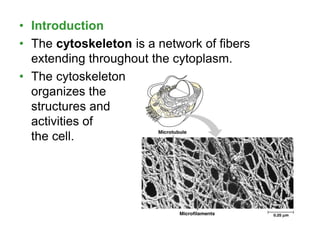
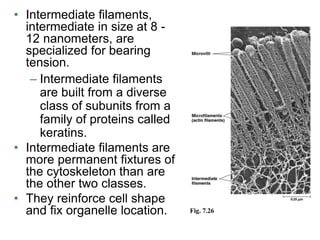
The cytoskeleton provides structural support to the cell and is involved in cell motility and regulation. It is a network of fibers made of three main types: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. Microtubules help maintain cell shape and transport organelles. Microfilaments are involved in cell motility, division, and structure. Intermediate filaments provide structural integrity. The cytoskeleton works with motor proteins to move components within the cell and allow cell movement.