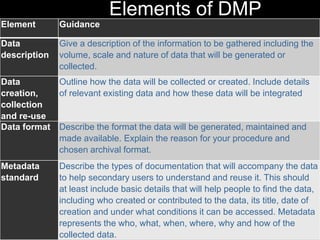
The document outlines an introduction to data management, emphasizing its significance for researchers in terms of data sharing, reuse, and recognition. It defines data management and explains its principles, including data quality, security, and organization. A detailed description of the data management plan (DMP) elements is also provided, covering aspects such as data storage, access, ethics, copyright, and responsibilities.