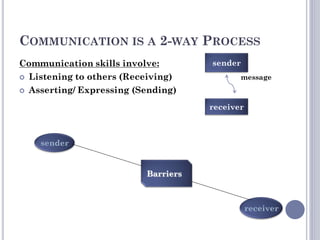
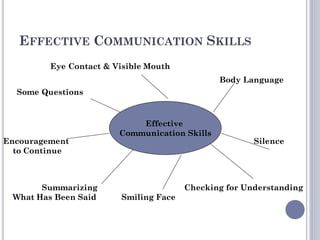
The document outlines essential customer service skills, emphasizing effective communication, active listening, and the importance of being attentive and courteous to customers. It provides strategies for addressing different types of customers, including techniques for handling talkative, suspicious, and angry individuals. Additionally, it stresses the need for knowledge about the organization and proactive planning for improved service.