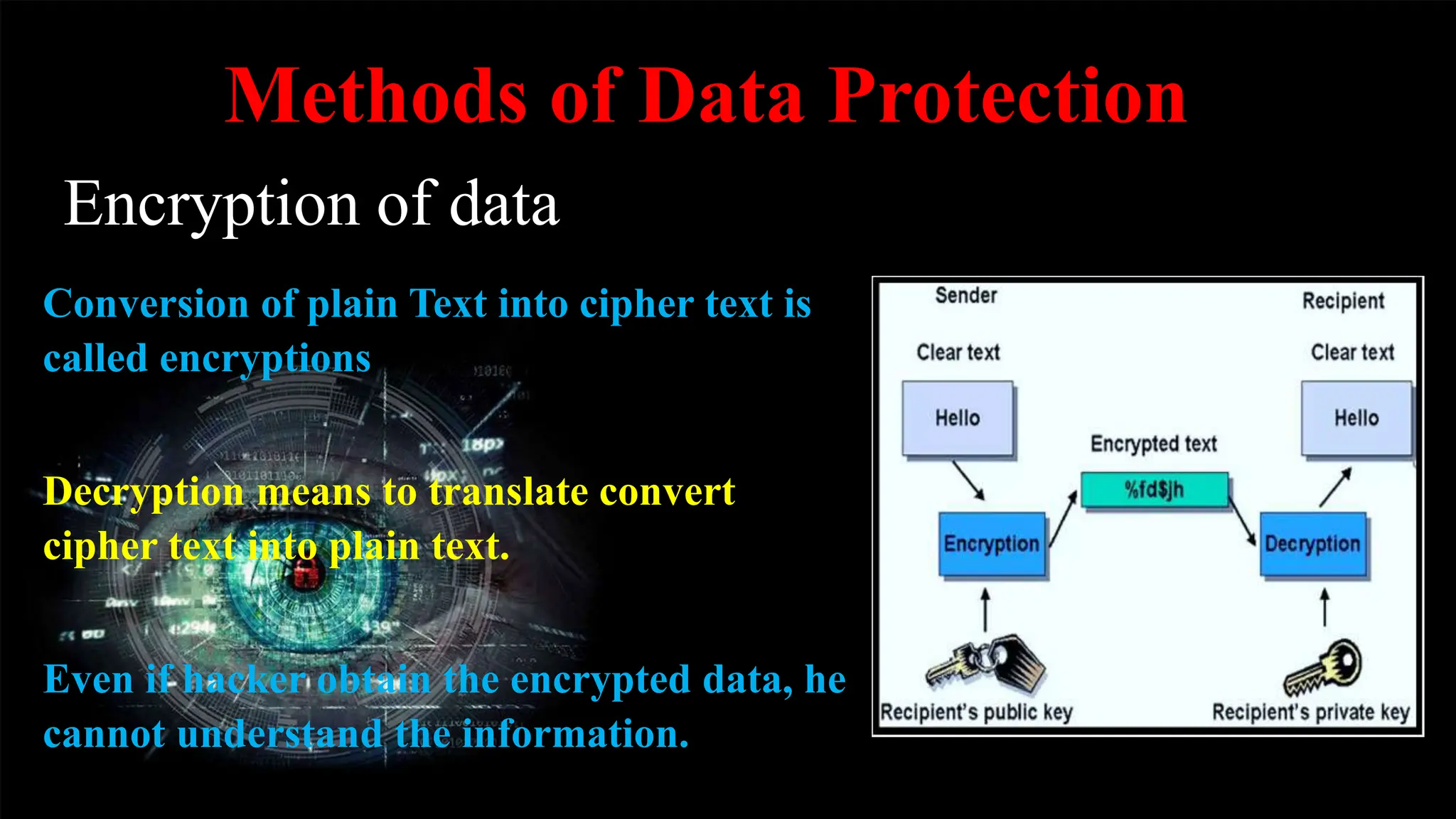
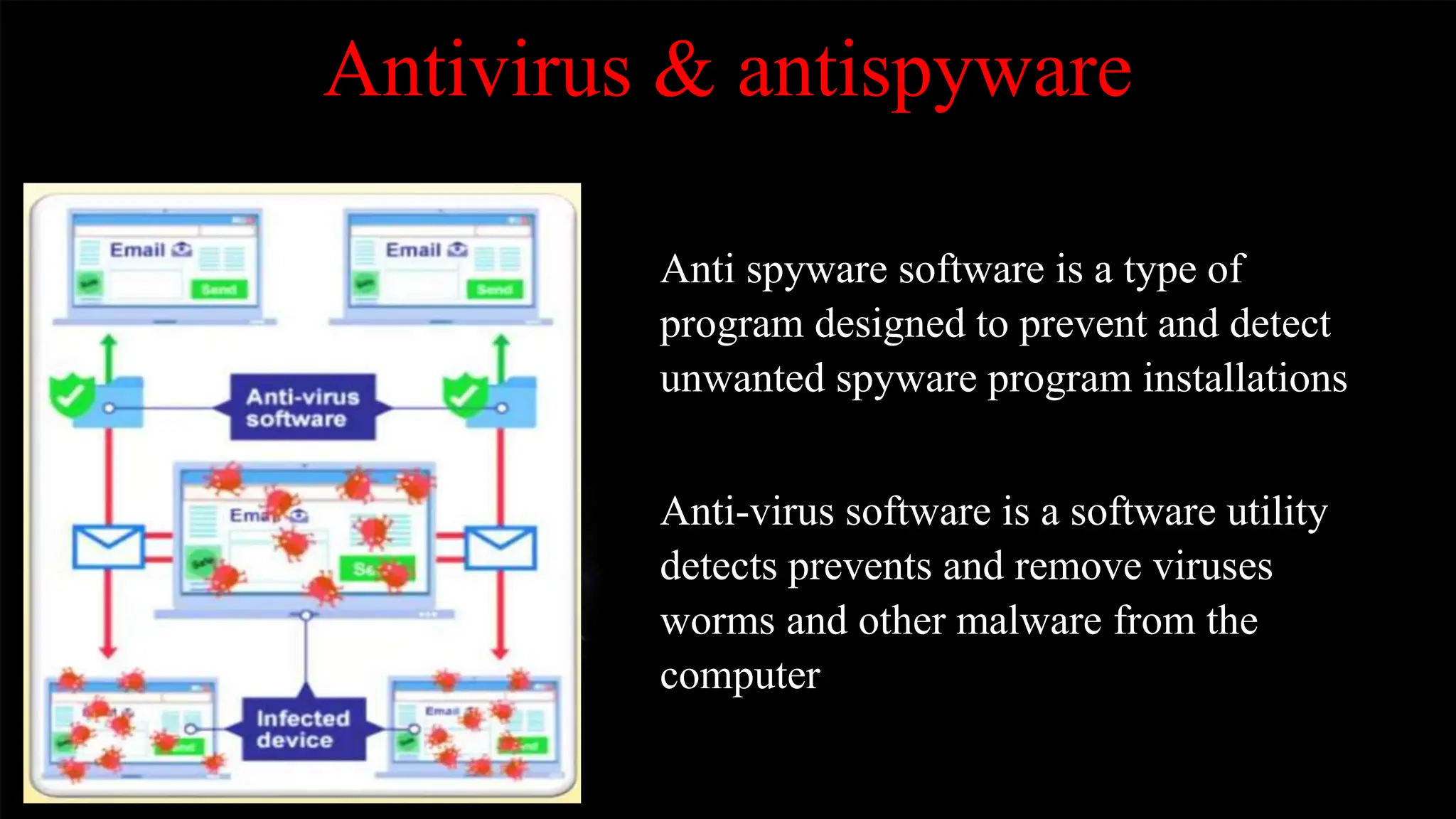
Data protection involves safeguarding important data from corruption, compromise or loss and enabling restoration of data to a functional state. Key methods of data protection include encryption, SSL, firewalls, antivirus software, and regular password changes. Privacy deals with controlling what personal data is shared with third parties and is protected by general and specific privacy laws regulating areas like communications, finances, health, and online data. Maintaining individual privacy helps limit corporate power over data and respects people's freedom of thought, speech, and activities. Privacy threats include web tracking, data collection, unsecured networks, oversharing on social media, and government surveillance.