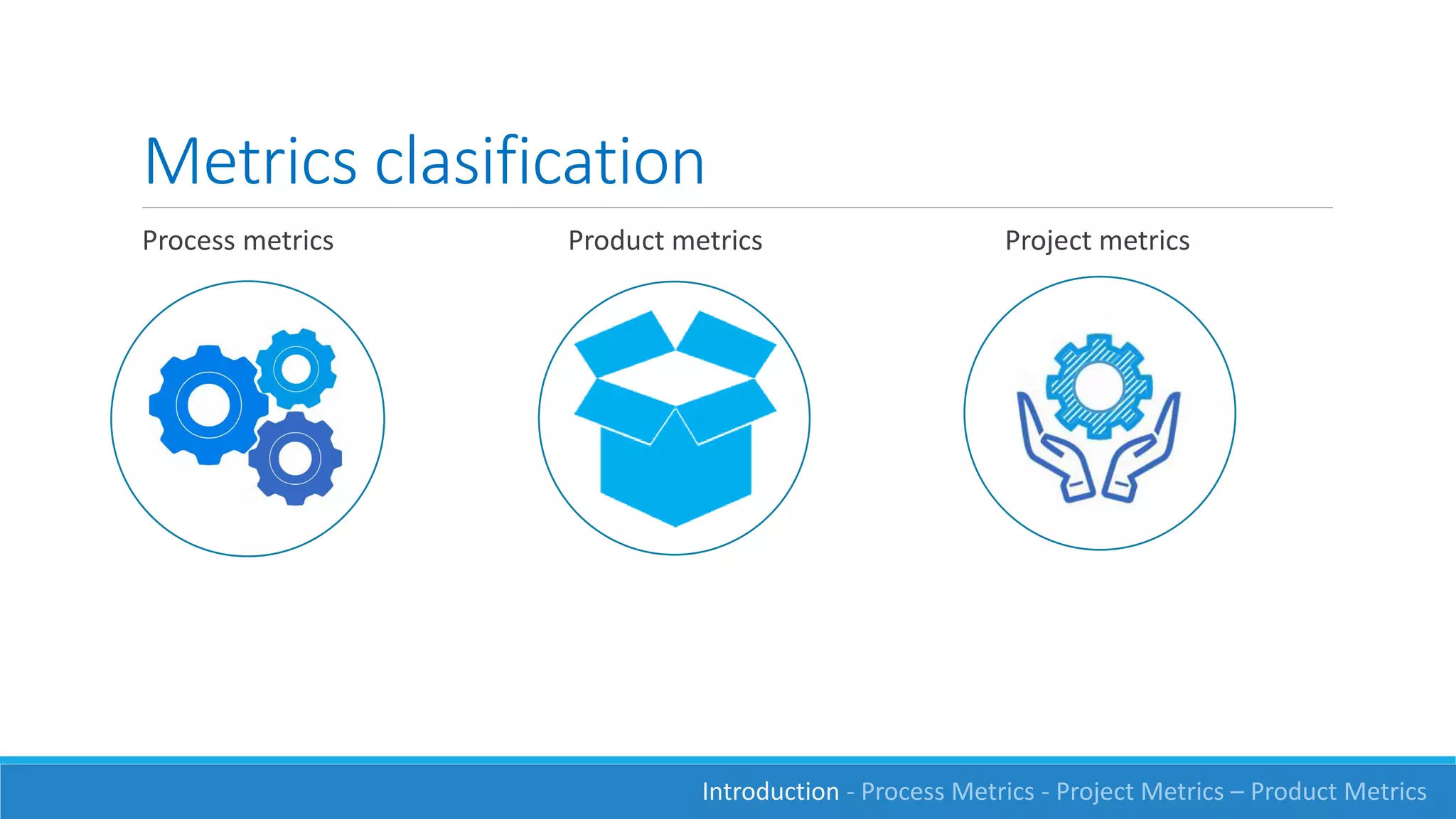
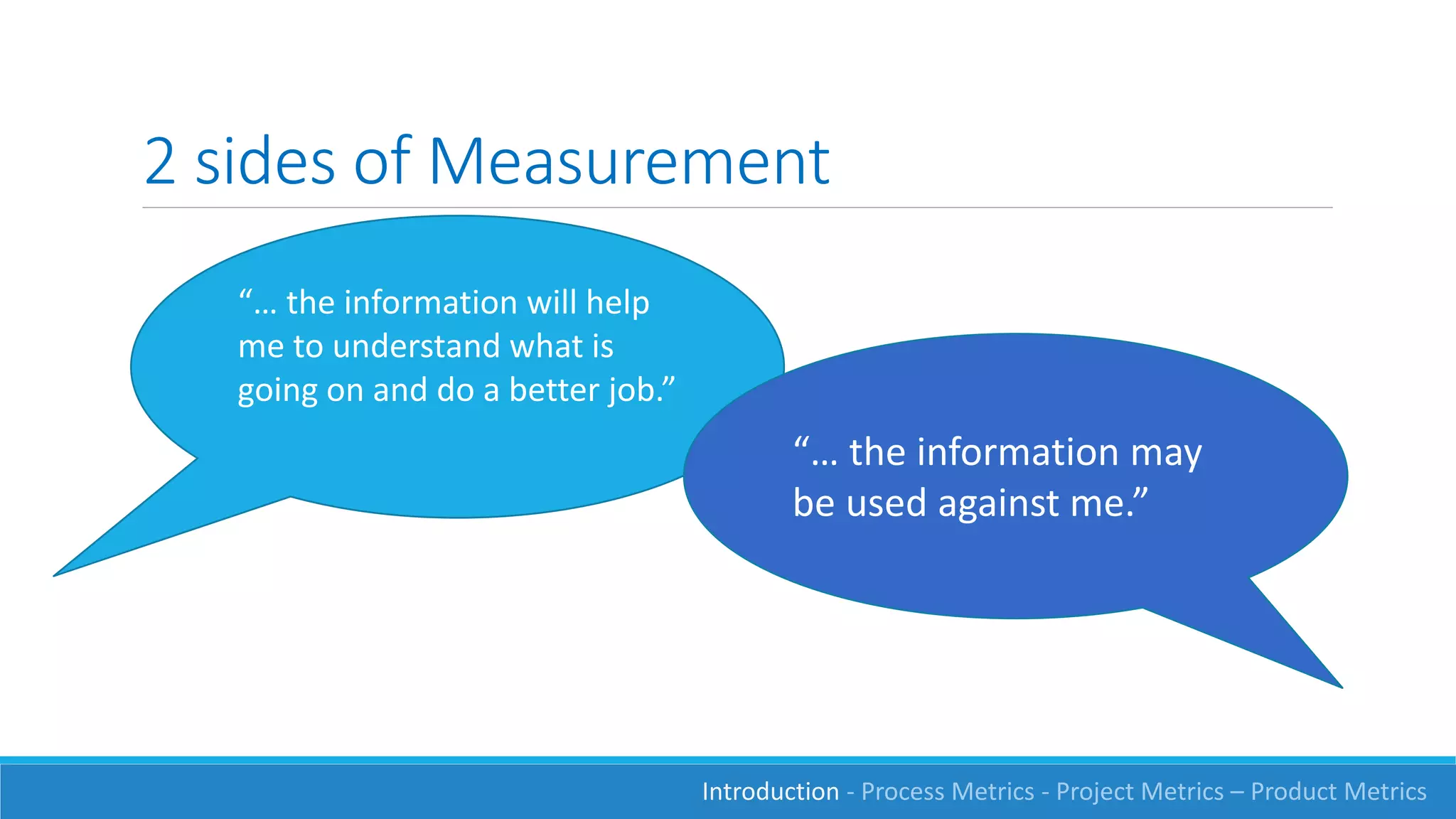
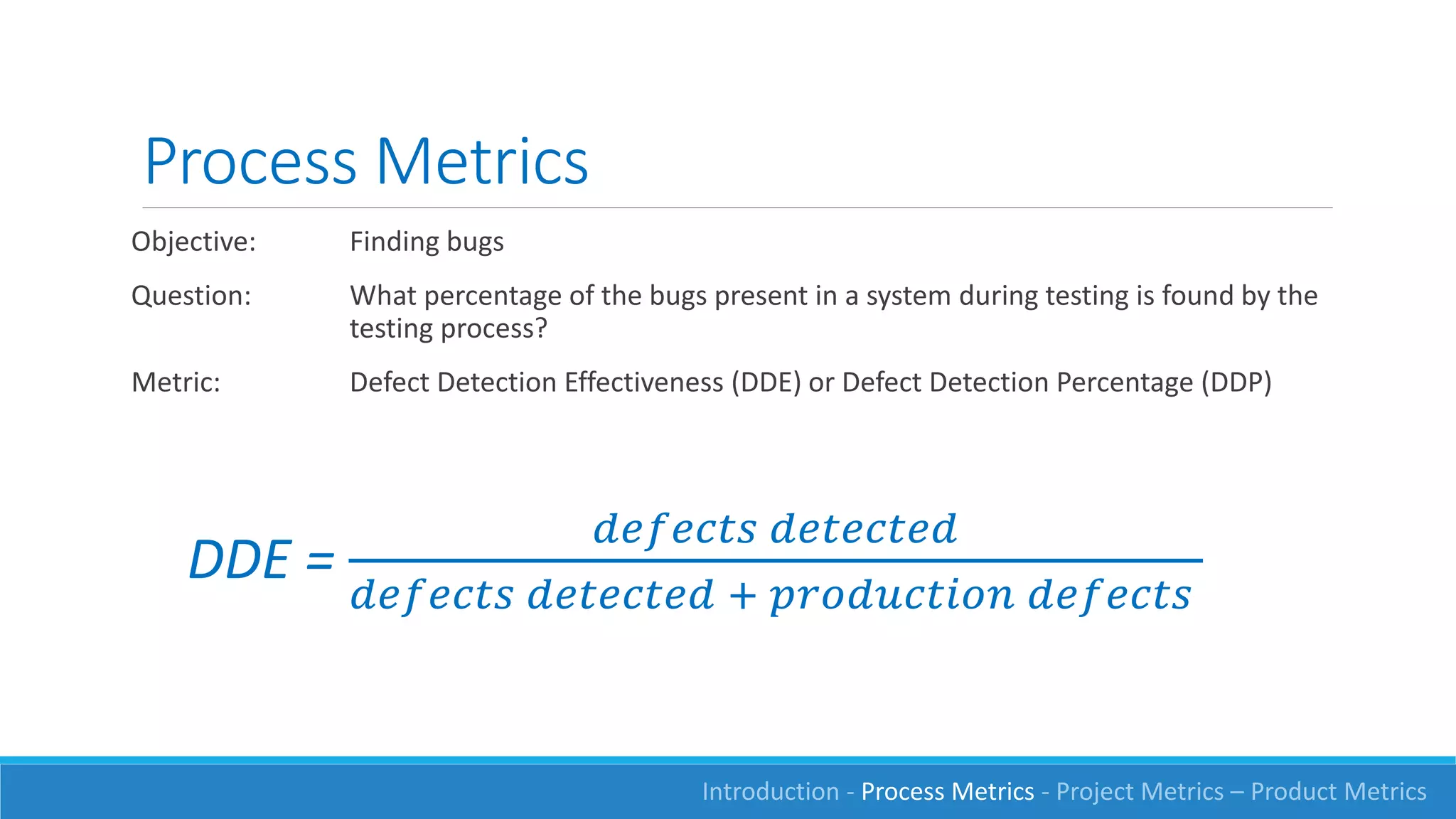
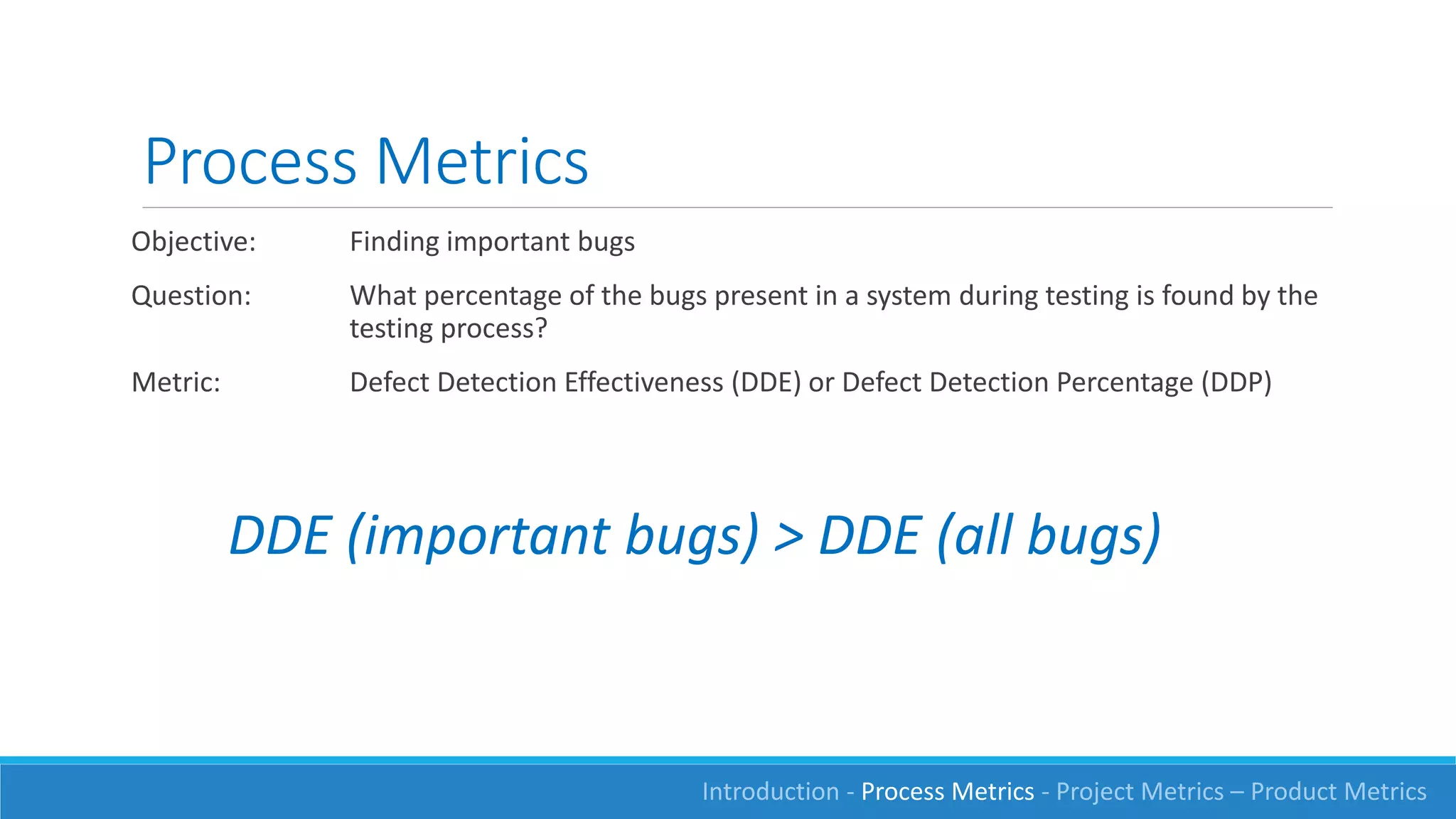
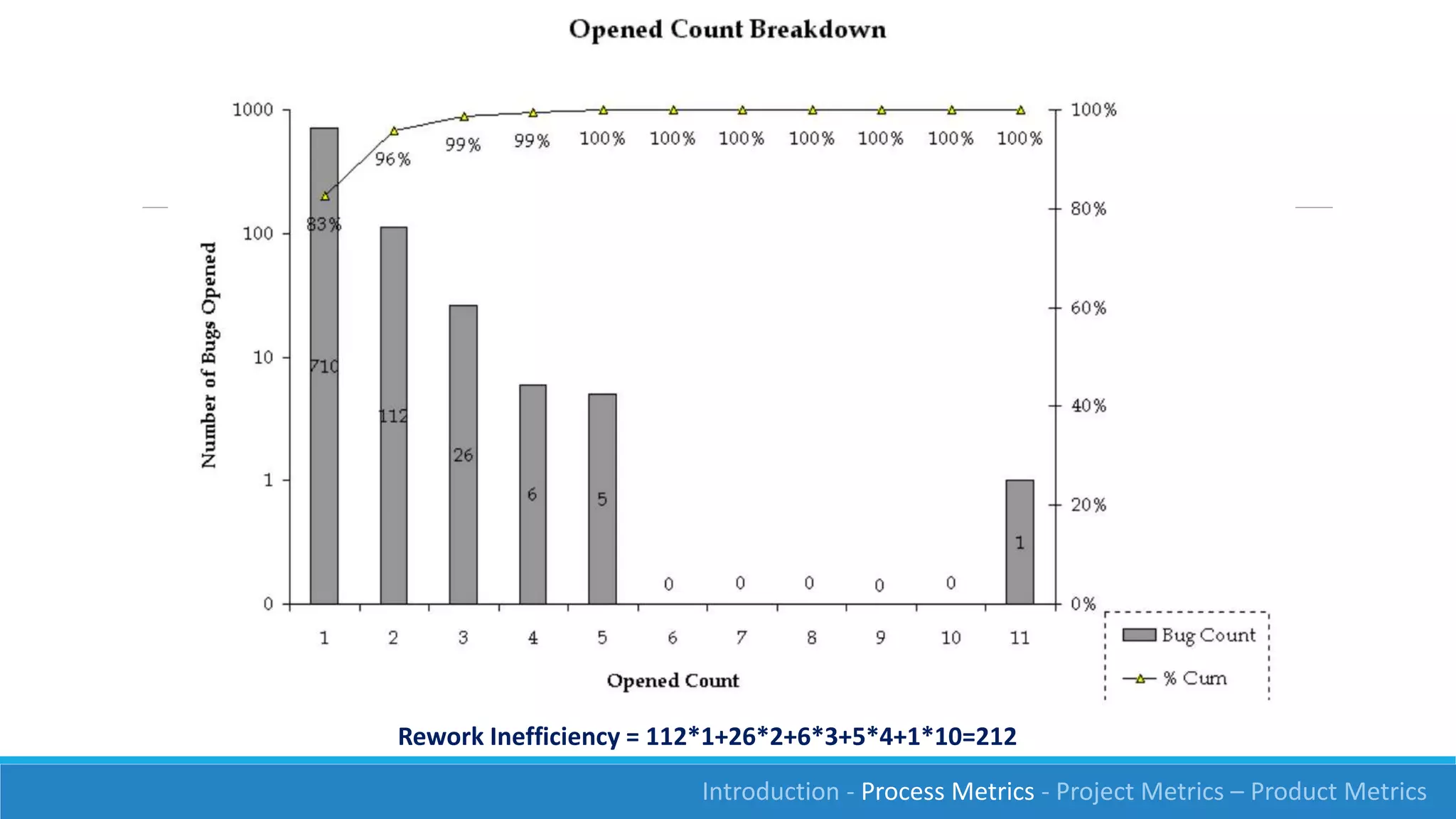
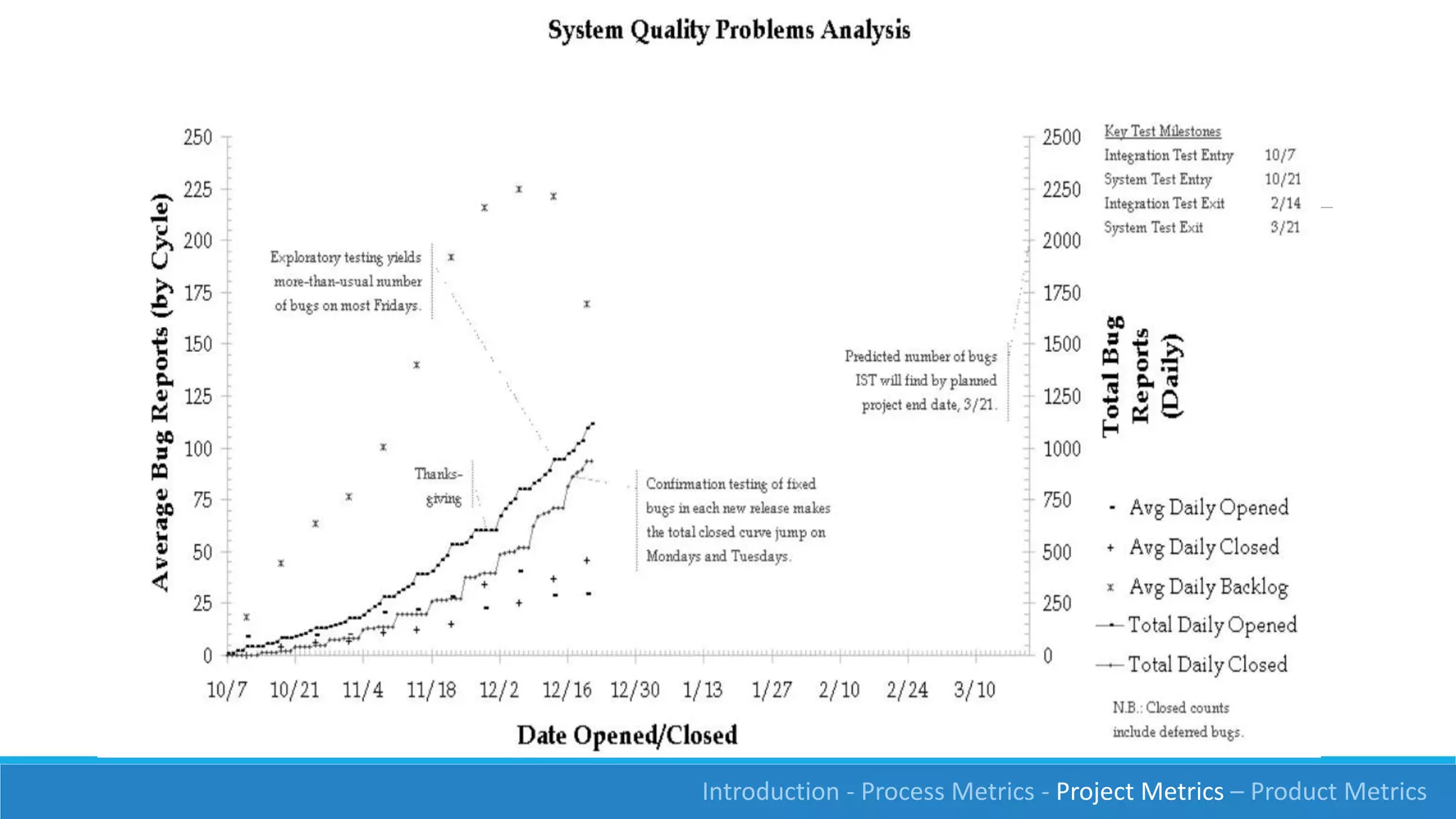
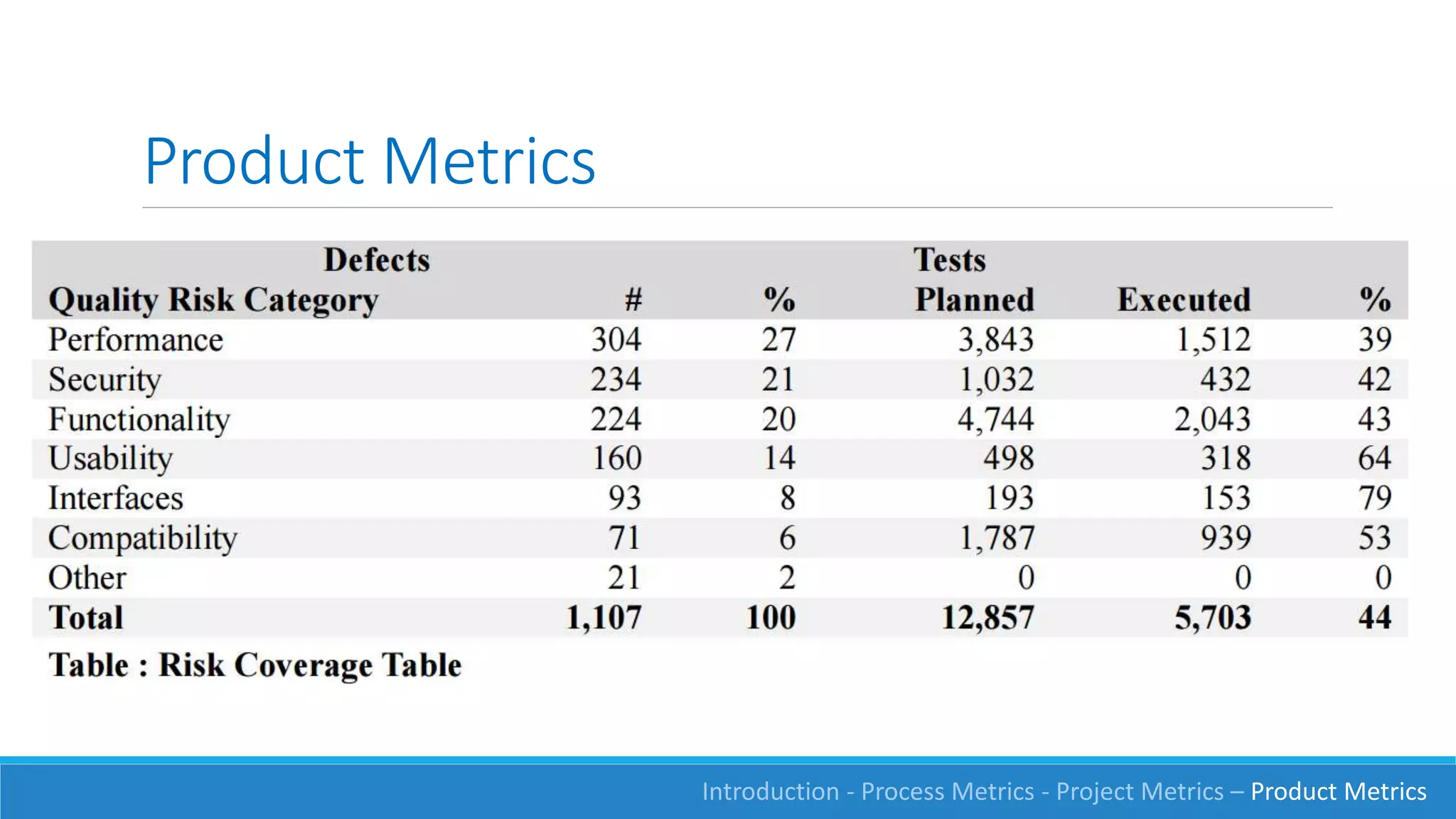
This document discusses software measurement and metrics. It defines software metrics as quantified observations about aspects of software products, processes, or projects. It notes that while it is easy to collect numbers, understanding what they mean is difficult. The document classifies metrics into process, product, and project metrics. It provides examples of metrics that could measure objectives like the effectiveness of the testing process in finding bugs. The document discusses challenges with metrics like the human element and presents a process for defining good metrics. It provides more details on examples of process, project, and product metrics.