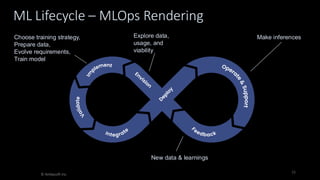
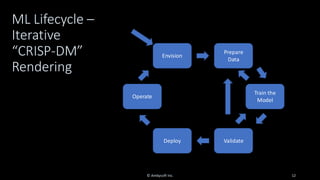
This presentation starts with an overview of GenAI and machine learning (ML) development lifecycles, with a focus on the impacts of data ingestion. It then works through recent research findings on the impact of data quality on the effectiveness of ML models, providing advice for where and where not to focus data cleansing efforts. We then explore why organizations need to go beyond project-level data cleansing strategies to instead fix data and the code that manipulates data at the source. It finishes with a context-driven approach for choosing between agile and traditional strategies for doing so.
Learning outcomes:
1. Understand why the potential of AI is undermined by your organizational data debt
2. Discover the potential impact of data cleansing techniques on AI development
3. Recognize the need to fix data quality problems at the source
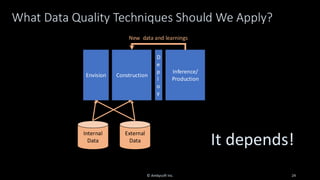
4. Identify how to choose the right data quality techniques for your context