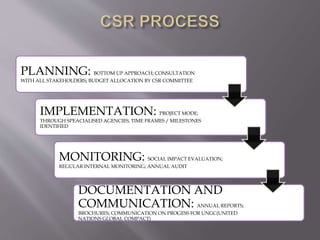
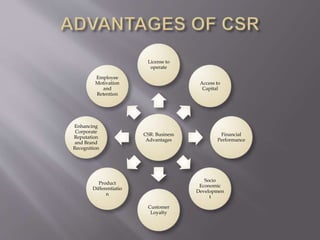
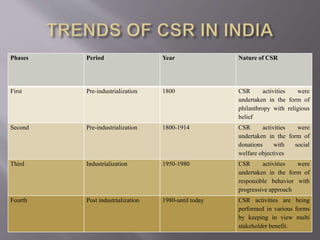
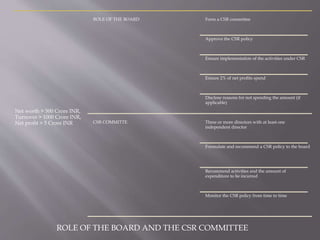
Green technology refers to environmentally friendly inventions that promote energy efficiency, recycling, renewable resources, and health and safety. Examples include ocean cleanup technologies to reduce plastic pollution, solar cells that convert sunlight to electricity, and sustainability experts that partner with companies to embed sustainability into business models. Corporate social responsibility involves companies assessing their impact on society and stakeholders such as customers, suppliers, communities, employees, and the environment. It aims to ensure companies not only comply with laws but also respect marginalized groups and environmental growth.