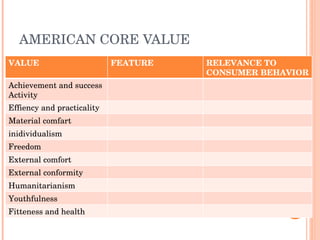
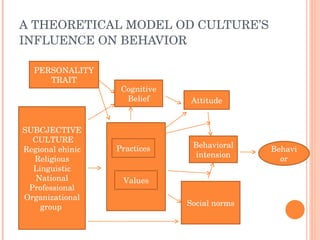
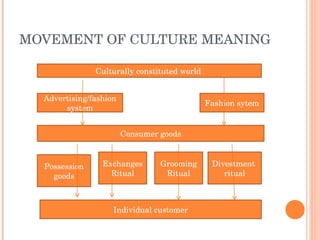
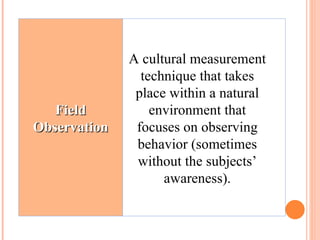
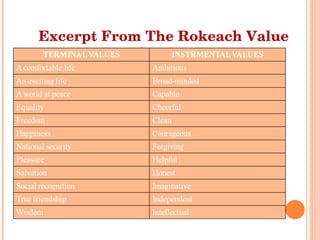
Culture is defined as the learned beliefs, values, and customs that influence consumer behavior within a society. There are three levels of subjective culture: supranational, national, and group. Personal traits and cultural influences like beliefs and values interact to shape behavioral intentions and actions. Culture is learned through both formal and informal means like education, advertising, and social interactions. Cultural symbols and meanings can spread and change over time through various movements and exchanges between societies.













![VIEWS OF FOREIGN EXPERTS IN THE U.S “ There are no small eggs in America. There are only jumbo, extra large, large, and medium.” “ If you are not aggressive, you’re not noticed.” “ For a foreigner to succeed in the United States… he needs to be more aggressive than in his own culture because Americans expect that.” Americans say “Come on over sometimes,” butforeigners learn (perhaps awkwardly) that this isnot really an invitation. “ Here that [socializing outside the business relationship] is not necessary. You can even do business with someone you do not like.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbb-101019121944-phpapp02/85/consumer-buying-behavior-19-320.jpg)