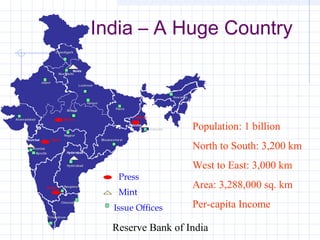
The document summarizes the distribution of currency notes and coins across India by the Reserve Bank of India. It notes that India has a large population spread across a vast geographic area. The RBI distributes currency to banks through a network of issue offices and currency chests. Notes and coins are produced by mints and printing presses then transported through RBI offices, chest branches, and commercial banks to the public. The RBI faces challenges in efficiently managing the large volume and wide distribution of currency throughout India.