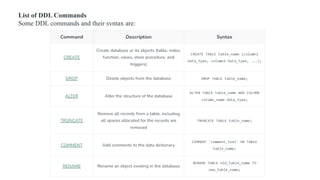
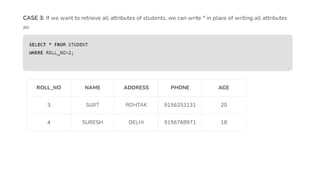
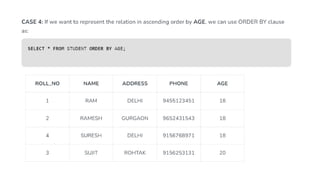
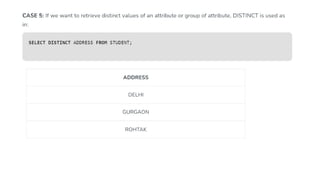
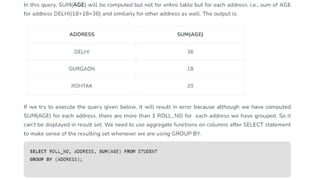
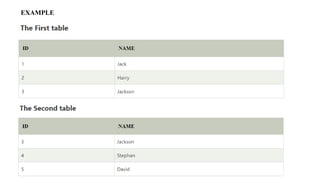
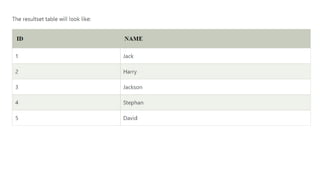
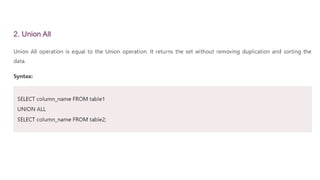
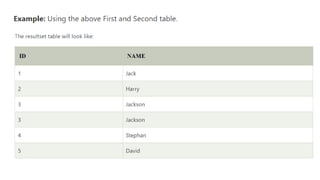
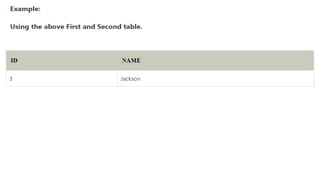
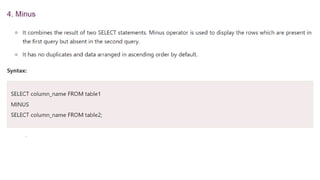
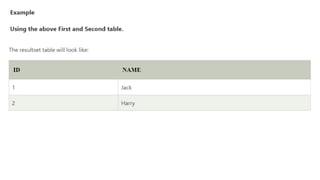
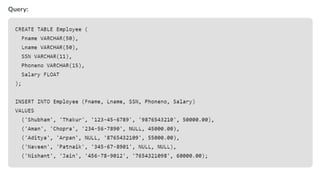
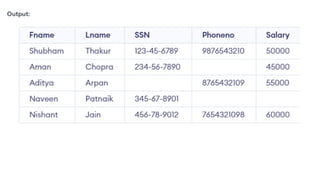
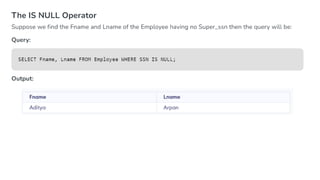
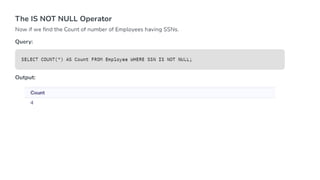
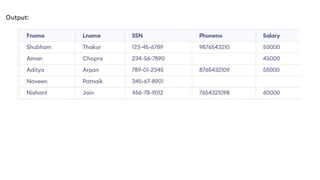
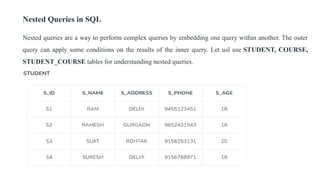
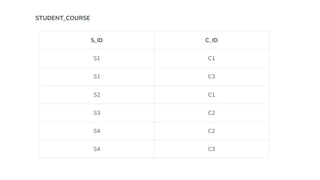
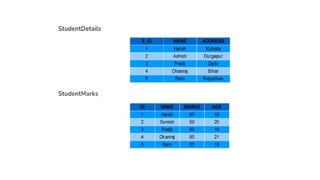
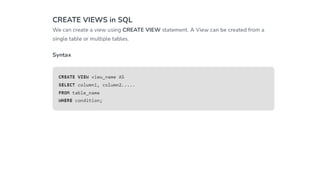
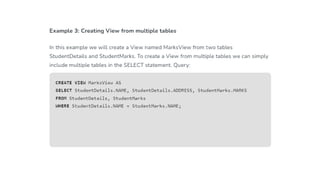
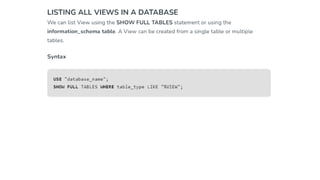
The document covers key components of SQL, including Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), and the structure of SQL queries. It explains set operations, null values, nested subqueries (both independent and co-related), and the concept of views in SQL as virtual tables that do not store data on disk. Examples illustrate how to utilize nested queries effectively for complex data retrieval.