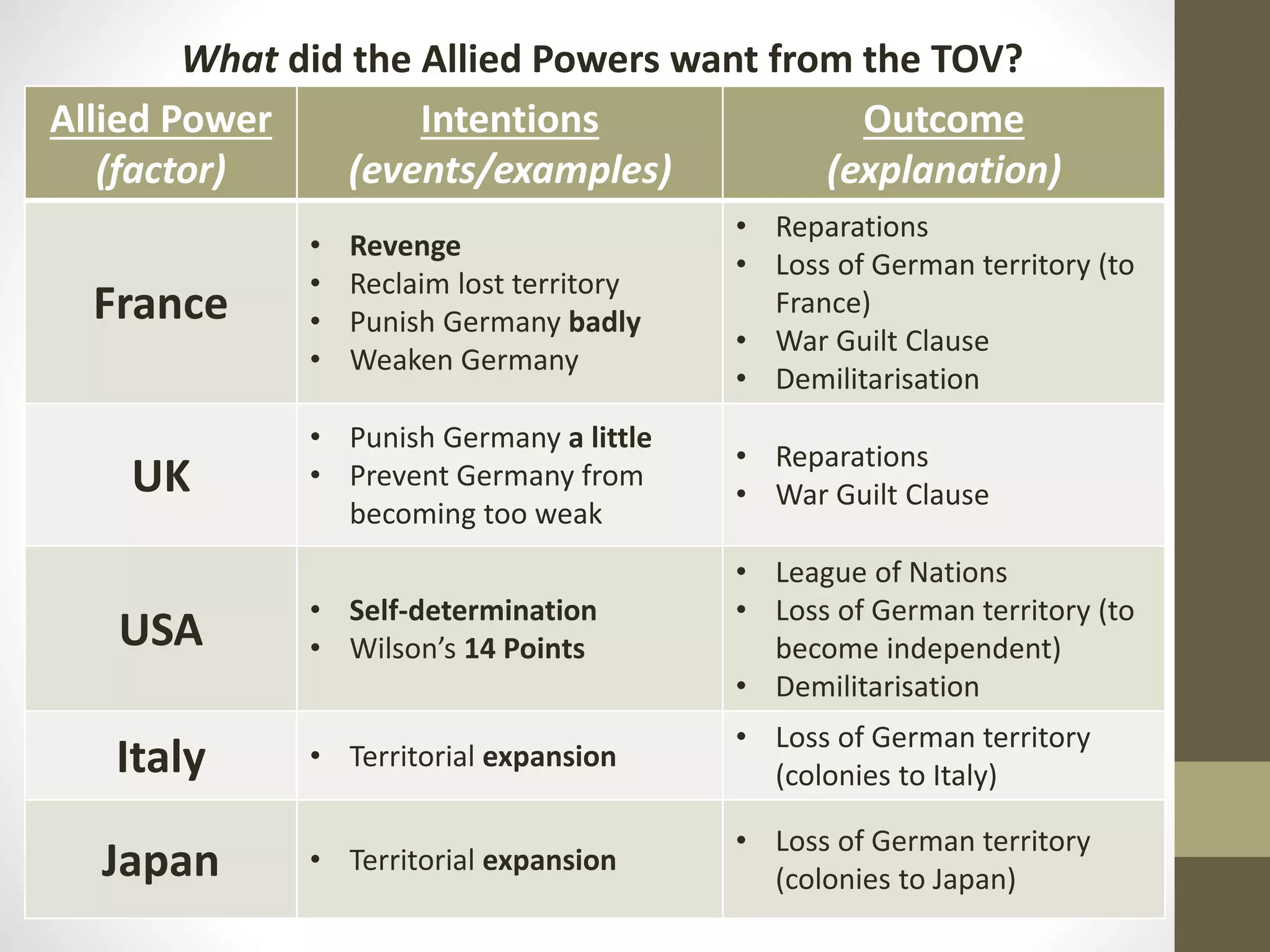
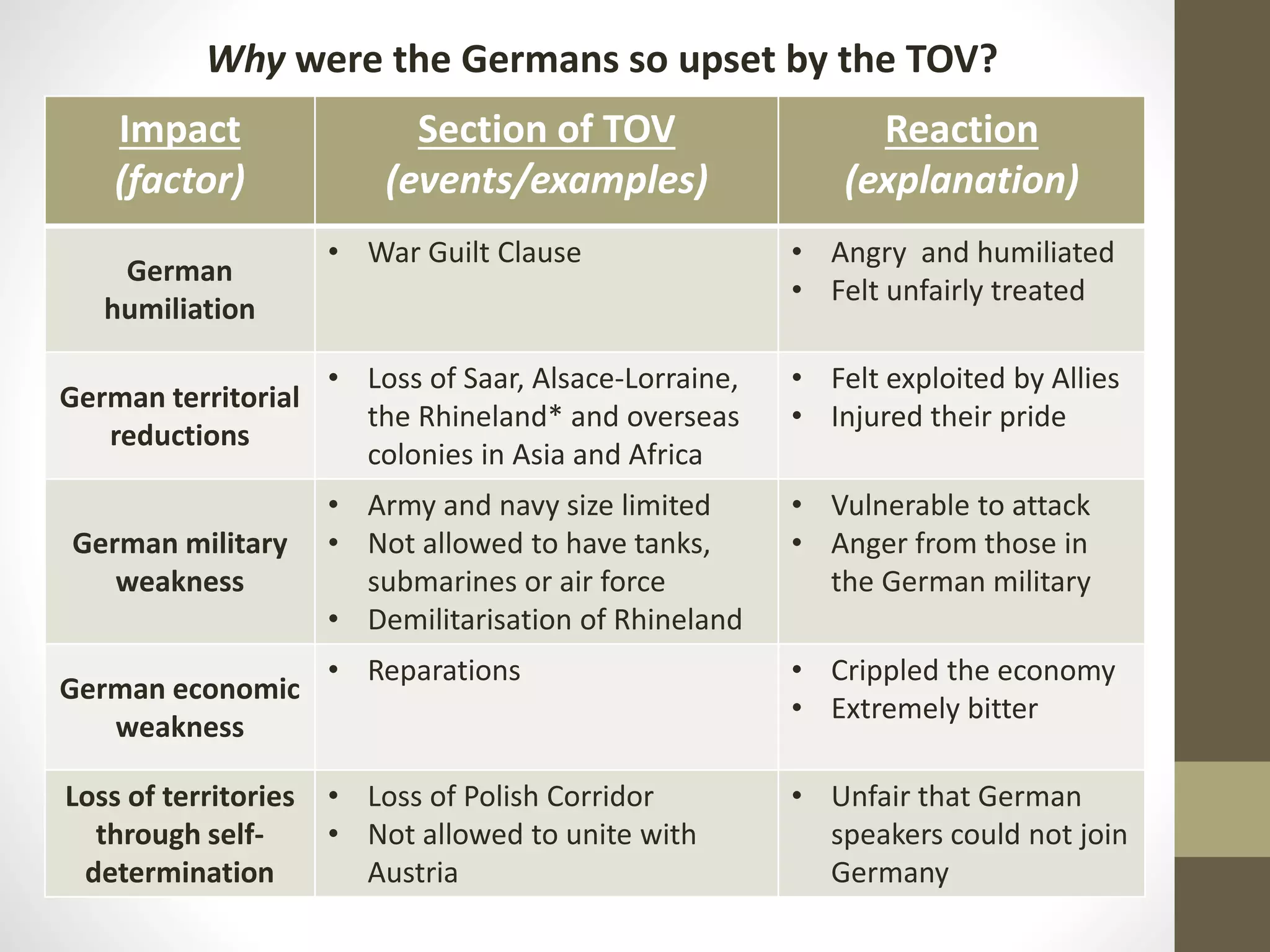
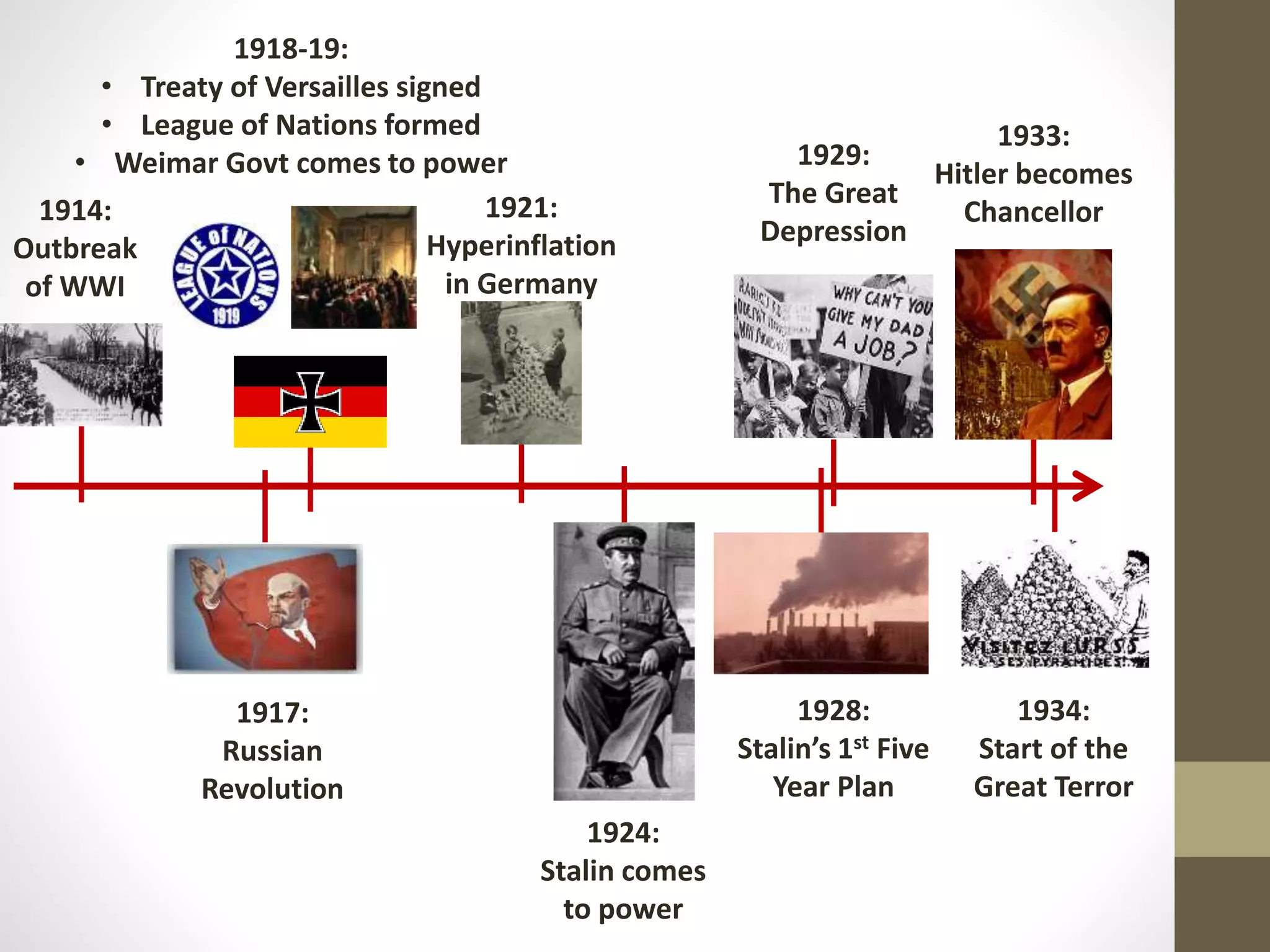
The document outlines the structure and rules for a combined history lecture. It will focus on developing source-based skills like inference, comparison, and evaluating reliability through examples from the Treaty of Versailles and League of Nations. Students are told to understand rather than copy material and that questions will only be taken at set times during the lecture.





















![SEQ – Quick Recap
History
8m 2 PEEL paragraphs (NOTE: 2x 8m in MYE)
[12m not tested for MYE]
Social Studies
5m 1 PEEL paragraph
10m 2 PEEL paragraph + evaluation (2m)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/combinedclasslecture-150504023858-conversion-gate01/75/CWSS-Sec-3E-CHUM-Combined-Class-Lecture-22-2048.jpg)