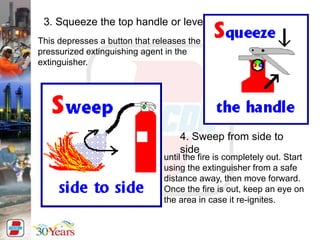
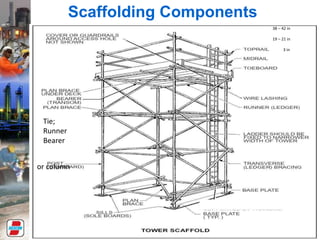
This document provides training instructions for basic health, safety, and environmental procedures for workers during a shutdown at the DAS Island gas plant. The key points covered include:
1. Not bringing ignition sources like lighters or phones, following rules like no smoking or drinking, attending safety training, and knowing emergency contact numbers.
2. Describing the DAS plant operations producing LNG, LPG, and CNG.
3. Outlining the emergency response plan and procedures for responding to incidents like fires, gas leaks, or equipment failures by stopping work, notifying supervisors, and evacuating to muster points.