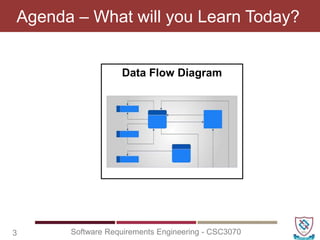
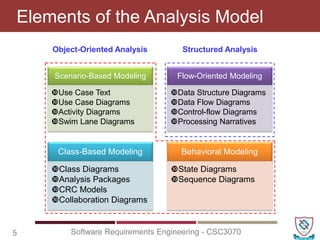
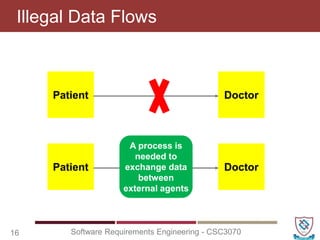
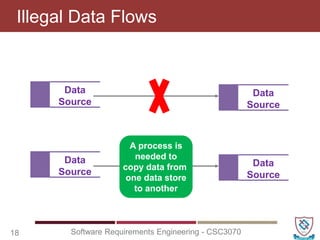
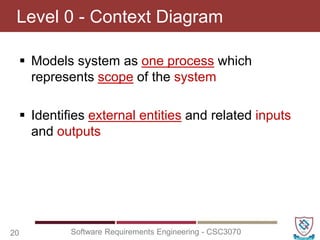
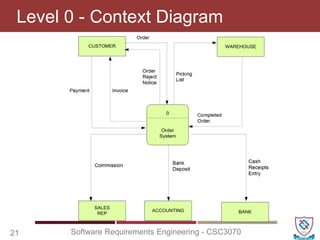
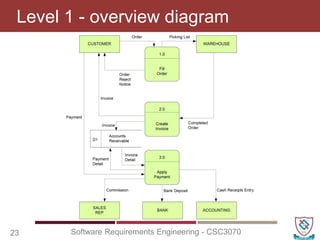
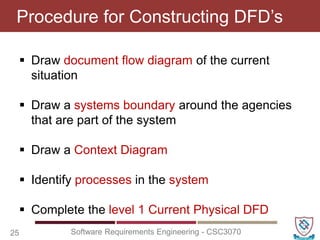
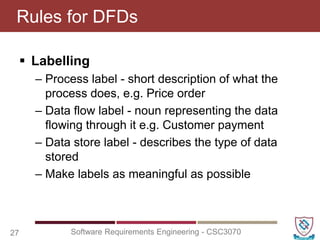
The document covers key concepts in software requirements engineering, specifically focusing on data flow diagrams (DFDs) and their importance in modeling systems. It details the four main elements of DFDs: process, data store, data flow, and external entity, along with the procedure for constructing DFDs and the significance of different levels of diagrams. Additionally, it discusses rules for effective DFD creation, ensuring clarity and proper representation of data flow within systems.