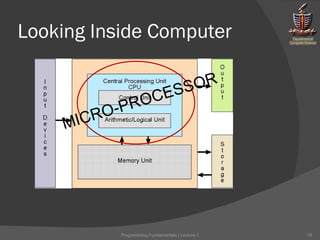
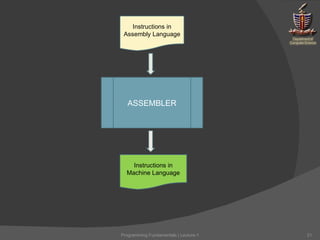
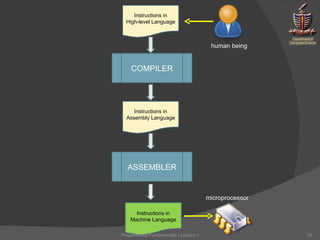
The document discusses key concepts in computer programming and fundamentals. It emphasizes that attitude and commitment are important for students. It also stresses avoiding plagiarism and being prepared for a fast pace. The document explains that programming fundamentals are crucial for the degree and future career. It defines computer programming as providing instructions to computers through languages like assembly and high-level languages, which are translated to machine code by assemblers and compilers. Practice is emphasized for performing well.