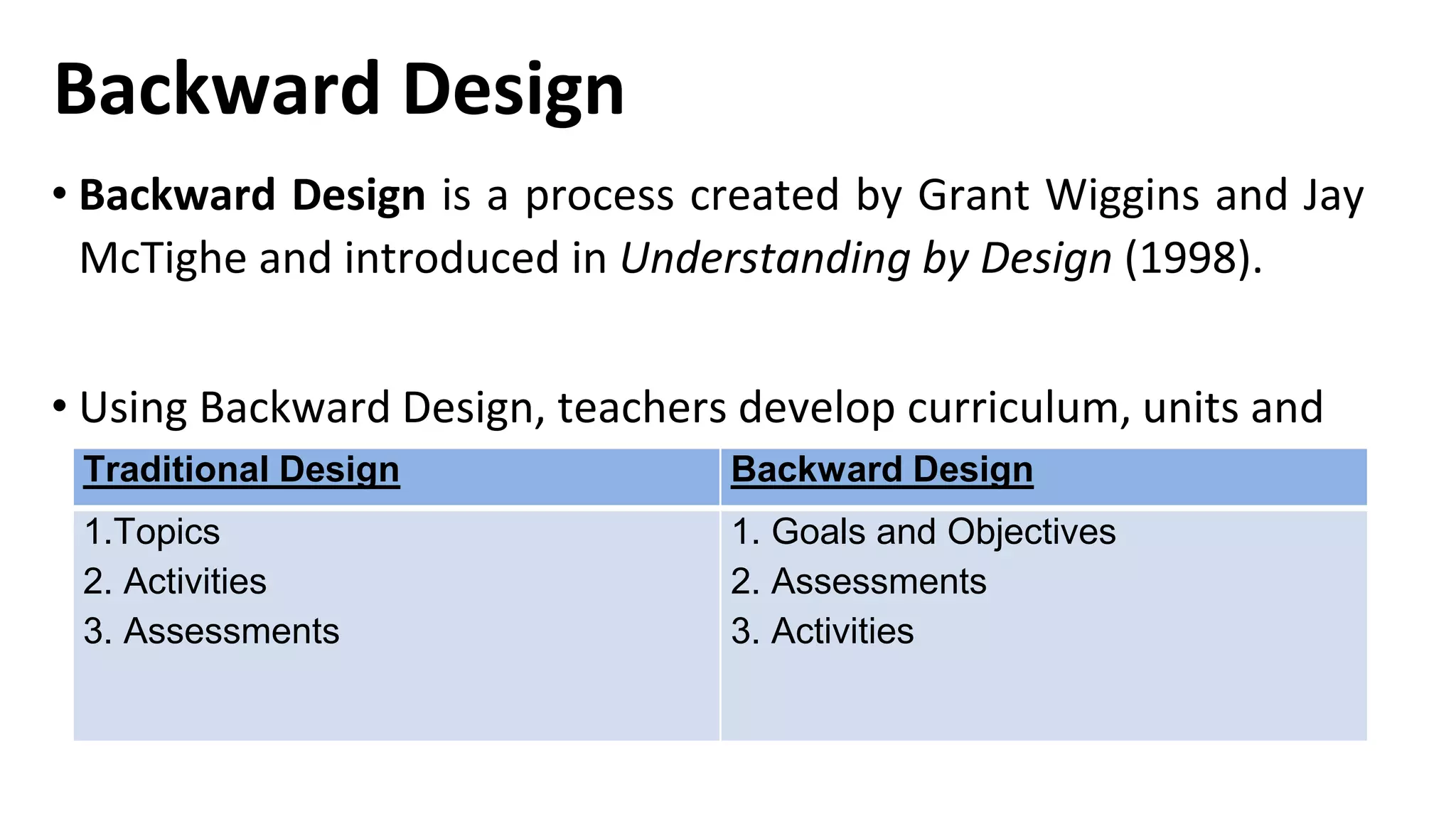
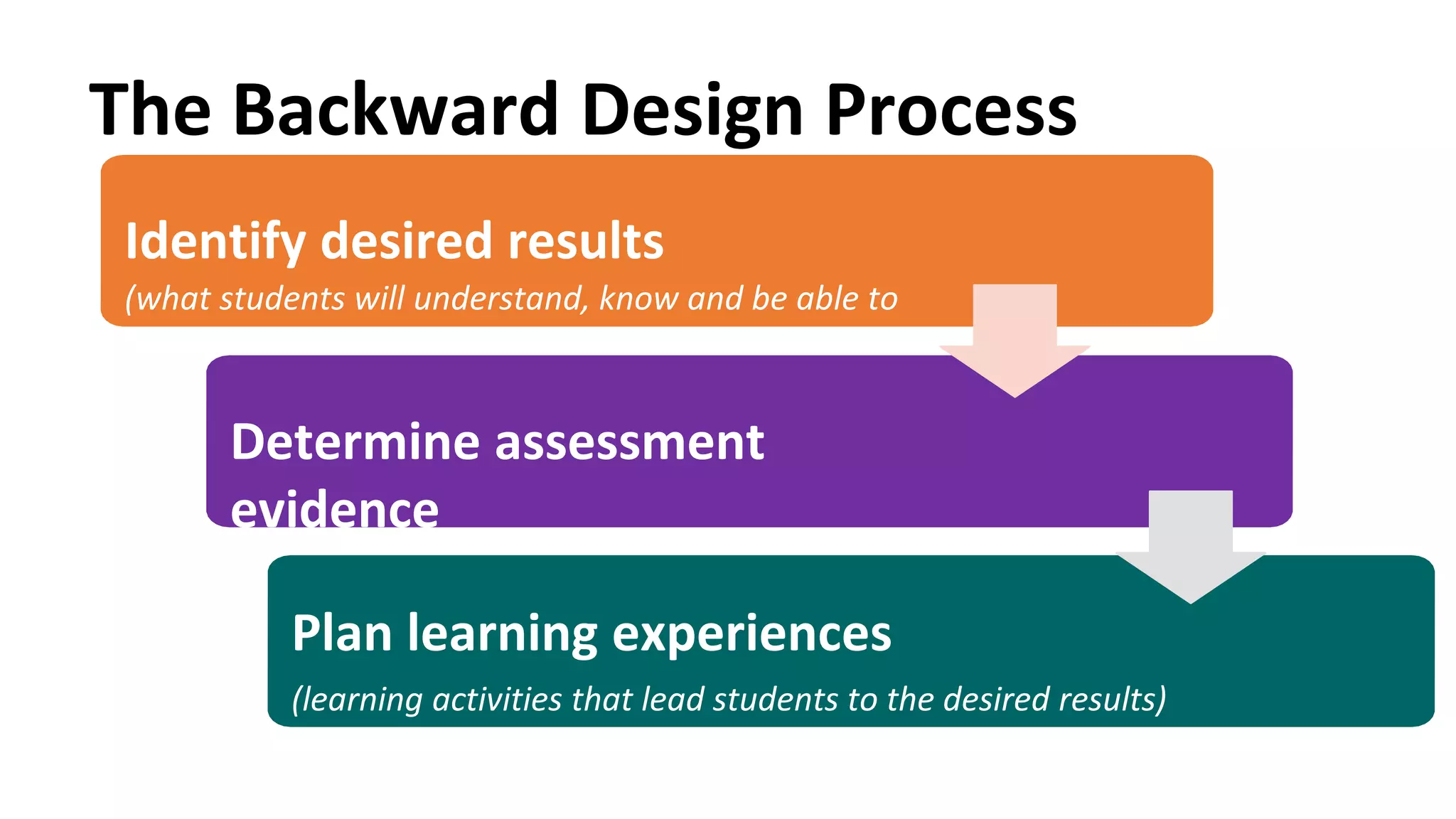
The document discusses the backward design process for curriculum planning. It involves 3 key steps: 1) Identifying desired learning outcomes and goals, 2) Determining assessments to measure student learning, and 3) Planning learning activities that will help students achieve the outcomes. Backward design puts assessment before instruction so teachers can work backwards from the desired results. The document also provides examples of standards and frameworks that can help teachers establish goals and assessments, and defines presentational communication as involving learners informing, explaining, persuading, or narrating for a specified audience using appropriate media.