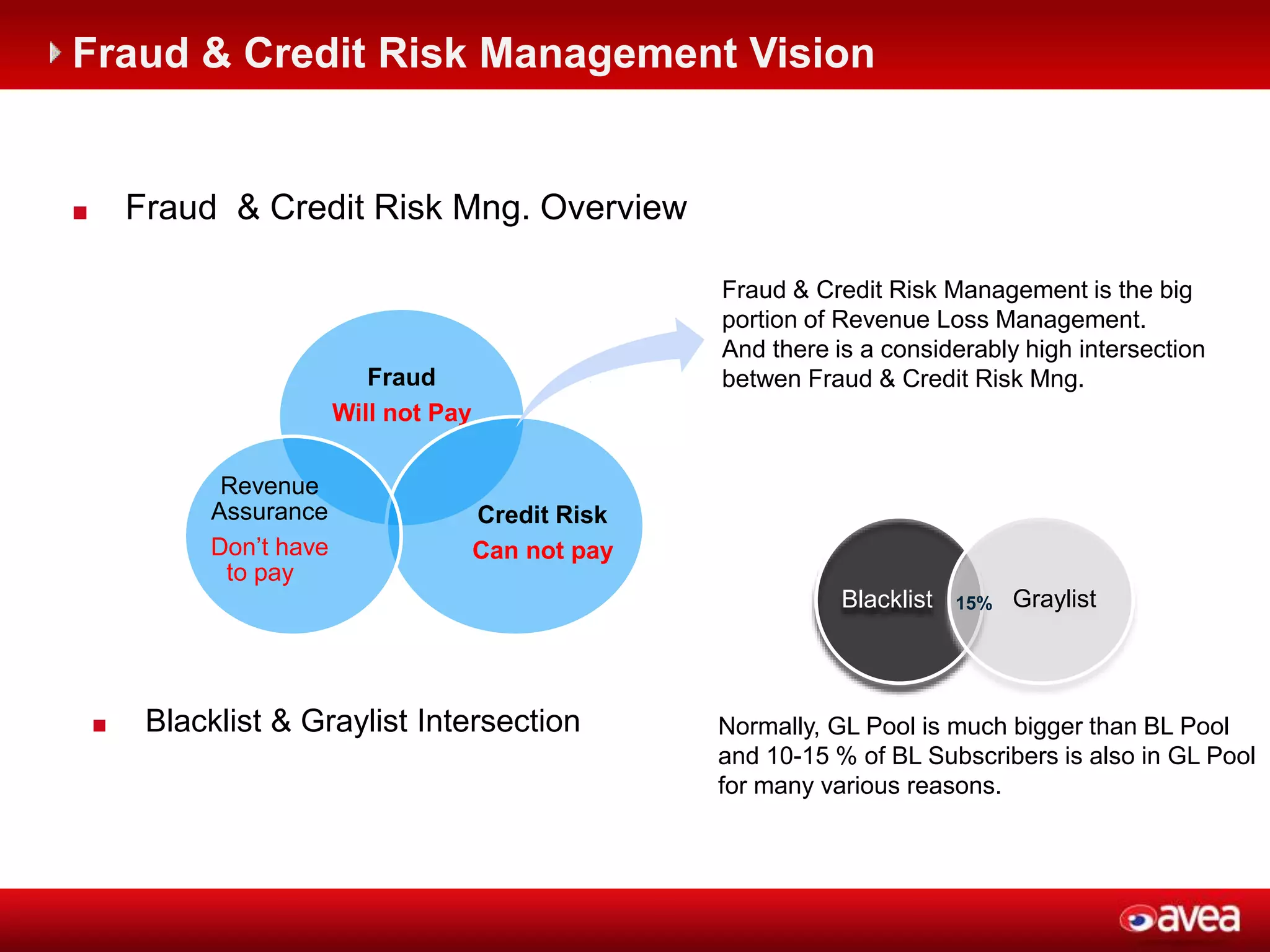
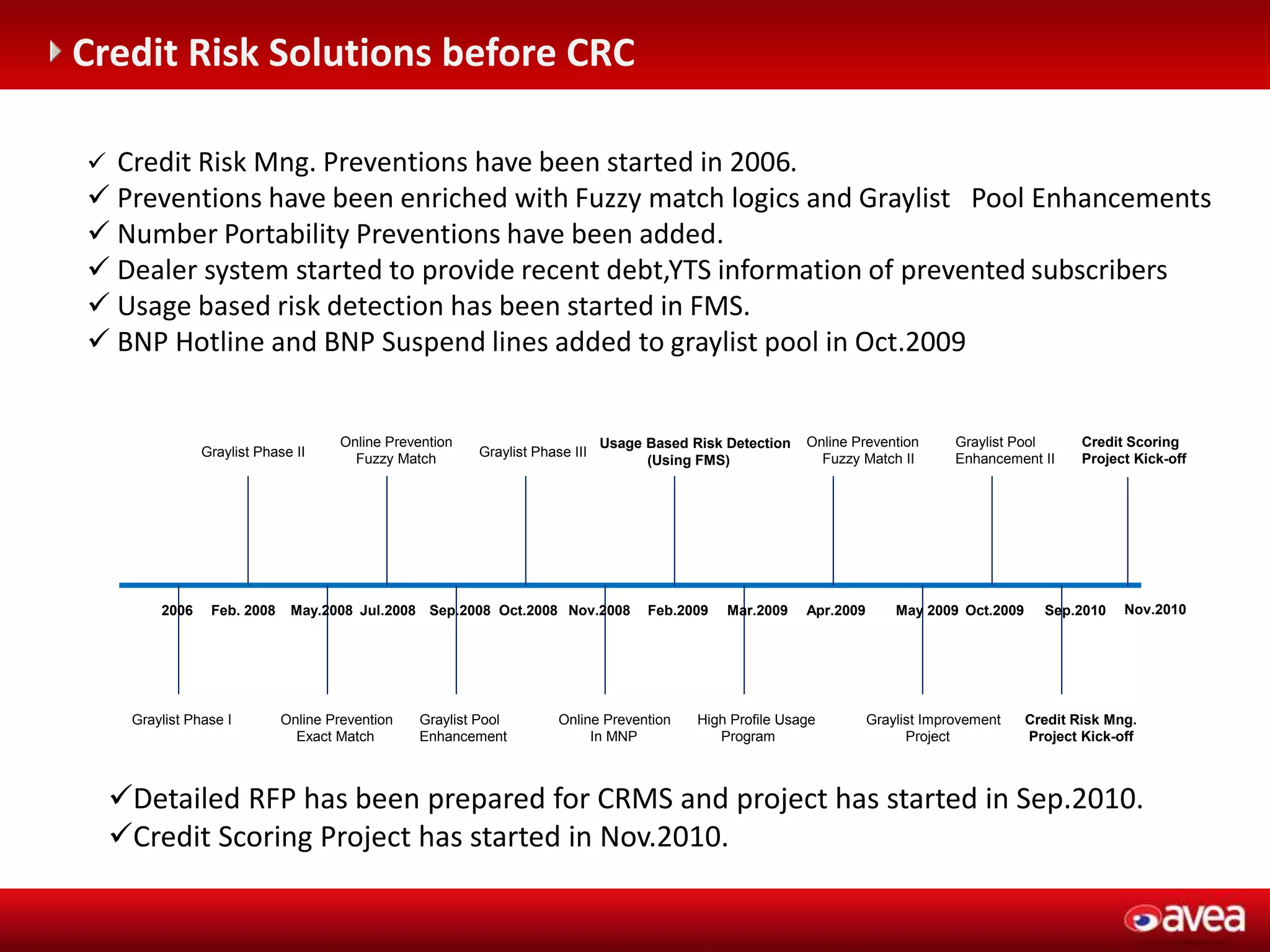
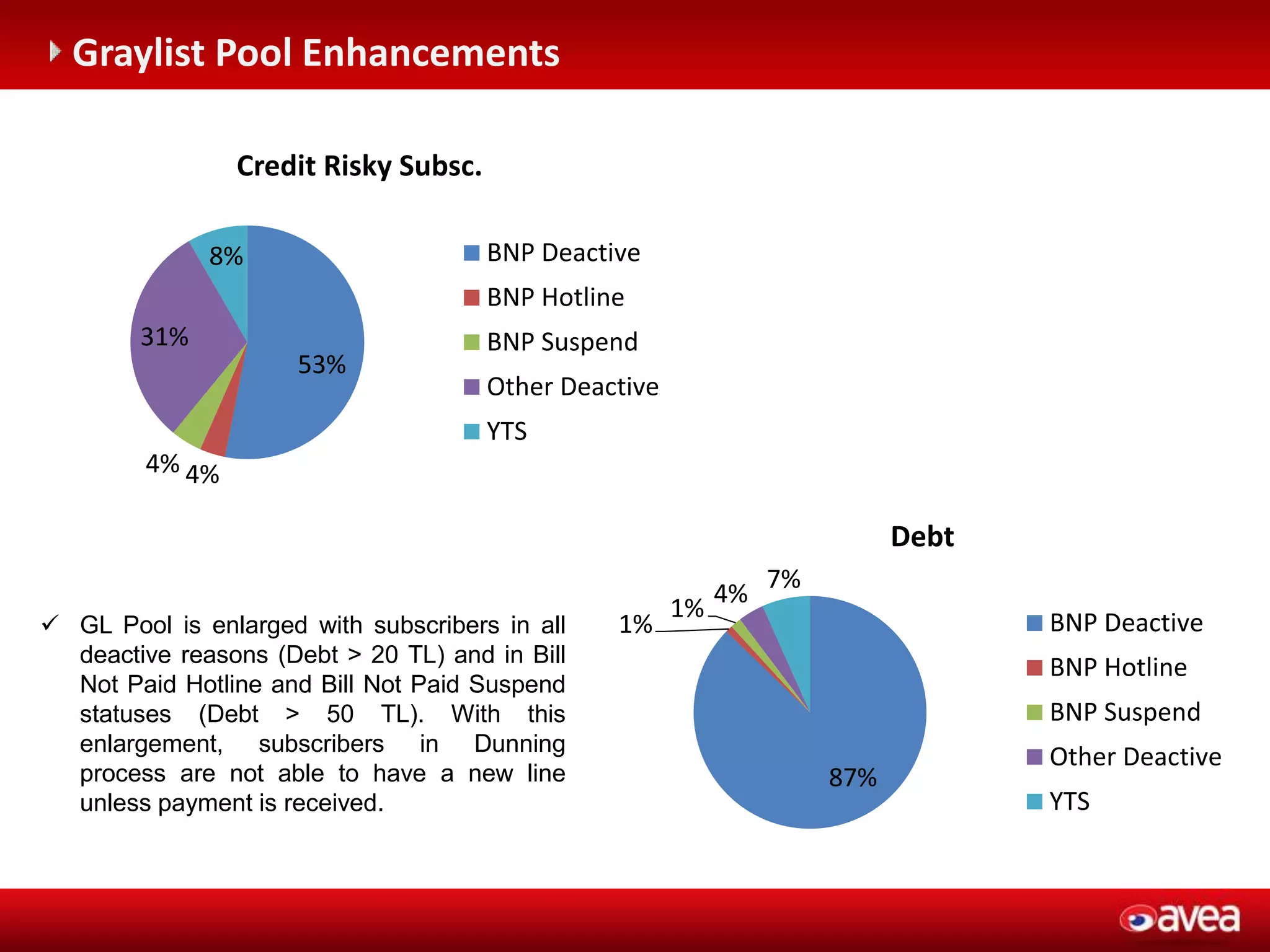
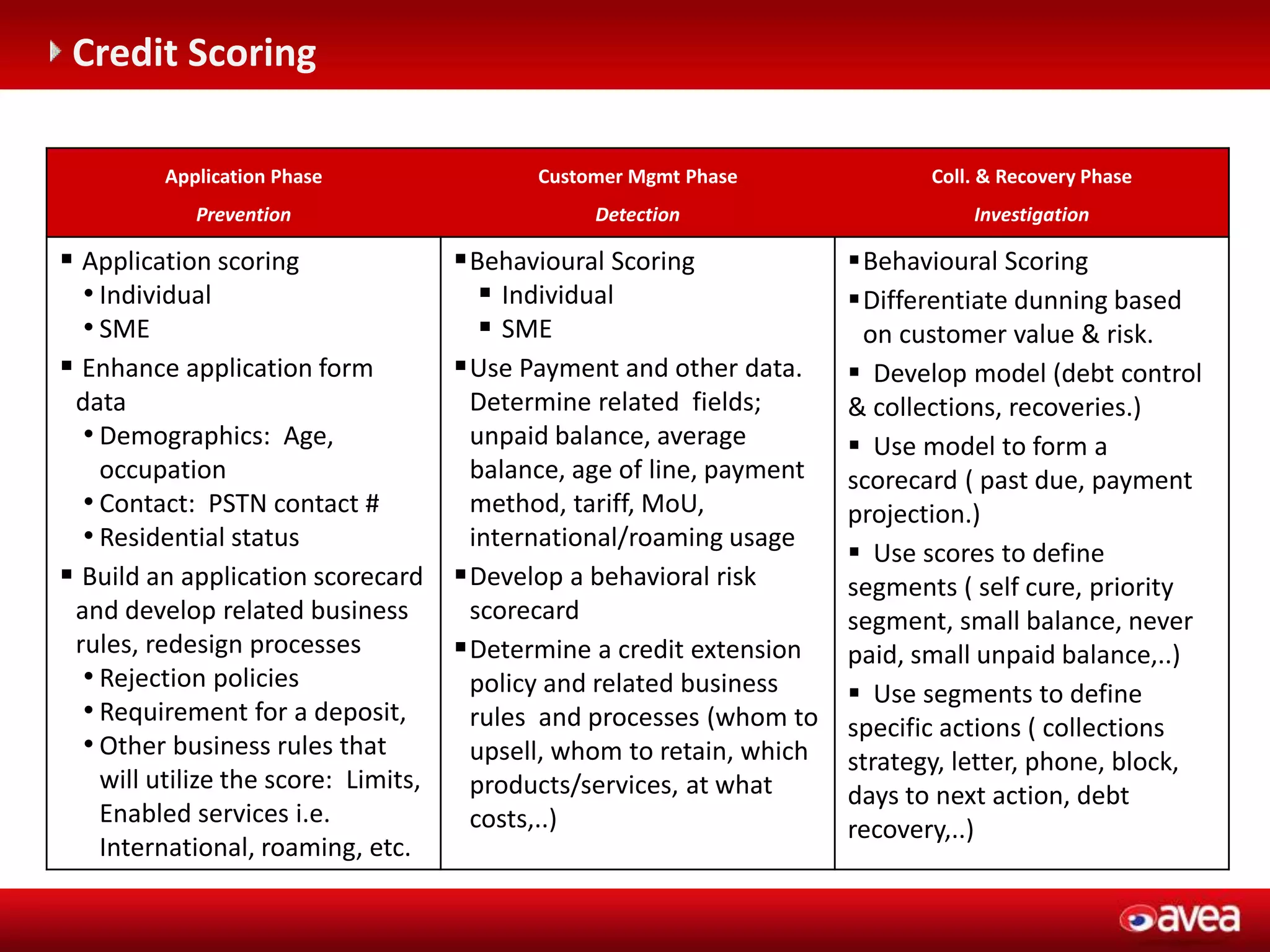
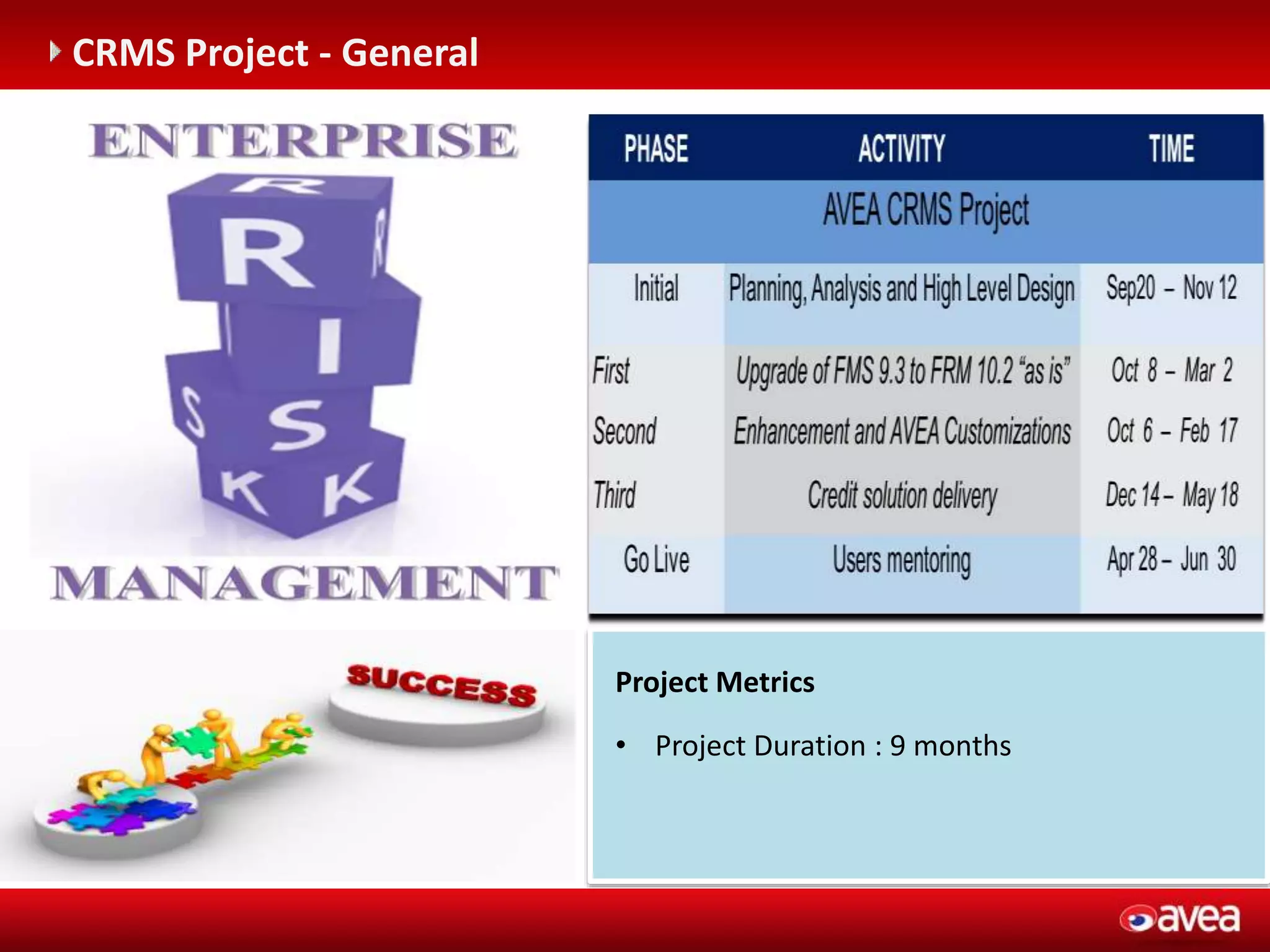
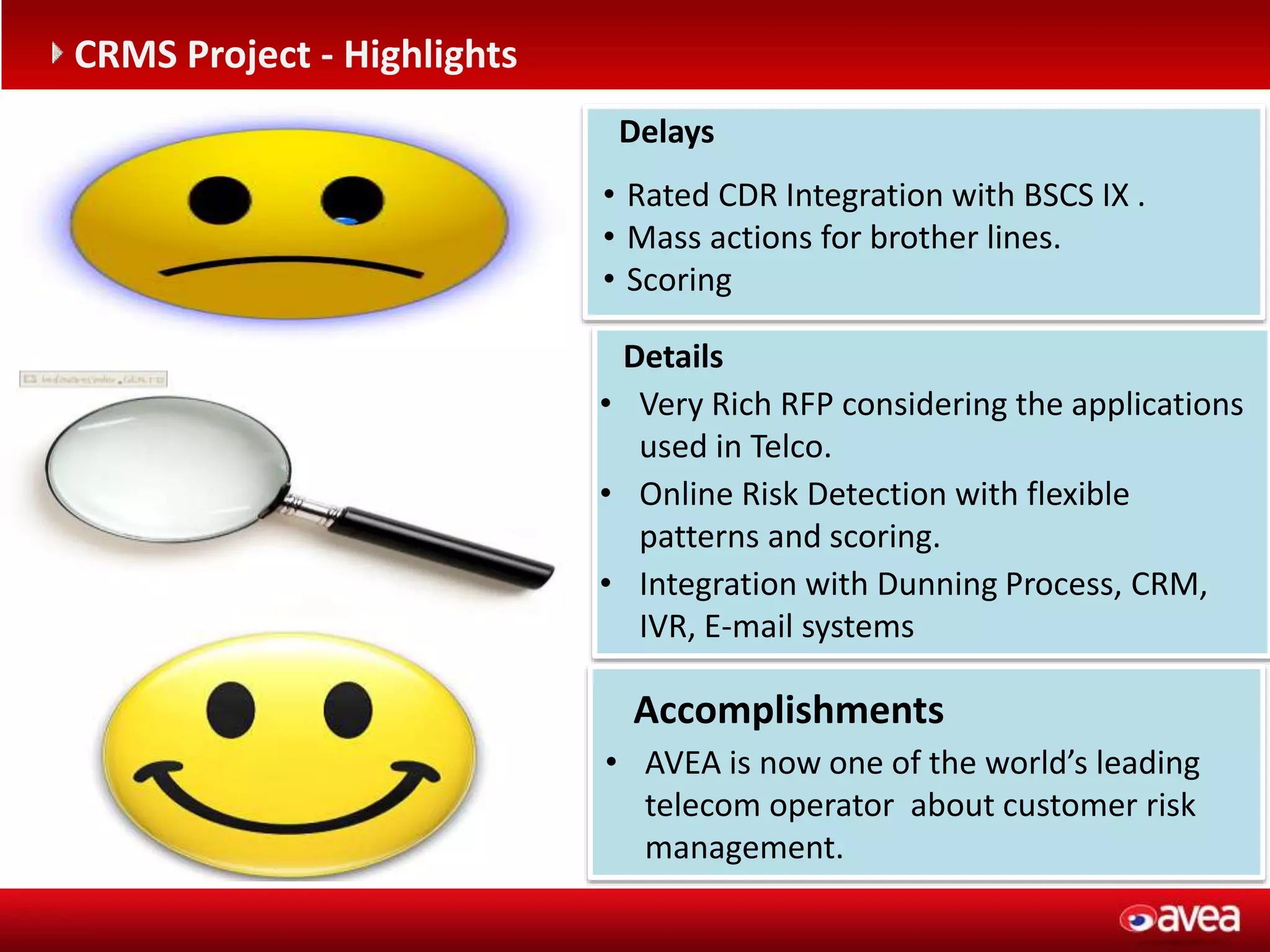
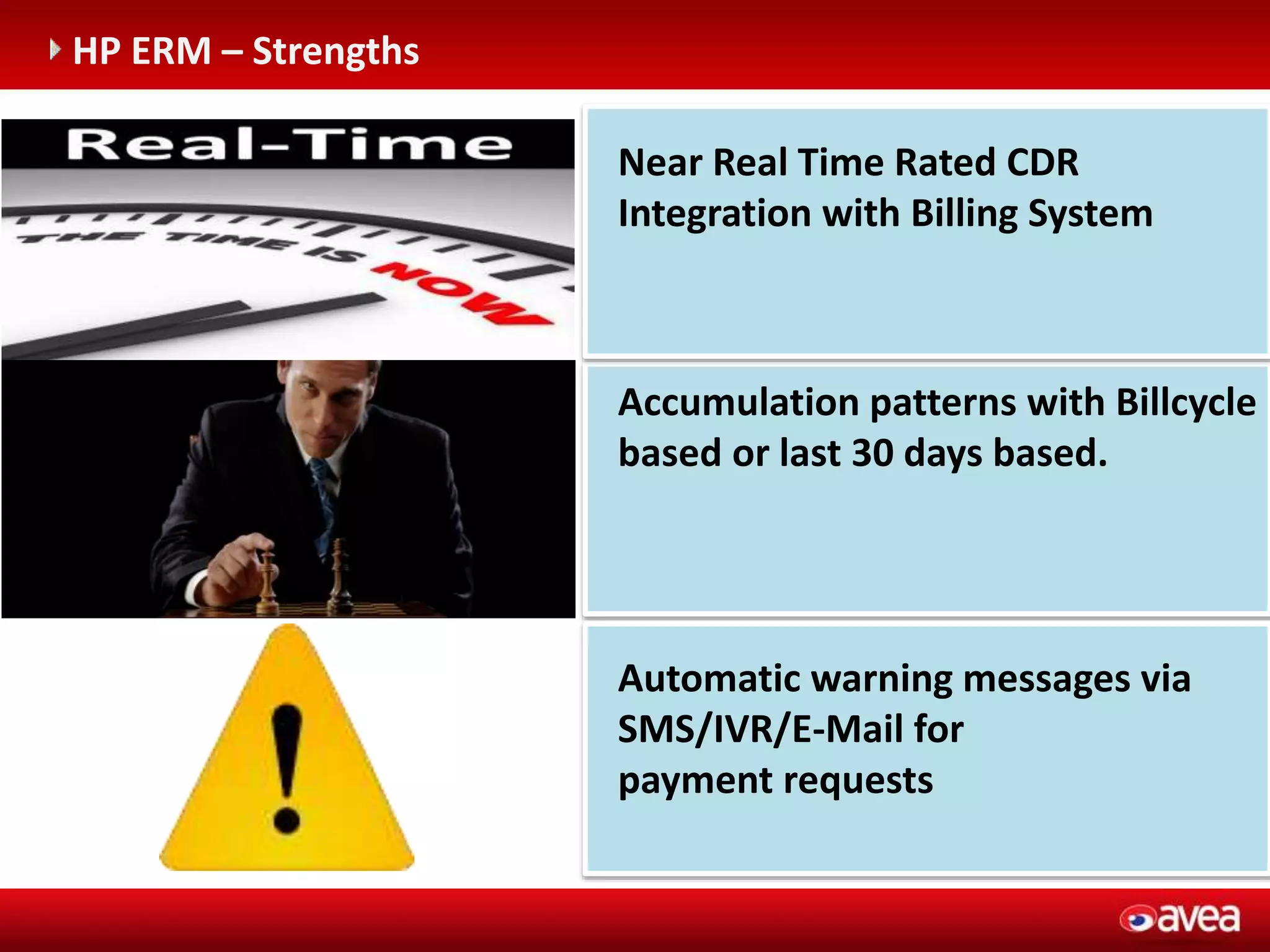
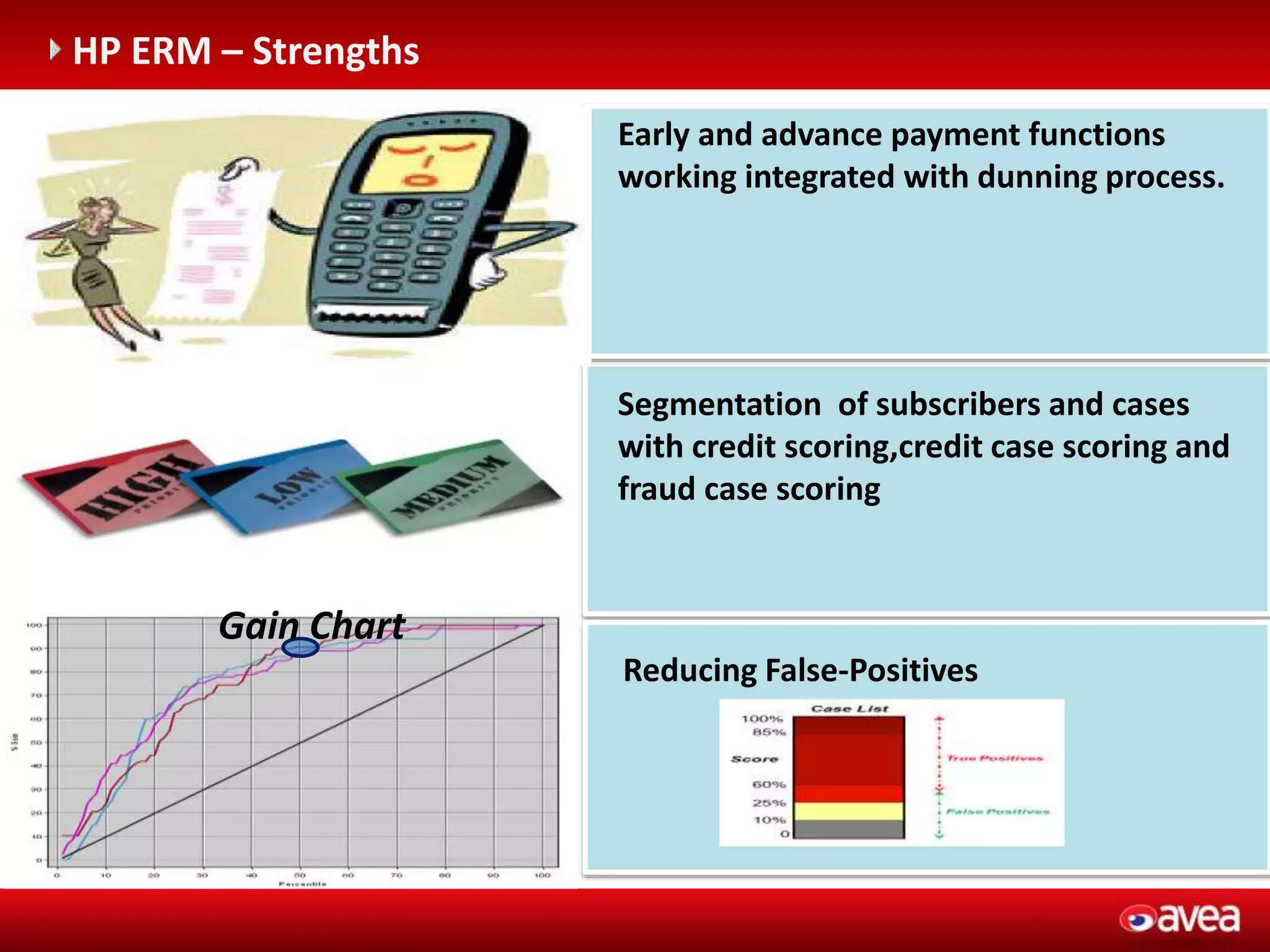
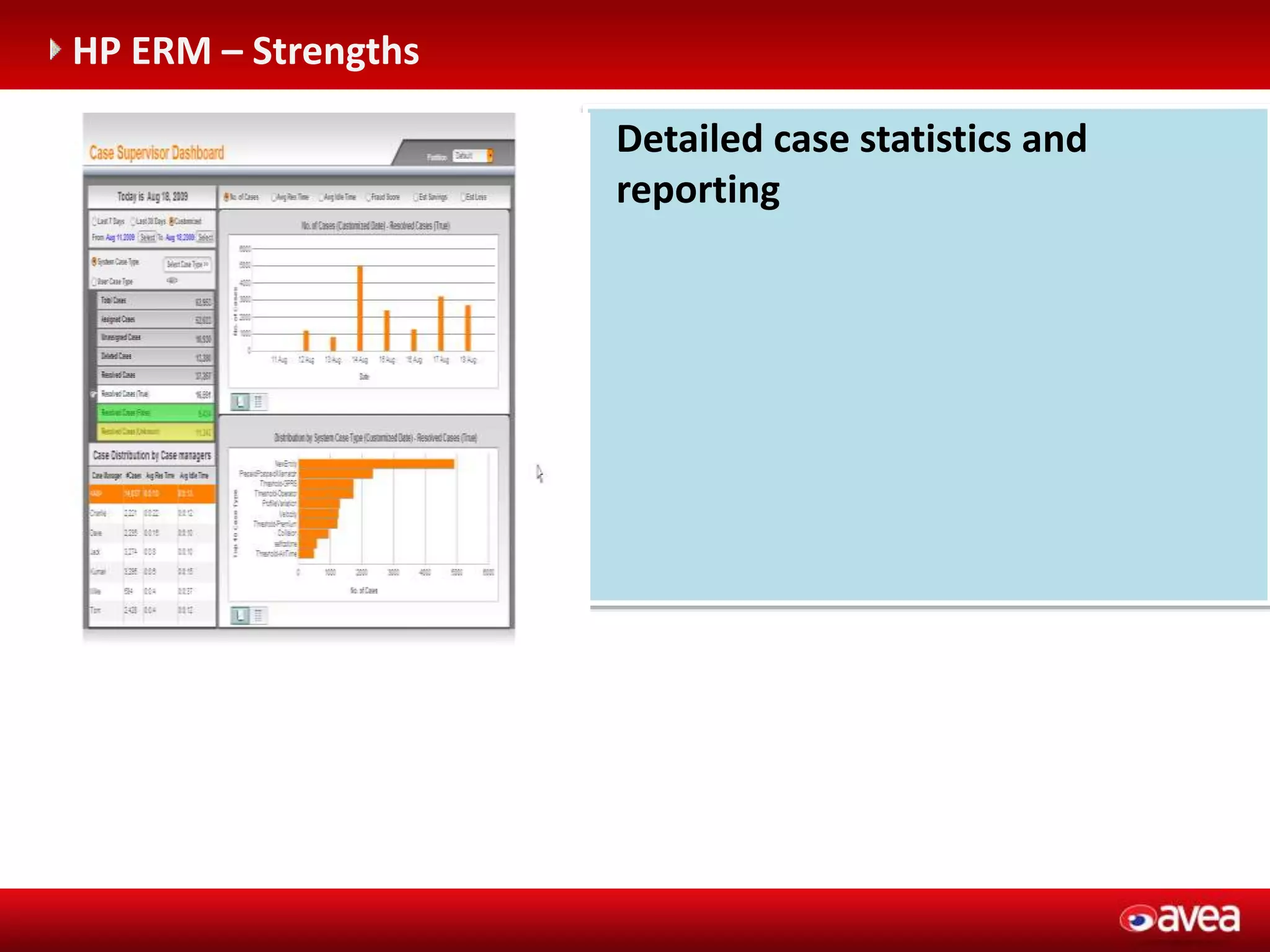
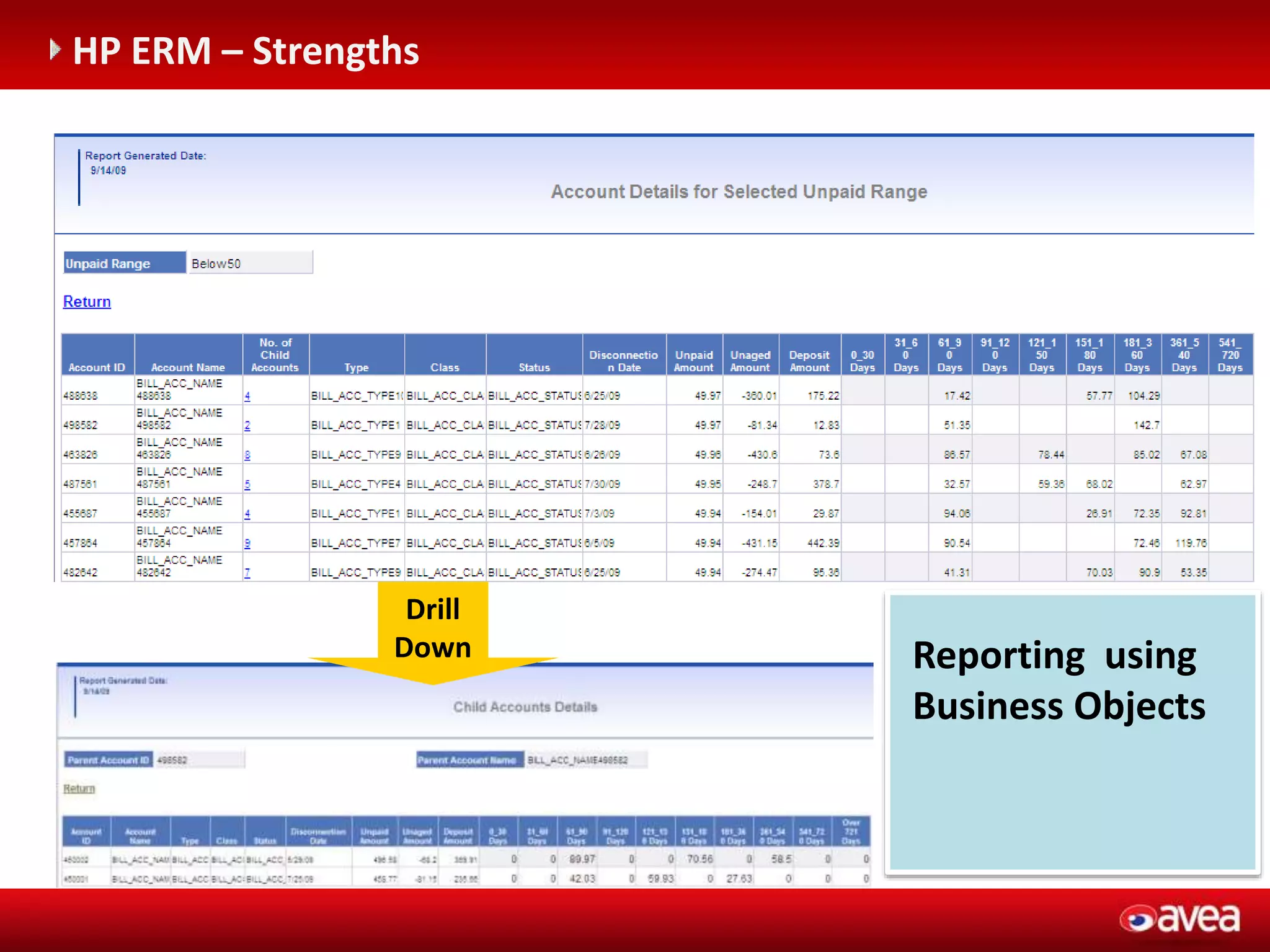
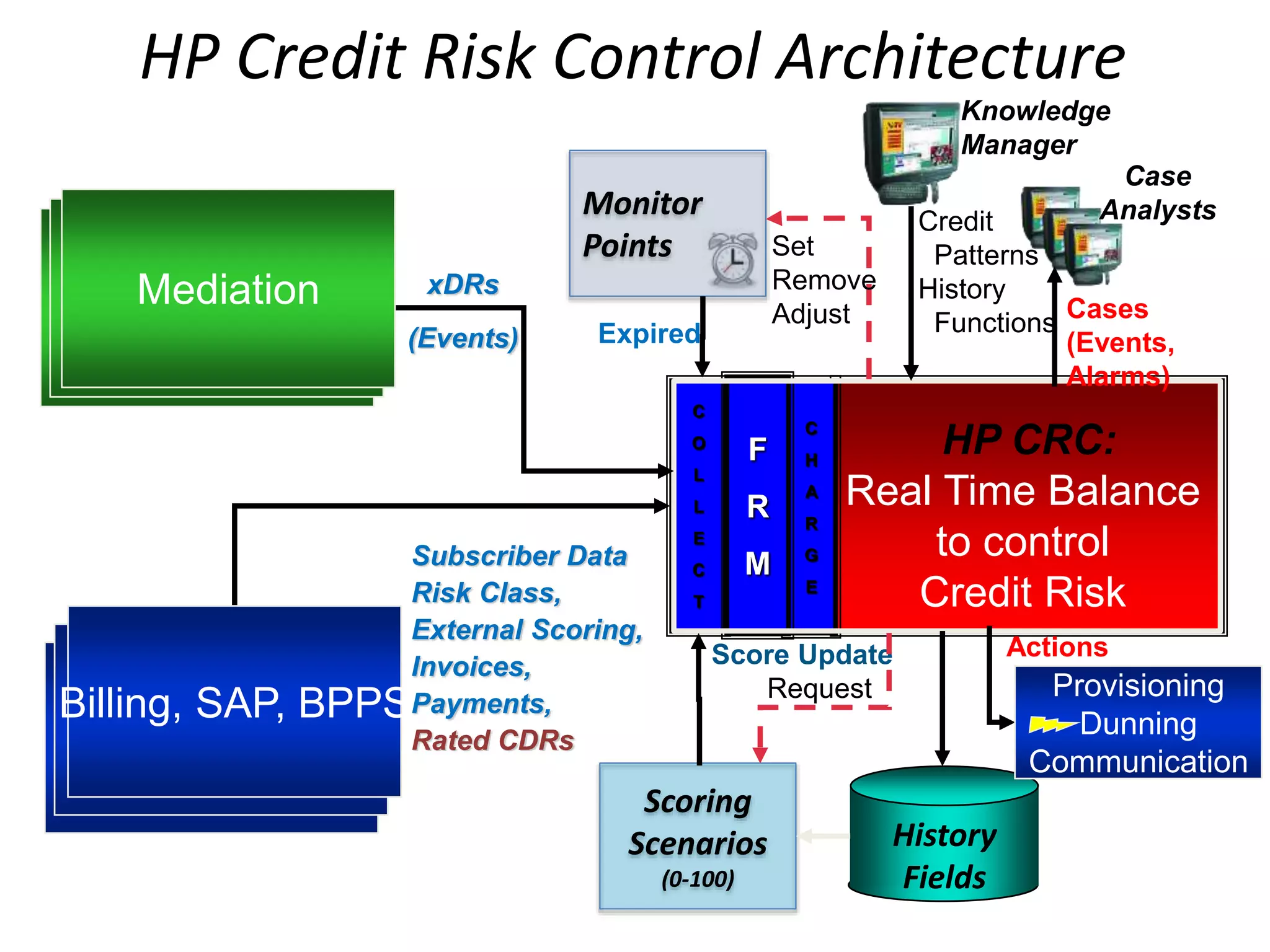
The document discusses a user forum for HP Revenue Intelligence that was held in Antalya, Turkey from March 19-20, 2012. It covers topics around fraud and credit risk management, including the relationship between fraud and credit risk systems, credit risk management solutions implemented between 2006-2010, enhancements to the graylist pool, expectations before implementing a new Credit Risk Management System (CRMS) project, highlights and accomplishments of the CRMS project, and examples of credit risk operations with the new system.