1) Field observations revealed an irregular elevation profile and the presence of a deep, V-shaped ravine extending from the university to the sea, despite the low gradients typical of coastal areas.
2) Layers of alternating sandstone and conglomerate were found, with conglomerate deposits atypical for coastal areas.
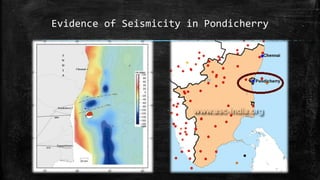
3) Evidence suggests neo-tectonic activity, including a syn-sedimentary uplift allowing conglomerate deposition, followed by erosion forming the ravine during a subsequent uplift. Seismic activity in the region supports the interpretation of reactivated faulting.