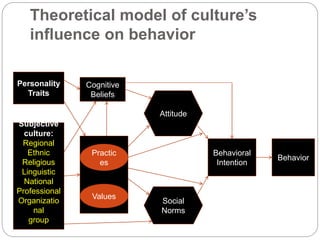
Culture consists of learned beliefs, values, and customs that guide consumer behavior. It is influenced by various subjective factors like personality, practices, values, and social norms. Each individual perceives the world through their own cultural lens.
Elements of culture include language, shelter, clothing, economy, religion, education, values, climate, and government. There are three levels of culture - supranational, national, and group. Culture satisfies needs like food, clothing, and helps distinguish needs from luxuries.
Culture is learned through enculturation, acculturation, language, symbols, and rituals. Rituals are associated with products and extend through life events. Culture is shared and transmitted between generations and institutions.