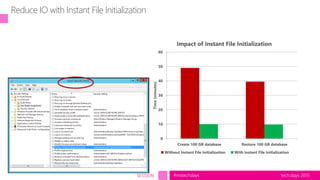
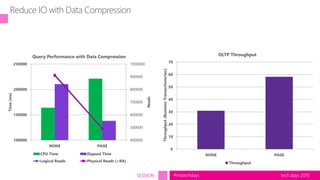
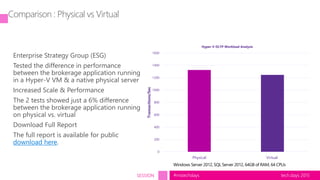
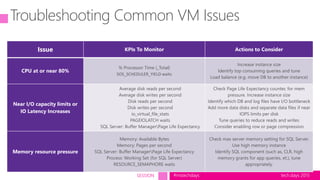
The document outlines a presentation on SQL Server virtualization from the TechDays 2015 event, highlighting the advantages and best practices of virtualizing databases. It covers topics such as performance optimization, resource management, troubleshooting methods, and includes a case study comparing physical and virtual server performance. Recommendations for effective virtualization strategies and monitoring KPIs are also provided.