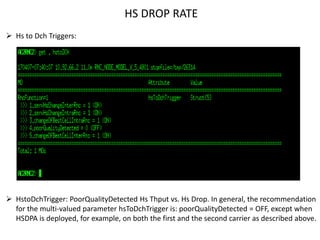
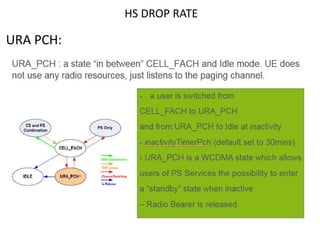
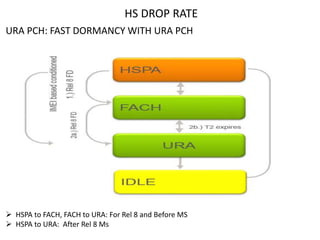
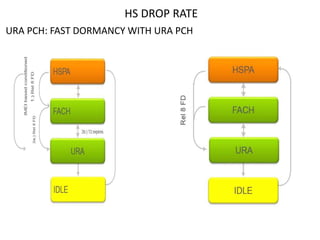
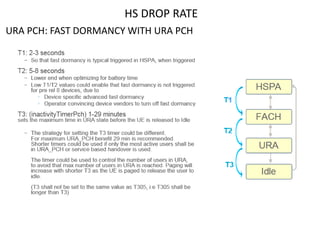
The document discusses various strategies and parameters for optimizing HS and speech call drops in a mobile network. It analyzes call drop reasons like congestion, soft handover failures, missing neighbors, and synchronization issues. It provides guidance on improving neighbor planning, resource utilization, interference reduction features, HS mobility parameters, load balancing between carriers, and URA PCH configuration for fast dormancy. The optimization strategies aim to reduce specific counter metrics for different call drop causes and improve key performance indicators for HS connections.