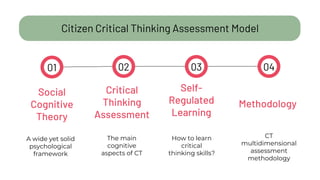
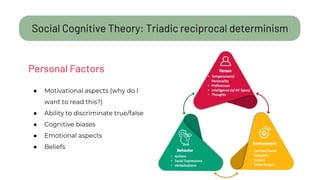
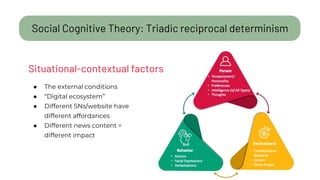
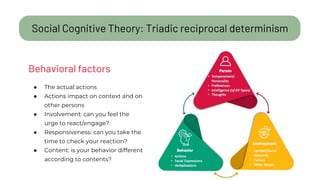
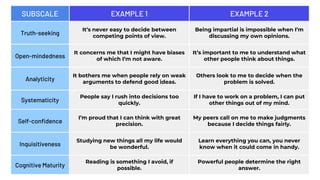
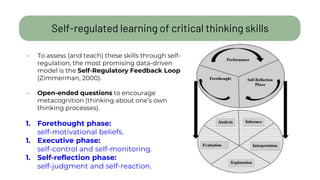
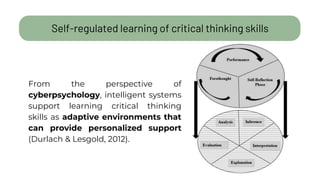
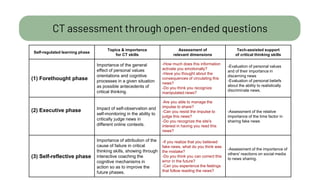
The document details a citizen critical thinking assessment model presented at a workshop in Athens, focusing on the psychological framework of social cognitive theory and critical thinking skills. It outlines the main cognitive aspects of critical thinking, including self-regulated learning methodologies and a multidimensional assessment approach using open-ended questions to foster critical thinking skills. Additionally, it discusses the California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory (CCTDI) as a valid tool for measuring critical thinking mindsets.