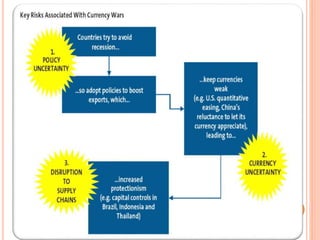
Currency wars occur when countries deliberately devalue their currencies to gain a competitive advantage in international trade and boost exports. There have been several periods of currency wars throughout history. Most notably in the 1930s during the Great Depression when countries abandoned the gold standard and pursued policies of competitive devaluation, dubbed "beggar thy neighbor". More recently, after the 2008 financial crisis, export-focused countries like China devalued their currencies, which led other nations like the US and UK to also devalue their currencies to remain competitive in export markets. Currently, the European Central Bank has launched a large quantitative easing program while China and other Asian countries have also devalued currencies, risking another wave of global currency wars.