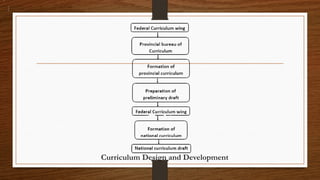
The document provides an overview of the curriculum development process in Pakistan, detailing its objectives, characteristics, and differences among curriculum, syllabus, courses, and educational programs. Key responsibilities include the federal Ministry of Education and provincial curriculum centers, which oversee the development of curriculum standards, syllabi, textbooks, and teacher training. It also highlights pitfalls such as the lack of subject area experts and the disconnect between written curriculum and actual classroom implementation.