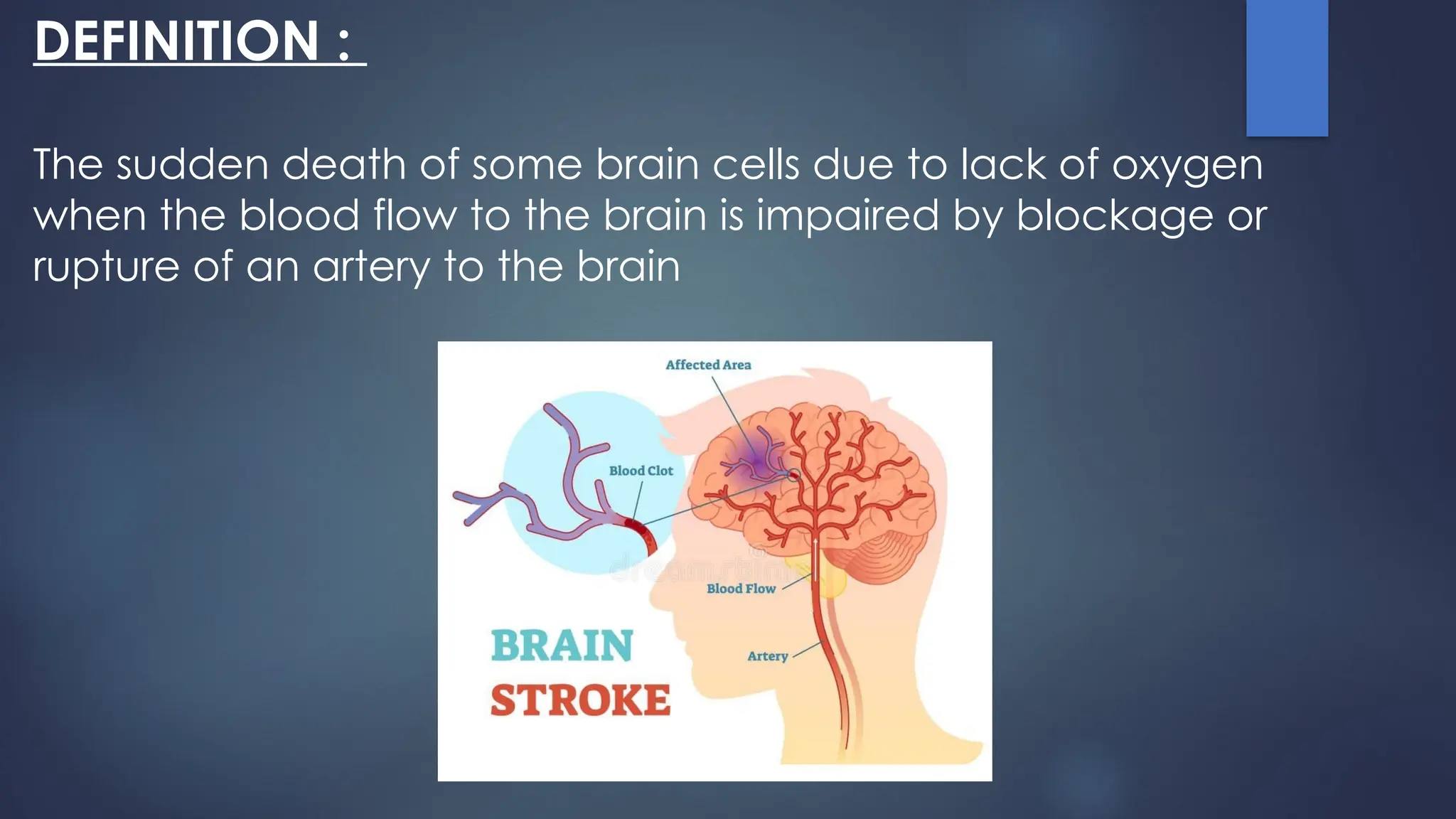
The document discusses cerebrovascular accidents, commonly known as strokes, which involve the sudden death of brain cells due to impaired blood flow. Key causes include transient ischemic attacks, cerebral thrombosis, embolism, and hemorrhage, with various modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors identified. Diagnosis and management strategies are outlined, including medical and surgical approaches to restore blood flow to the brain.



![RISK FACTORS:
MODIFIBALE RISK FACTORS
• Hypertension
• Smoking
• Diabetes
• High cholesterol
• Obesity
• Physical inactivity
• Unhealthy diet
• Previous TIA
• Heart disease
NON-MODIFIBALE RISK FACTORS
• Age
• Gender[men have higher
risk]
• Family history
• Race](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strokeorcva-240903141316-6c7a9266/75/CVA-OR-STROKE-5-2048.jpg)



![FRONTAL LOBE
• Weakness or paralysis on
the opposite side of the
body
• Difficulty with speech
• Problem with decision
making & planning
TEMPORAL LOBE
• Difficulty understanding
spoken/written words
• Loss of memory
• Hearing changes
• Trouble recognizing objects /
faces
PARIETAL LOBE
• Loss of sensation
• Loss of co- ordination
• Balance problems
OCCIPETAL LOBE
• Loss of vision
• Blurred vision
• Diplopia
• Problem with visual
perception
BRAIN STEM
• Problem with vital
functions [HR, breathing,
BP]
• Dysphagia
• Dysarthria
CEREBELLUM
• Poor co-ordination
• Unsteady gait
• Tremors
• Fine motor issues](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strokeorcva-240903141316-6c7a9266/75/CVA-OR-STROKE-9-2048.jpg)




